Publications
Ordered in reversed chronological order.
2024
- Generative AI
 Beyond reality: The pivotal role of generative ai in the metaverseVinay Chamola, Gaurang Bansal, Tridib Kumar Das, Vikas Hassija, Siva Sai, Jiacheng Wang, Sherali Zeadally, Amir Hussain, Fei Richard Yu, Mohsen Guizani, and othersIEEE Internet of Things Magazine, 2024
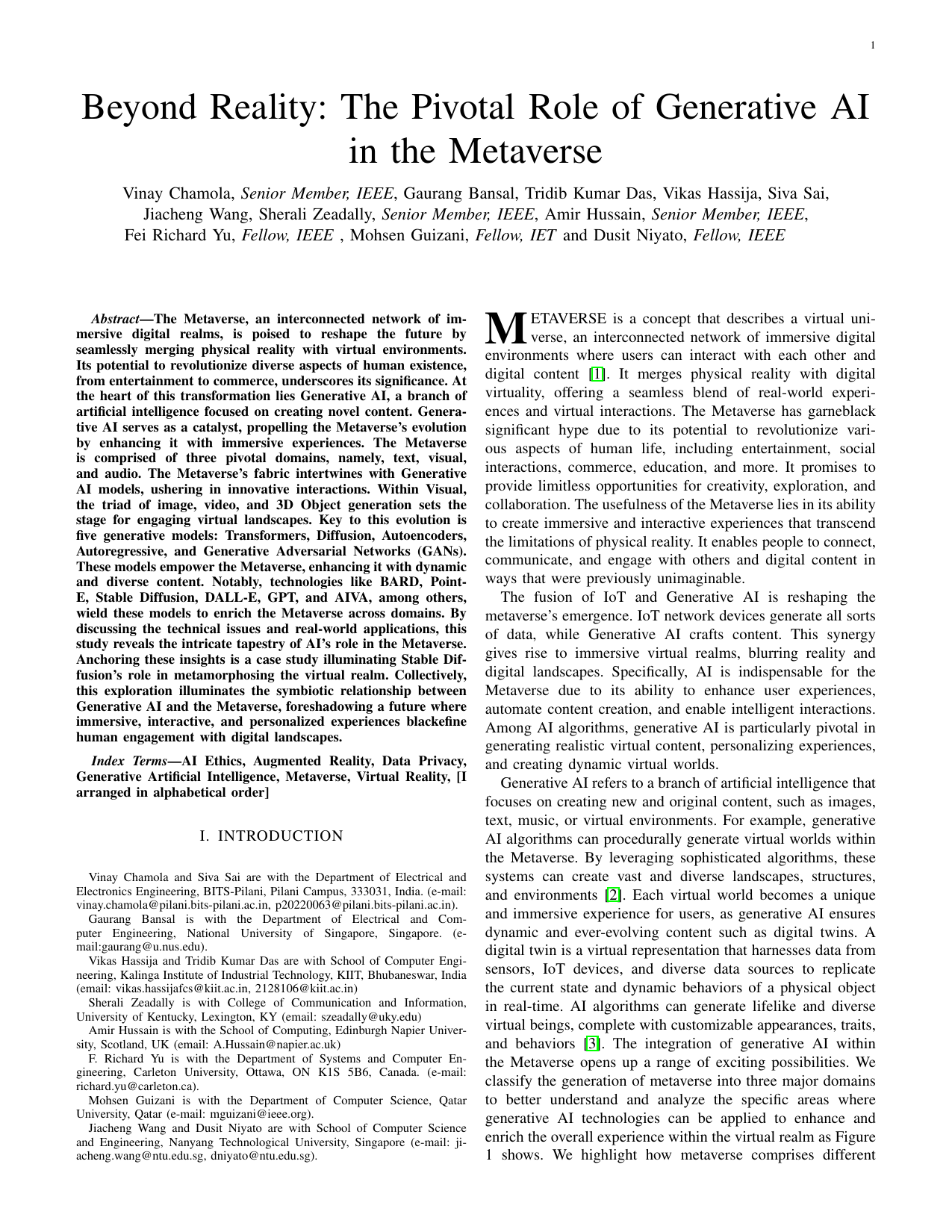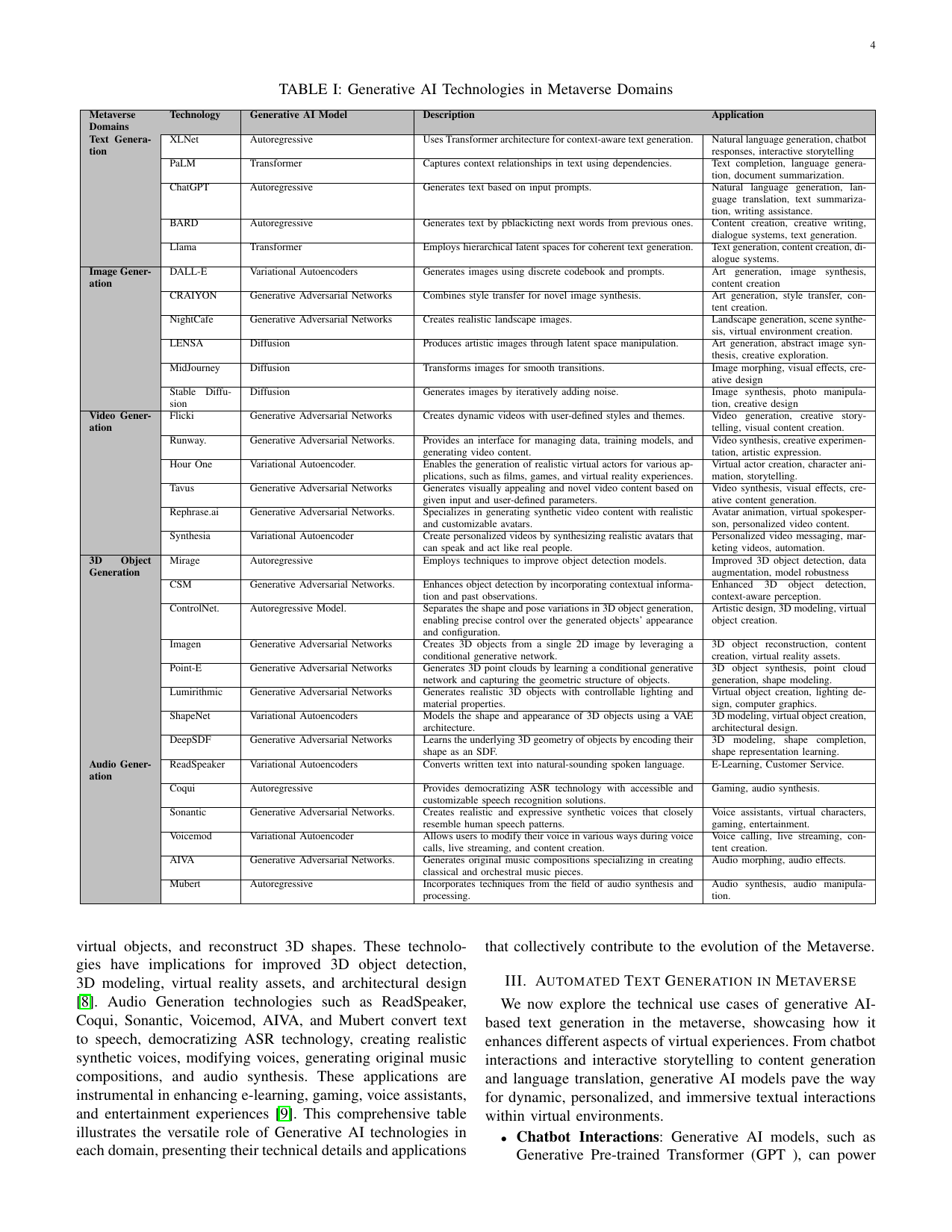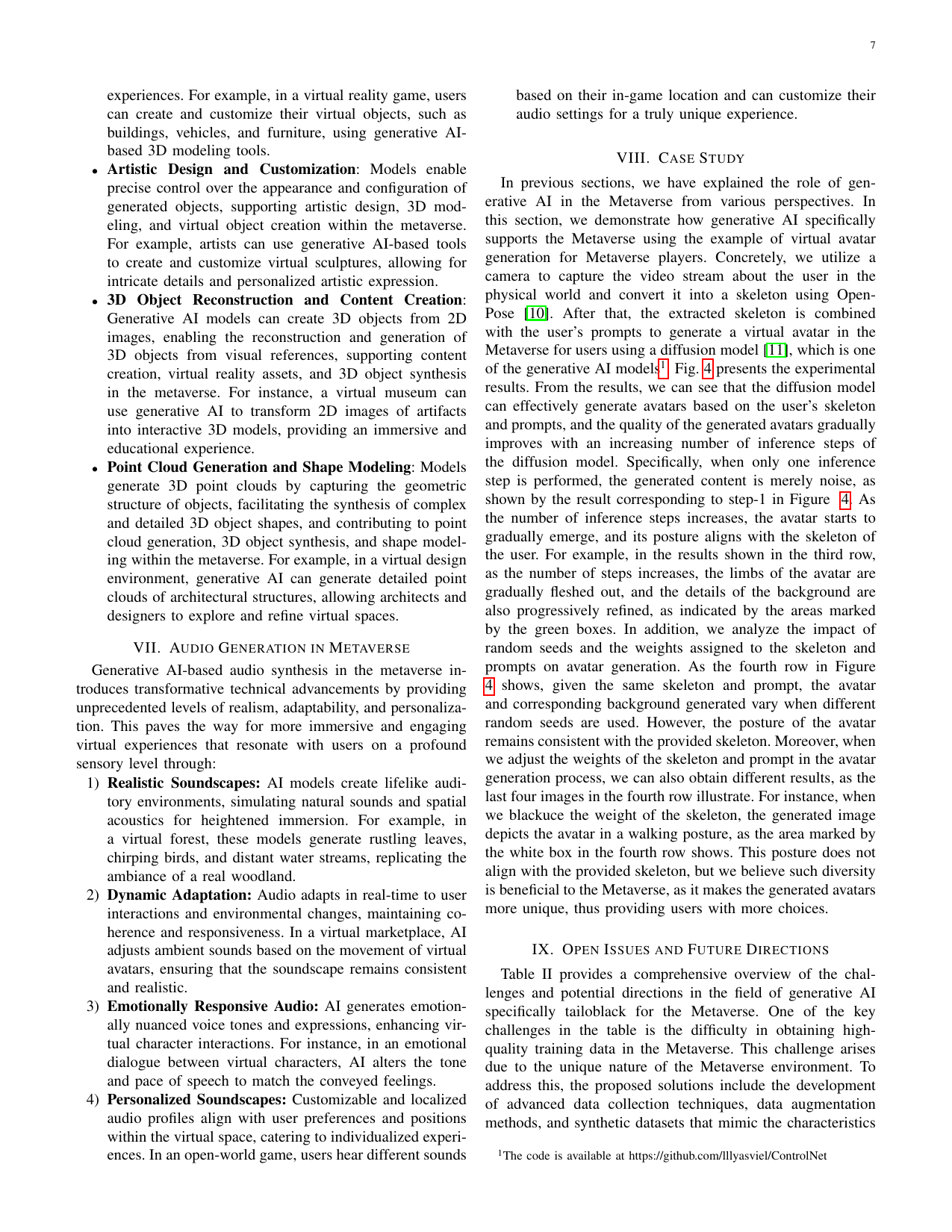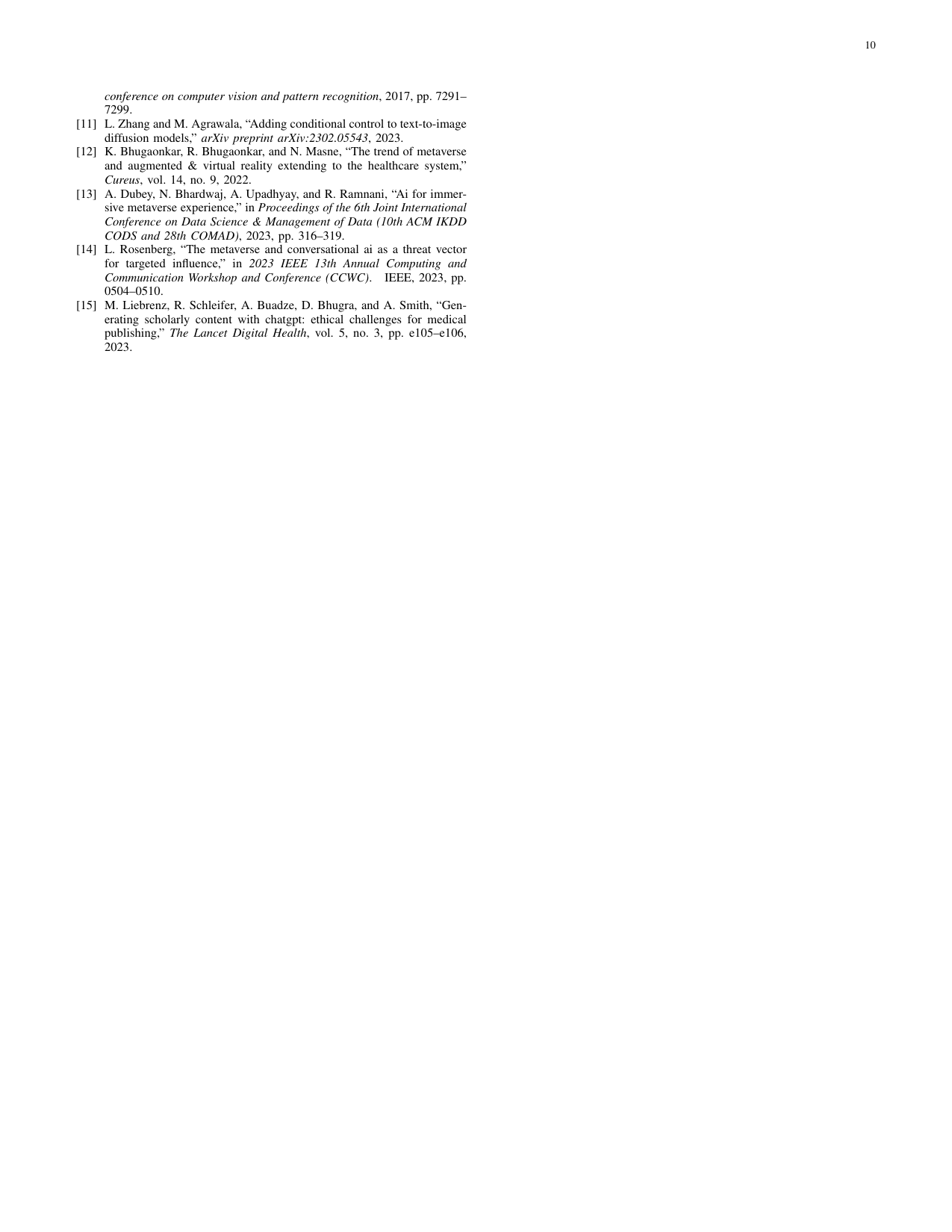
Beyond reality: The pivotal role of generative ai in the metaverseVinay Chamola, Gaurang Bansal, Tridib Kumar Das, Vikas Hassija, Siva Sai, Jiacheng Wang, Sherali Zeadally, Amir Hussain, Fei Richard Yu, Mohsen Guizani, and othersIEEE Internet of Things Magazine, 2024The Metaverse, an interconnected network of im- mersive digital realms, is poised to reshape the future by seamlessly merging physical reality with virtual environments. Its potential to revolutionize diverse aspects of human existence, from entertainment to commerce, underscores its significance. At the heart of this transformation lies Generative AI, a branch of artificial intelligence focused on creating novel content. Genera- tive AI serves as a catalyst, propelling the Metaverse’s evolution by enhancing it with immersive experiences. The Metaverse is comprised of three pivotal domains, namely, text, visual, and audio. The Metaverse’s fabric intertwines with Generative AI models, ushering in innovative interactions. Within Visual, the triad of image, video, and 3D Object generation sets the stage for engaging virtual landscapes. Key to this evolution is five generative models: Transformers, Diffusion, Autoencoders, Autoregressive, and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). These models empower the Metaverse, enhancing it with dynamic and diverse content. Notably, technologies like BARD, Point- E, Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, GPT, and AIVA, among others, wield these models to enrich the Metaverse across domains. By discussing the technical issues and real-world applications, this study reveals the intricate tapestry of AI’s role in the Metaverse. Anchoring these insights is a case study illuminating Stable Dif- fusion’s role in metamorphosing the virtual realm. Collectively, this exploration illuminates the symbiotic relationship between Generative AI and the Metaverse, foreshadowing a future where immersive, interactive, and personalized experiences blackefine human engagement with digital landscapes.
- AI
 Transforming conversations with AI—a comprehensive study of ChatGPTGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Amir Hussain, Mohsen Guizani, and Dusit NiyatoCognitive Computation, 2024
Transforming conversations with AI—a comprehensive study of ChatGPTGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Amir Hussain, Mohsen Guizani, and Dusit NiyatoCognitive Computation, 2024Recognizing the evolution and profound impact of ChatGPT holds paramount significance for researchers and developers at the forefront of AI innovation. In a rapidly evolving conversational AI landscape, ChatGPT emerges as a pivotal player, capable of reshaping the way we interact with AI systems across a wide array of applications.
- Security and Privacy
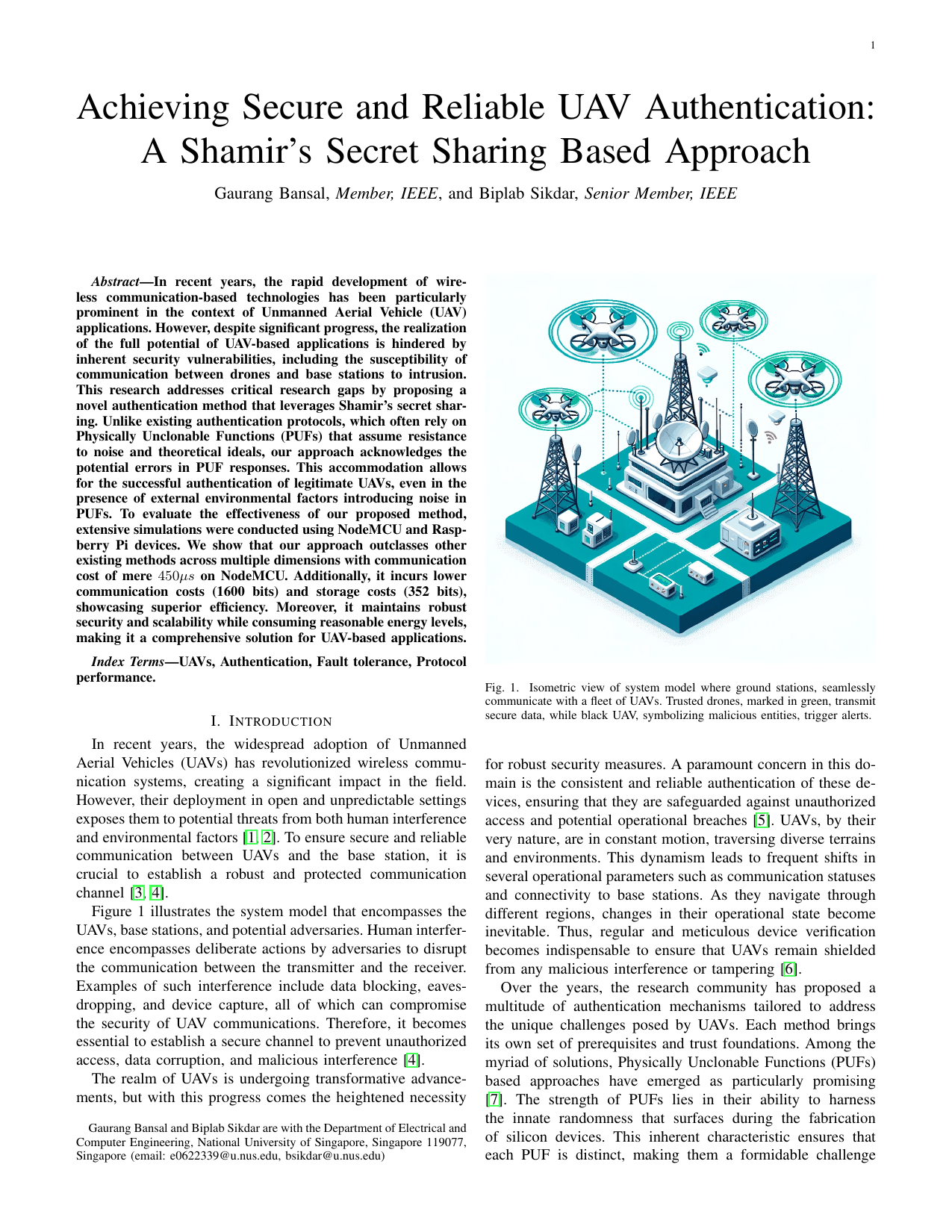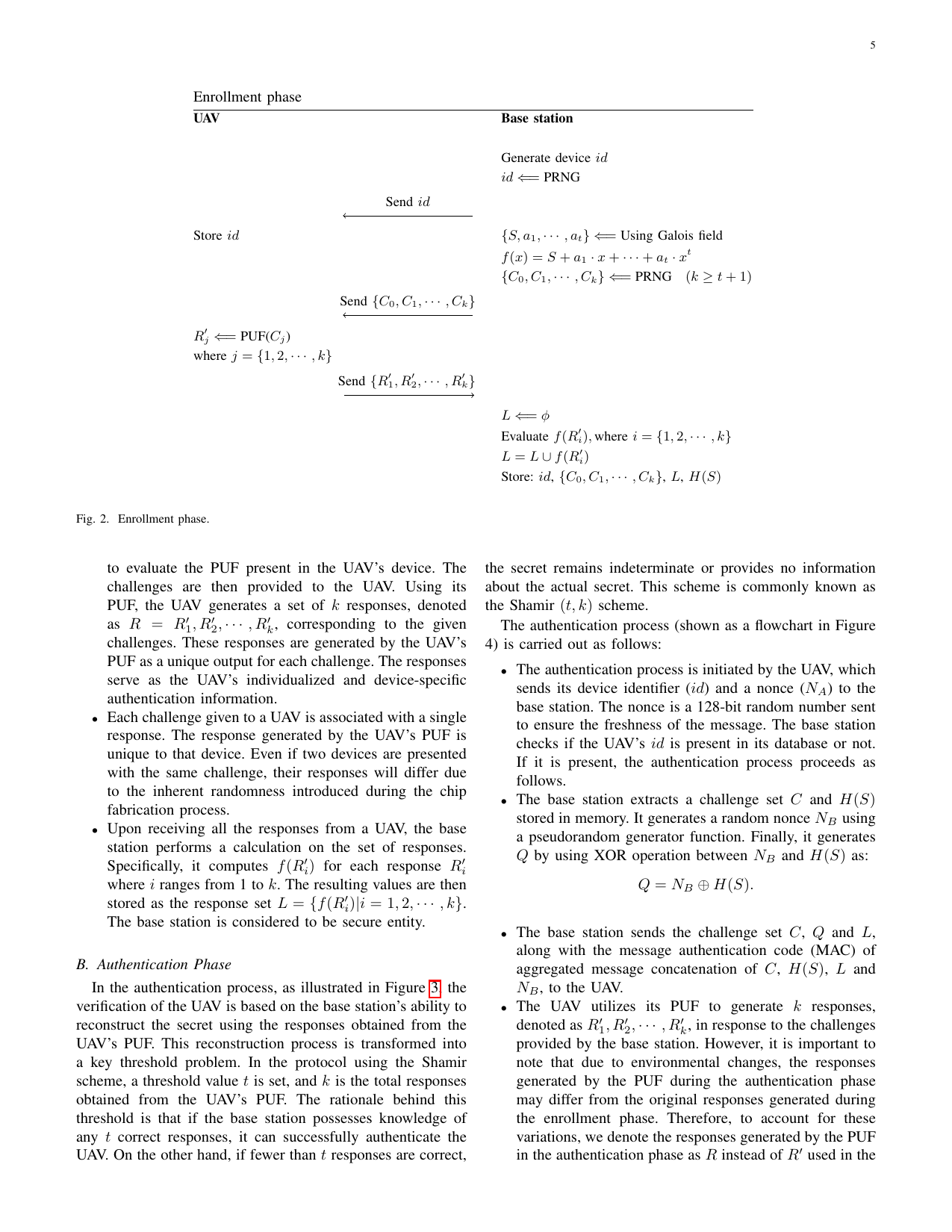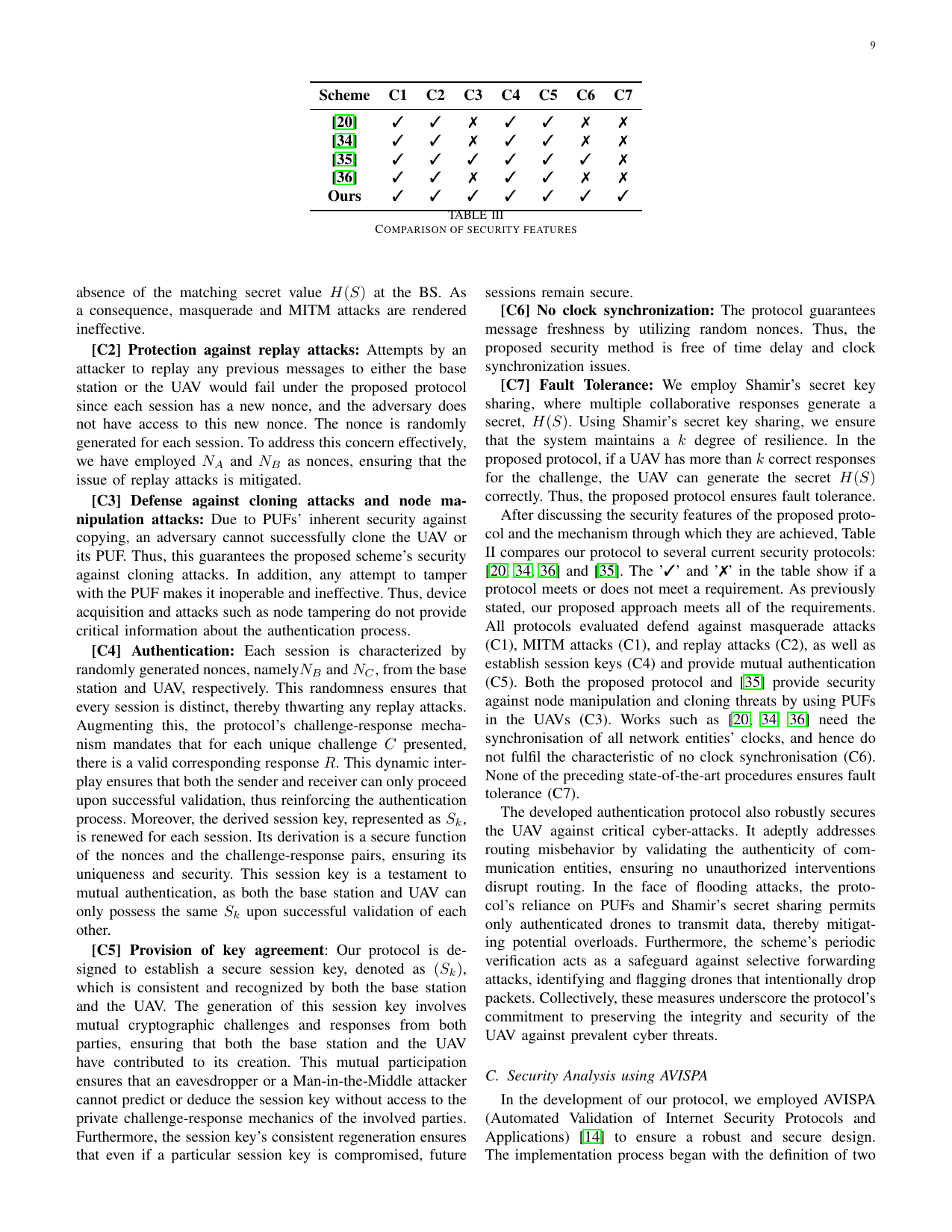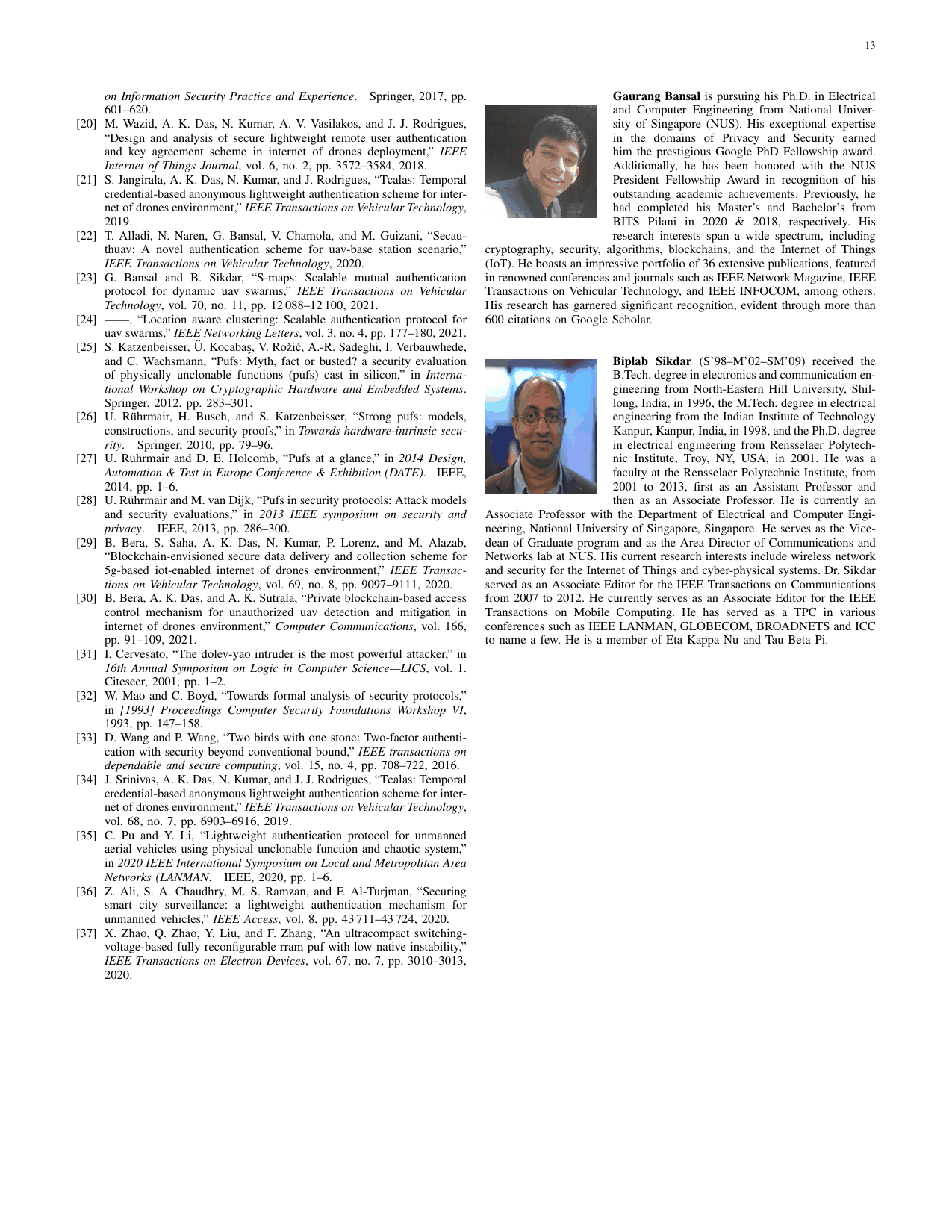 Achieving Secure and Reliable UAV Authentication: A Shamir’s Secret Sharing Based ApproachGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2024
Achieving Secure and Reliable UAV Authentication: A Shamir’s Secret Sharing Based ApproachGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2024In recent years, the rapid development of wireless communication-based technologies has been particularly prominent in the context of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) applications. However, despite significant progress, the realization of the full potential of UAV-based applications is hindered by inherent security vulnerabilities, including the susceptibility of communication between drones and base stations to intrusion. This research addresses critical research gaps by proposing a novel authentication method that leverages Shamir’s secret sharing. Unlike existing authentication protocols, which often rely on Physically Unclonable Functions (PUFs) that assume resistance to noise and theoretical ideals, our approach acknowledges the potential errors in PUF responses. This accommodation allows for the successful authentication of legitimate UAVs, even in the presence of external environmental factors introducing noise in PUFs. To evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed method, extensive simulations were conducted using NodeMCU and Raspberry Pi devices. We show that our approach outclasses other existing methods across multiple dimensions with communication cost of mere 450 ms on NodeMCU. Additionally, it incurs lower communication costs (1600 bits) and storage costs (352 bits), showcasing superior efficiency. Moreover, it maintains robust security and scalability while consuming reasonable energy levels, making it a comprehensive solution for UAV-based
- Healthcare
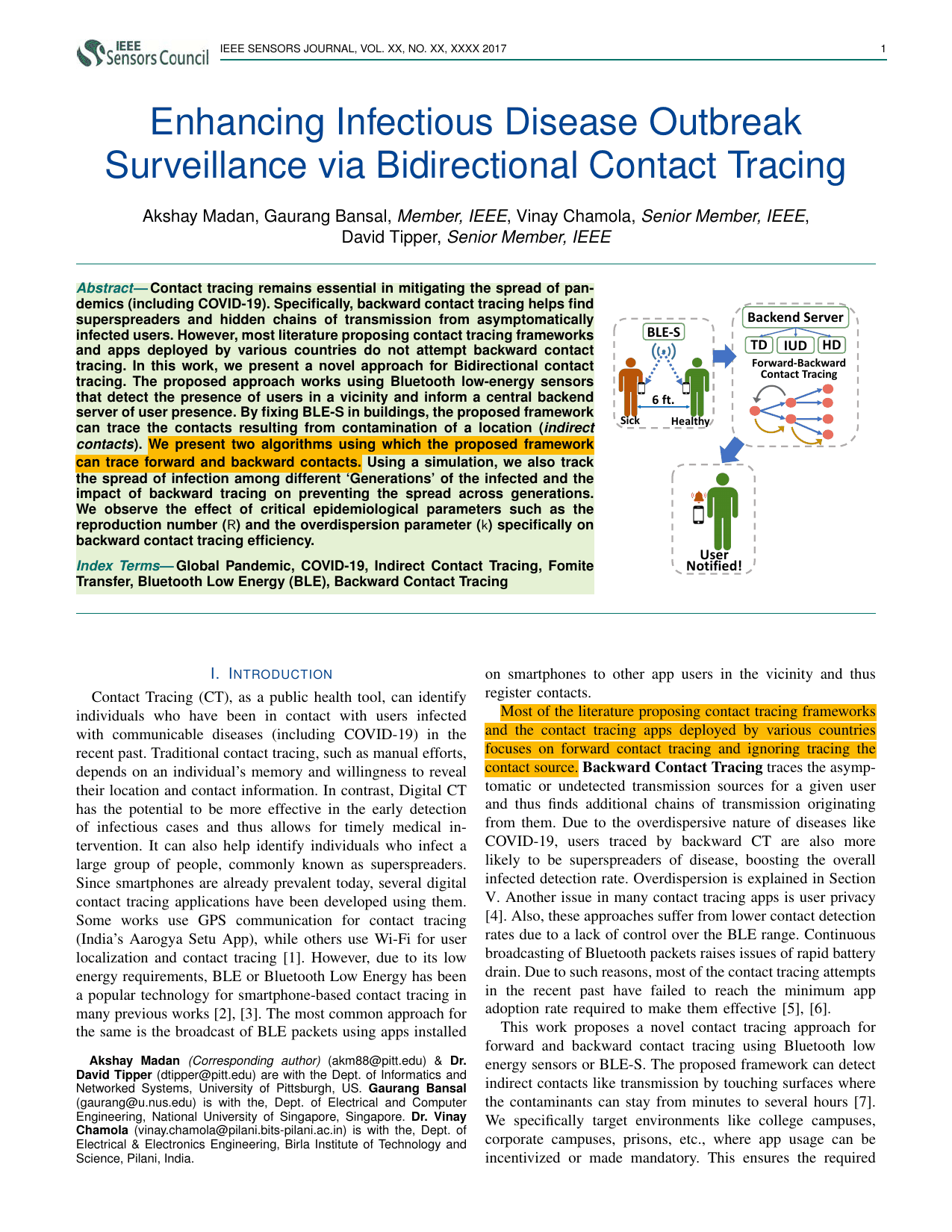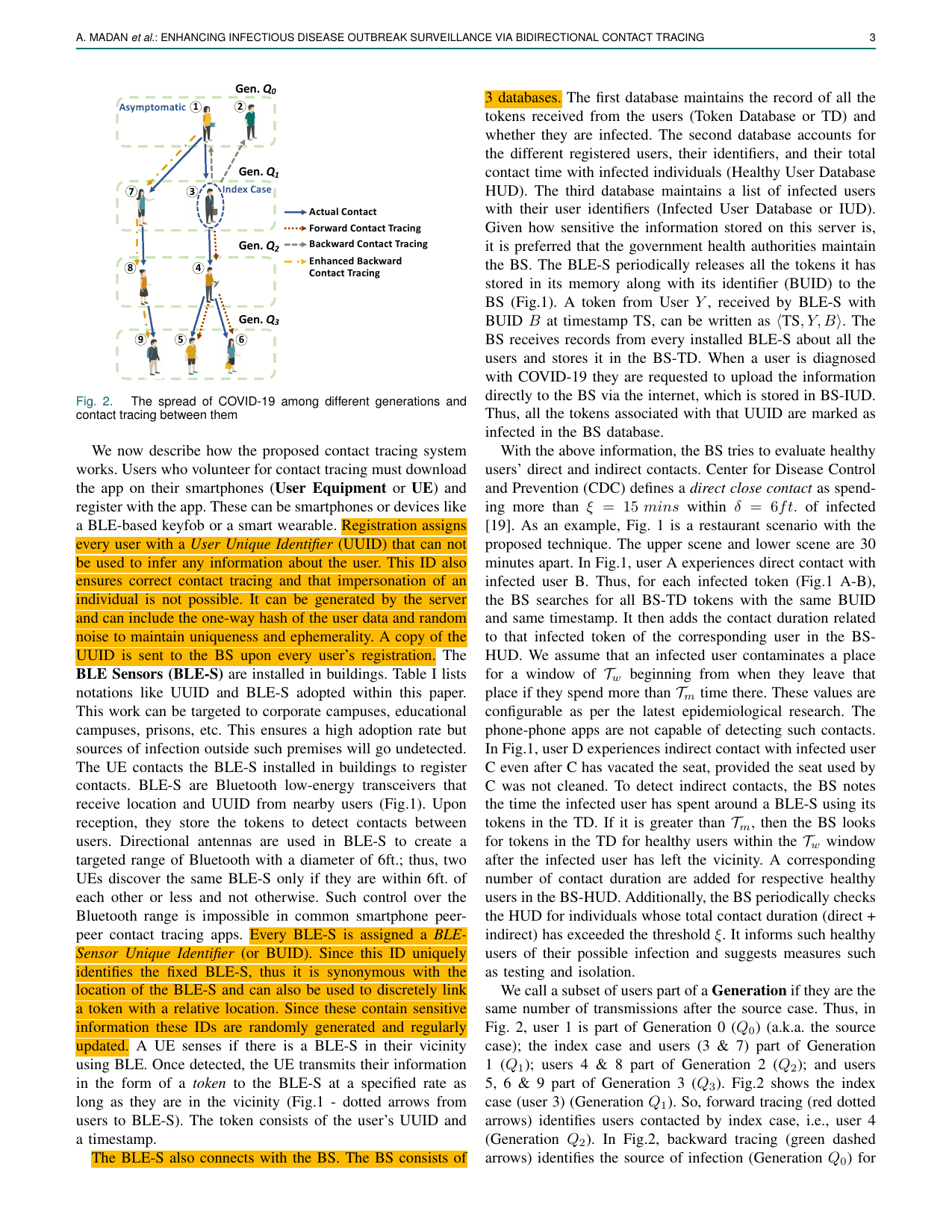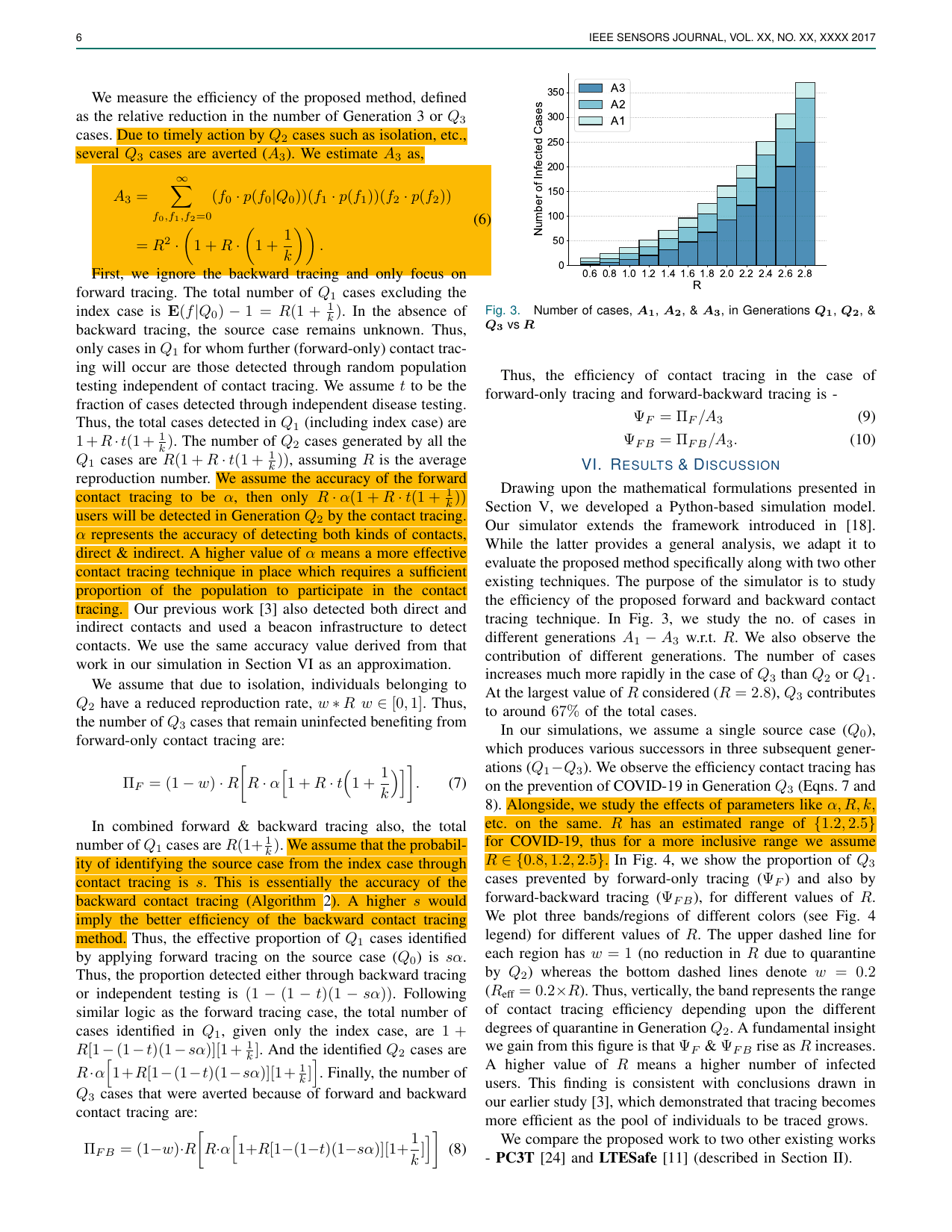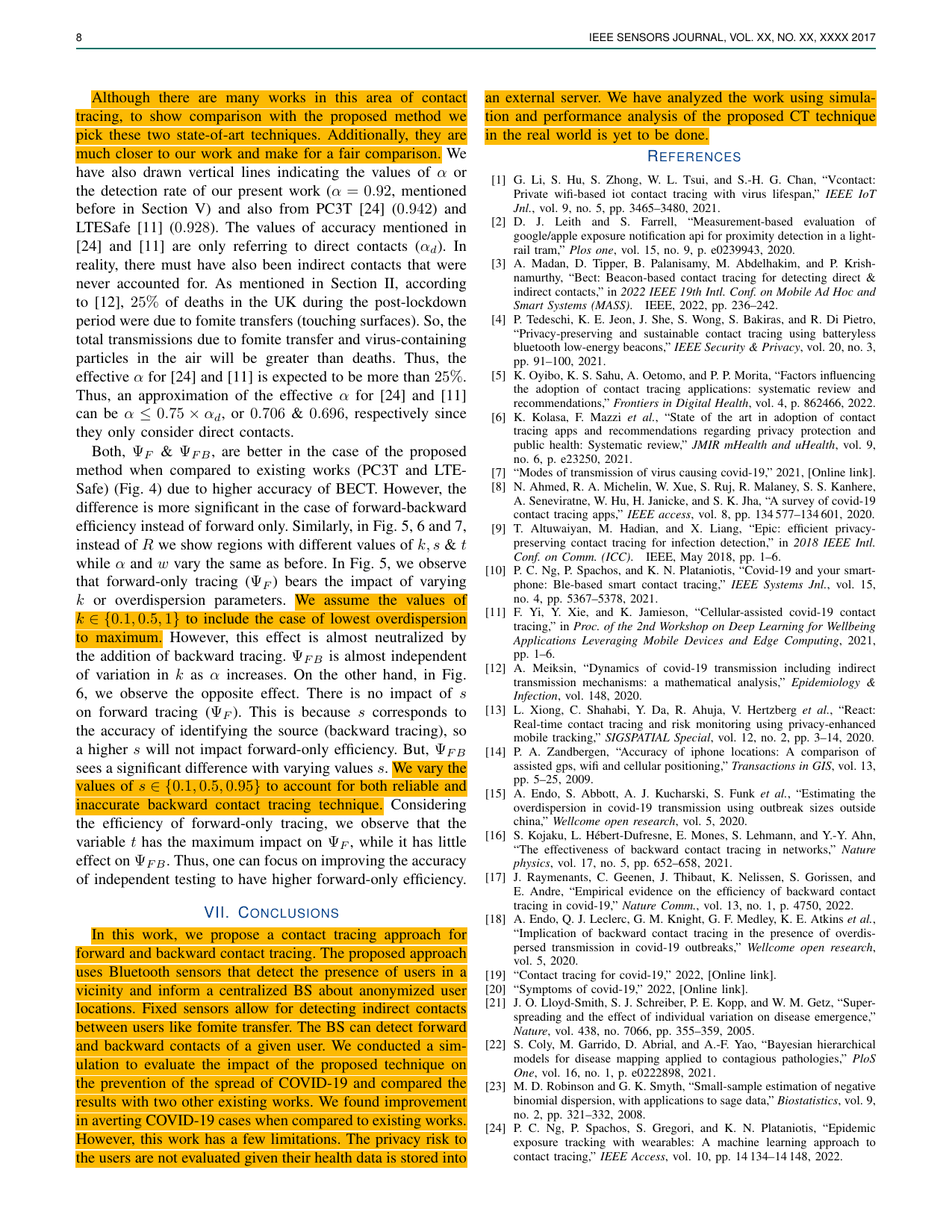 Enhancing Infectious Disease Outbreak Surveillance via Bidirectional Contact TracingAkshay Madan, Gaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, and David TipperIEEE Sensors Journal, 2024
Enhancing Infectious Disease Outbreak Surveillance via Bidirectional Contact TracingAkshay Madan, Gaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, and David TipperIEEE Sensors Journal, 2024Contact tracing remains essential in mitigating the spread of pan- demics (including COVID-19). Specifically, backward contact tracing helps find superspreaders and hidden chains of transmission from asymptomatically infected users. However, most literature proposing contact tracing frameworks and apps deployed by various countries do not attempt backward contact tracing. In this work, we present a novel approach for Bidirectional contact tracing. The proposed approach works using Bluetooth low-energy sensors that detect the presence of users in a vicinity and inform a central backend server of user presence. By fixing BLE-S in buildings, the proposed framework can trace the contacts resulting from contamination of a location (indirect contacts). We present two algorithms using which the proposed framework can trace forward and backward contacts. Using a simulation, we also track the spread of infection among different ‘Generations’ of the infected and the impact of backward tracing on preventing the spread across generations. We observe the effect of critical epidemiological parameters such as the reproduction number (R) and the overdispersion parameter (k) specifically on backward contact tracing efficiency
- Security and Privacy
 Secure and Efficient Peer2Peer Authentication-Attestation Protocol for UAV NetworksGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024
Secure and Efficient Peer2Peer Authentication-Attestation Protocol for UAV NetworksGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024The accelerating deployment of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) is accompanied by escalating security concerns, especially with regard to communication protocols. Traditional cryptographic mechanisms, while functional, fall short in computational efficiency and low-latency requirements that are critical for UAV networks. Addressing these challenges, this paper introduces a novel hardware-secured authentication and attestation mechanism tailored for UAV-to-UAV data exchange. The mechanism is designed to scale efficiently with UAV swarms and withstand rigorous post-deployment verifications. Our research contributions are multi-faceted, comprising: 1) a feasibility and security validation of the proposed protocol via Mao-Boyd logic, providing a robust theoretical foundation, 2) empirical results that confirm the protocol’s superior performance over contemporary solutions in both speed and security, and 3) a comprehensive security and performance analysis to ensure the protocol’s resilience against potential vulnerabilities. Thus, the paper presents a balanced and effective approach to secure UAV communications, satisfying both computational and security demands.
- Computer Vision
 Revolutionizing Visuals: The Role of Generative AI in Modern Image GenerationACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and Applications, 2024
Revolutionizing Visuals: The Role of Generative AI in Modern Image GenerationACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and Applications, 2024Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are becoming very popular nowadays due to the emergence of application areas such as the Internet of Drones (IoD). They are finding wide applicability in areas ranging from package delivery systems to automated military applications. Nevertheless, communication security between a UAV and its ground station (GS) is critical for completing its task without leaking sensitive information either to the adversaries or to unauthenticated users. UAVs are especially vulnerable to physical capture and node tampering attacks. Further, since UAV devices are generally equipped with small batteries and limited memory storage, lightweight security techniques are best suited for them. Addressing these issues, a lightweight mutual authentication scheme based on Physical Unclonable Functions (PUFs) for UAV-GS authentication is presented in this paper. The UAV-GS authentication scheme is extended further to support UAV-UAV authentication. We present a formal security analysis as well as old-fashioned cryptanalysis and show that our protocol provides various security features such as mutual authentication, user anonymity, etc, and is resilient against many security attacks such as masquerade, replay, node tampering, and cloning attacks, etc. We also compare the performance of our protocol with state-of-the-art authentication protocols for UAVs, based on computation, communication, and memory storage cost.
2023
- Deep Learning
 Cracking the anonymous iot routing networks: A deep learning approachGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Amir Hussain, and Muhammad Khurram KhanIEEE Internet of Things Magazine, 2023
Cracking the anonymous iot routing networks: A deep learning approachGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Amir Hussain, and Muhammad Khurram KhanIEEE Internet of Things Magazine, 2023In recent years, IoT technology has been one of the most rapidly expanding fields, connecting over 27 billion connected devices worldwide. Increasing security concerns, such as software flaws and cyberattacks, limit the use of IoT devices. Tor, also known as "The Onion Router," is one of the most popular, secure, and widely deployed anonymous routing systems in IoT networks. Tor is based on a worldwide network of relays operated by volunteers worldwide. Tor continues to be one of the most popular and secure tools against network surveillance, traffic analysis, and information censorship due to its robust use of encryption, authentication, and routing protocols. However, ToR is not anticipated to be entirely safe. The increasing computational capabilities of adversaries threaten Tor’s ability to withstand adversarial attacks and maintain anonymity. This paper describes the foundation of the Tor network, how it operates, potential attacks against Tor, and the network’s defense strategies. In addition, the authors present a framework for deep learning that uses bandwidth performance to identify the server’s location in Tor, thereby compromising anonymity. This paper examines Tor’s network’s current and projected future in the Internet of Things.
2022
- Security and Privacy
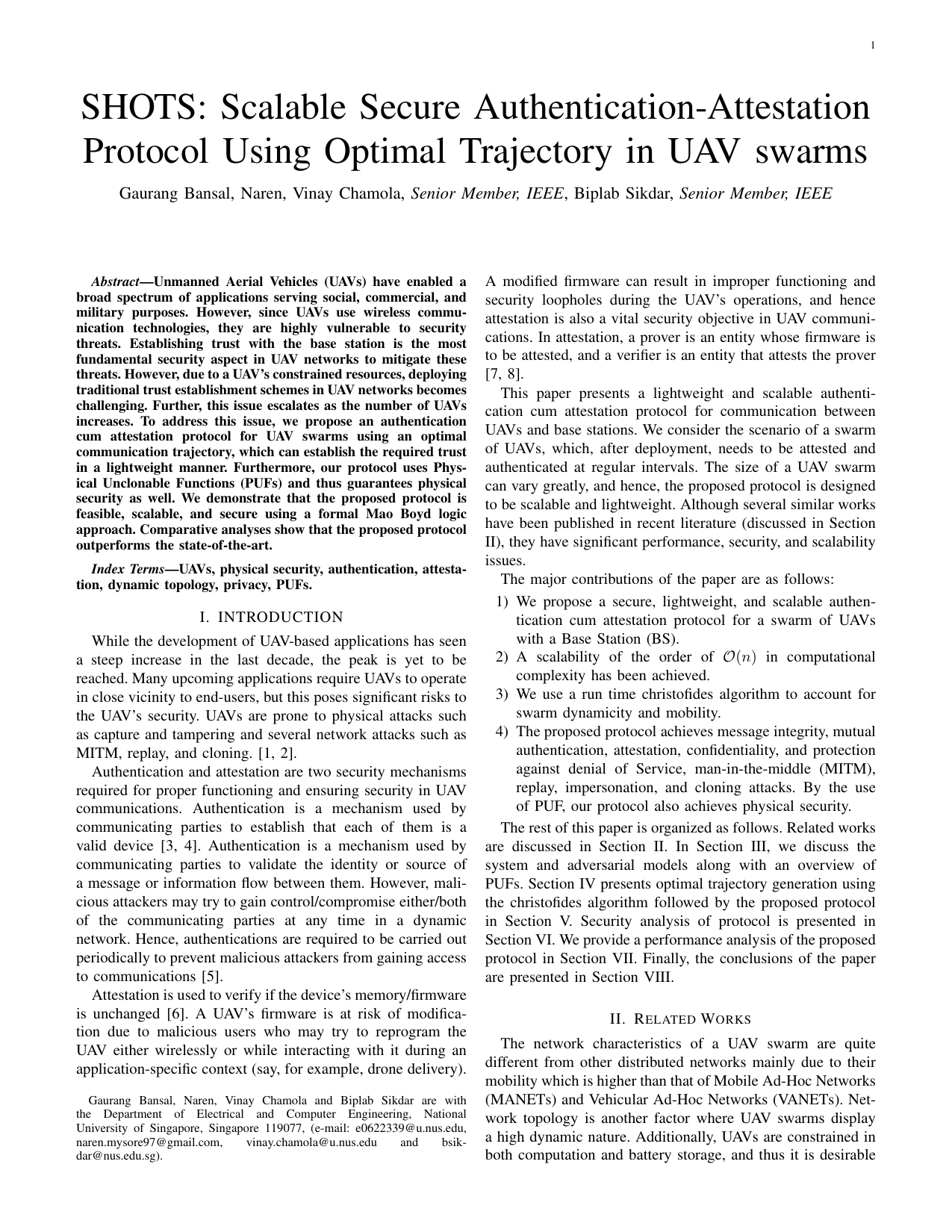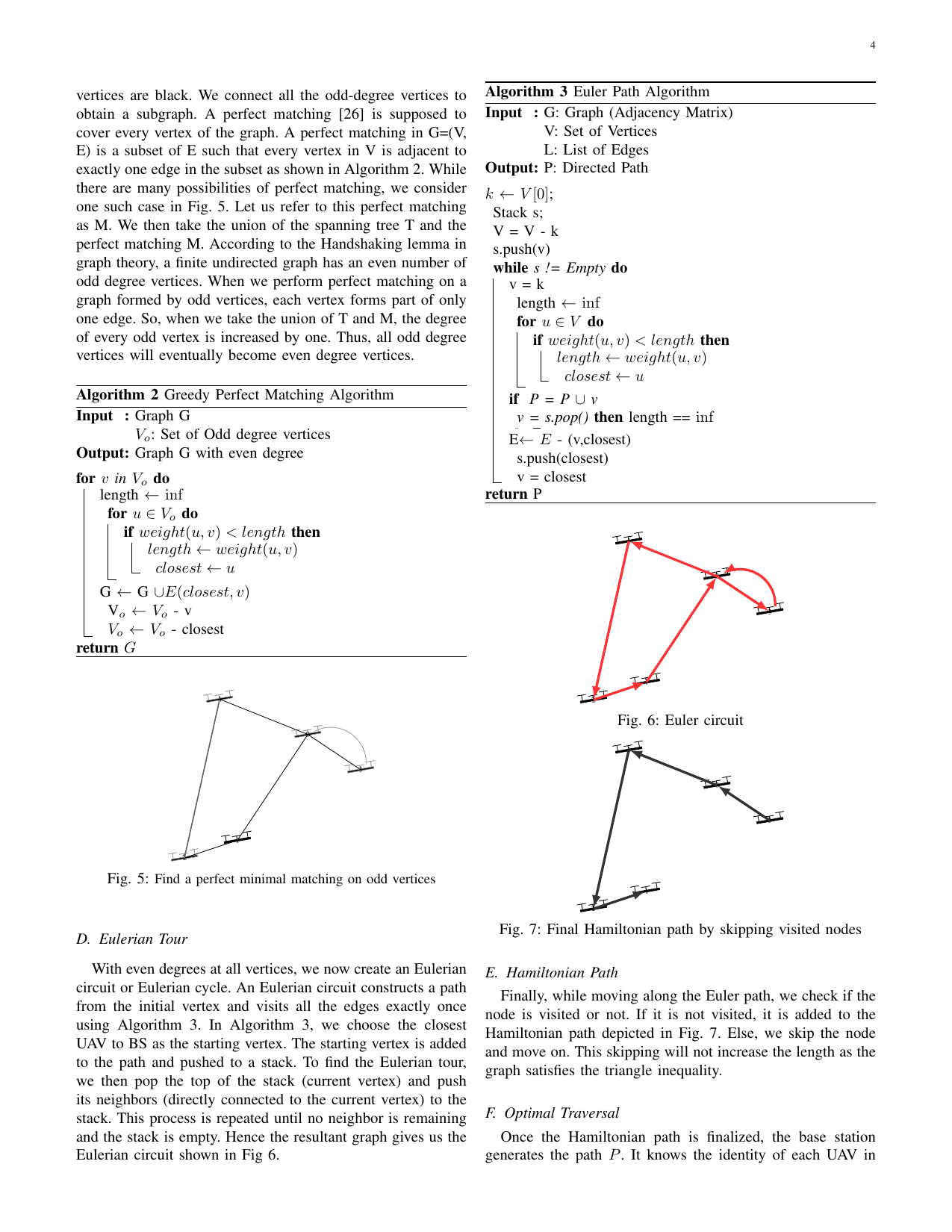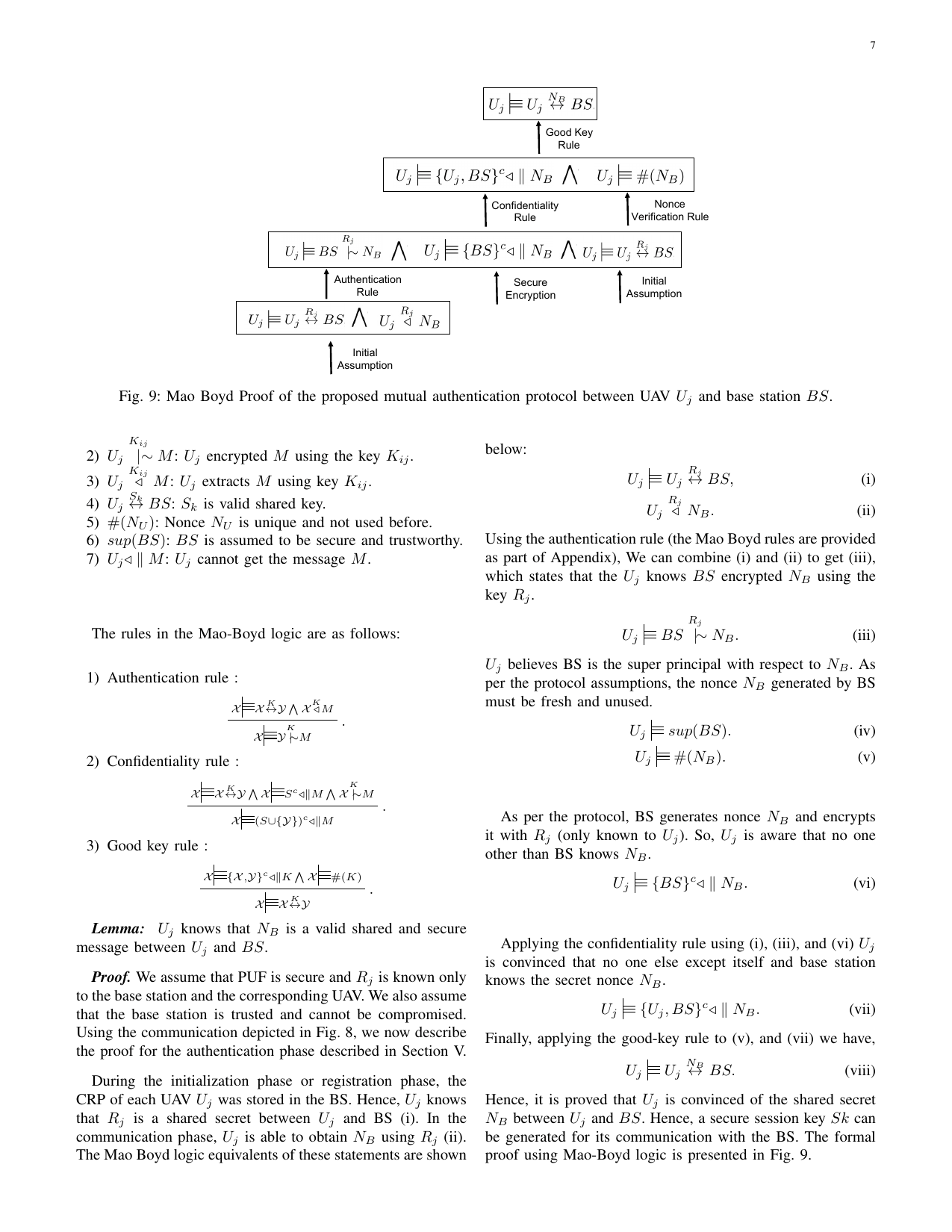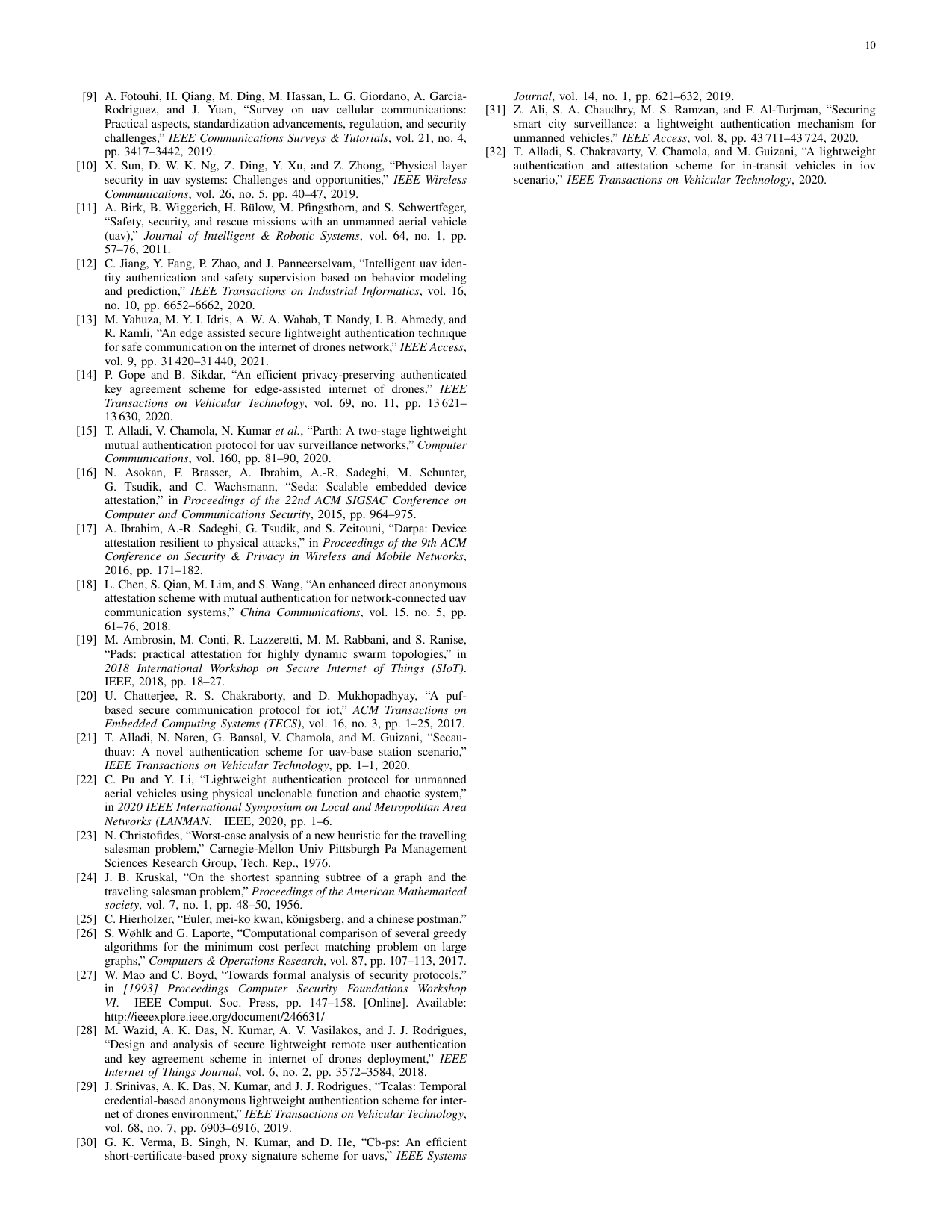 SHOTS: Scalable secure authentication-attestation protocol using optimal trajectory in UAV swarmsGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Biplab Sikdar, and othersIEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022
SHOTS: Scalable secure authentication-attestation protocol using optimal trajectory in UAV swarmsGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Biplab Sikdar, and othersIEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have enabled a broad spectrum of applications serving social, commercial, and military purposes. However, since UAVs use wireless communication technologies, they are highly vulnerable to security threats. Establishing trust with the base station is the most fundamental security aspect in UAV networks to mitigate these threats. However, due to a UAV’s constrained resources, deploying traditional trust establishment schemes in UAV networks becomes challenging. Further, this issue escalates as the number of UAVs increases. To address this issue, we propose an authentication cum attestation protocol for UAV swarms using an optimal communication trajectory, which can establish the required trust in a lightweight manner. Furthermore, our protocol uses Physical Unclonable Functions (PUFs) and thus guarantees physical security as well. We demonstrate that the proposed protocol is feasible, scalable, and secure using a formal Mao Boyd logic approach. Comparative analyses show that the proposed protocol outperforms the state-of-the-art
- Security and Privacy
 Scalable topologies for time-optimal authentication of UAV swarmsGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Nirwan Ansari, and Biplab SikdarIEEE Network, 2022
Scalable topologies for time-optimal authentication of UAV swarmsGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Nirwan Ansari, and Biplab SikdarIEEE Network, 2022Swarm-based Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) applications require a large number of UAVs to be deployed across a region to work cooperatively. To operate a large number of unattended UAVs in hostile environments, it is critical to secure UAV-BS (base station) communications. UAV authentication based on Physical Unclonable Functions (PUFs) has recently emerged as a potential solution for overcoming adversarial attacks. The performance of PUF-based authentication protocols is strongly influenced by various factors, including the time required to generate the topology, the number of bottleneck connections, and the network’s traffic load. This article investigates how the authentication time for a UAV swarm is affected by various factors such as the type of topology, number of UAVs in the swarm and the number of parallel connections.
- Security and Privacy
 Secure and trusted attestation protocol for UAV fleetsGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIn IEEE INFOCOM 2022-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), 2022
Secure and trusted attestation protocol for UAV fleetsGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIn IEEE INFOCOM 2022-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), 2022Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are capable of a wide variety of social, economic, and military applications. Due to the fact that UAVs communicate through wireless technology, they are vulnerable to security assaults. Establishing trust between the UAV and the base station is a vital component of reducing these hazards in UAV networks. Due to the restricted resources available to UAVs, adopting typical trust-building procedures in UAV networks becomes challenging. Additionally, as the number of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) increases, this issue gets more critical. To address this issue, we offer a lightweight attestation mechanism for unmanned aerial vehicle swarms. Comparative analyses reveal that the proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art already available
- Security and Privacy
 Fault resilient authentication architecture for drone networksGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIn 2022 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), 2022
Fault resilient authentication architecture for drone networksGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIn 2022 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), 2022Wireless communication technology, particularly in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) applications, has advanced rapidly recently. However, owing to security flaws, UAV-based applications have not reached their full potential. Interception of drone-based station communication is possible. Many authentication mechanisms, including Physical Unclonable Functions (PUF) based protocols, have been developed to address this problem. However, prior studies require noise-resistant and theoretically perfect PUF. This assumption restricts the usage of UAV-based authentication. This assumption limits the use-cases for UAV-based authentication systems. So we propose a novel distributed authentication approach based on Shamir’s secret sharing that is resistant to noisy PUFs.
- Metaverse
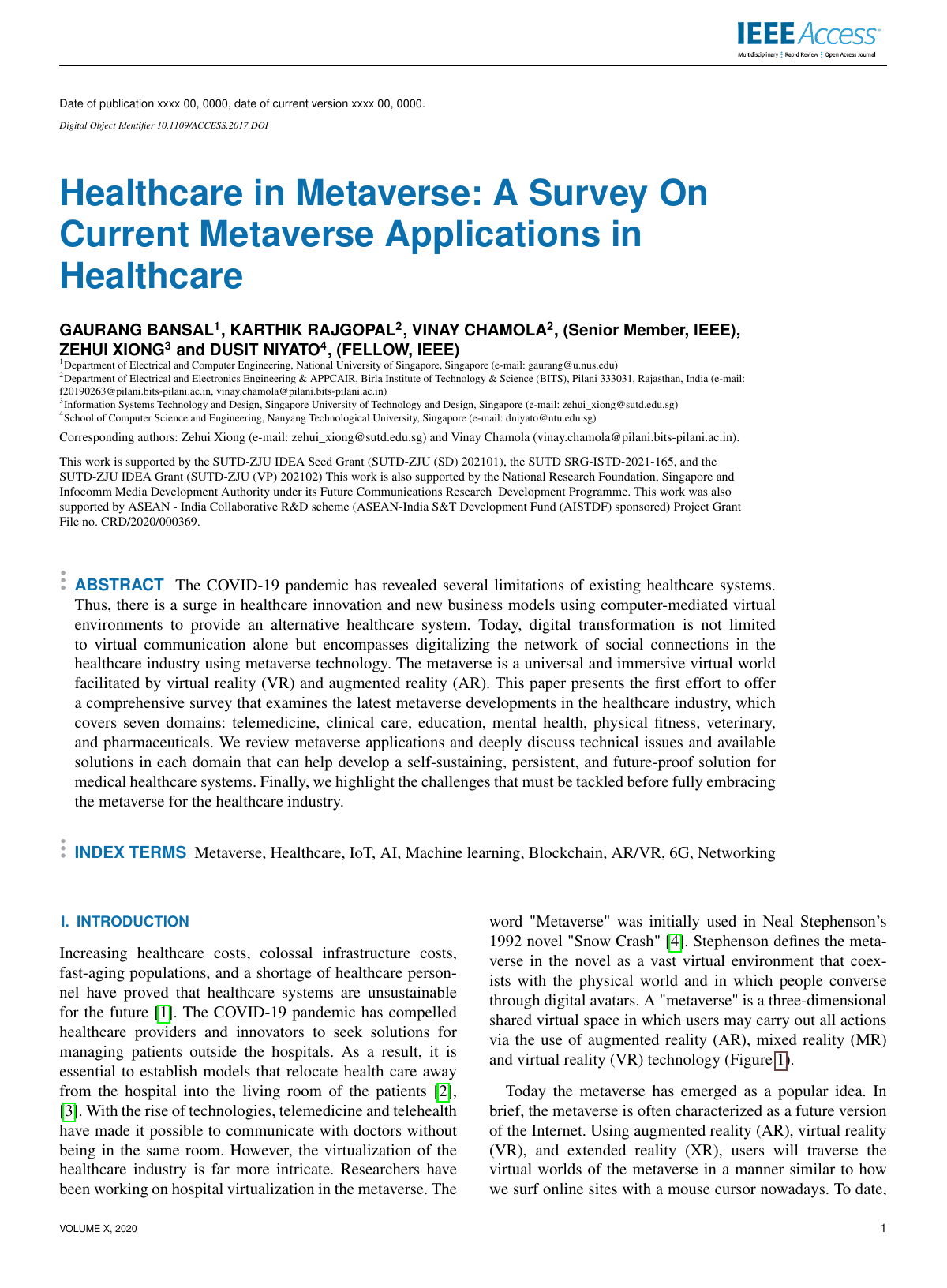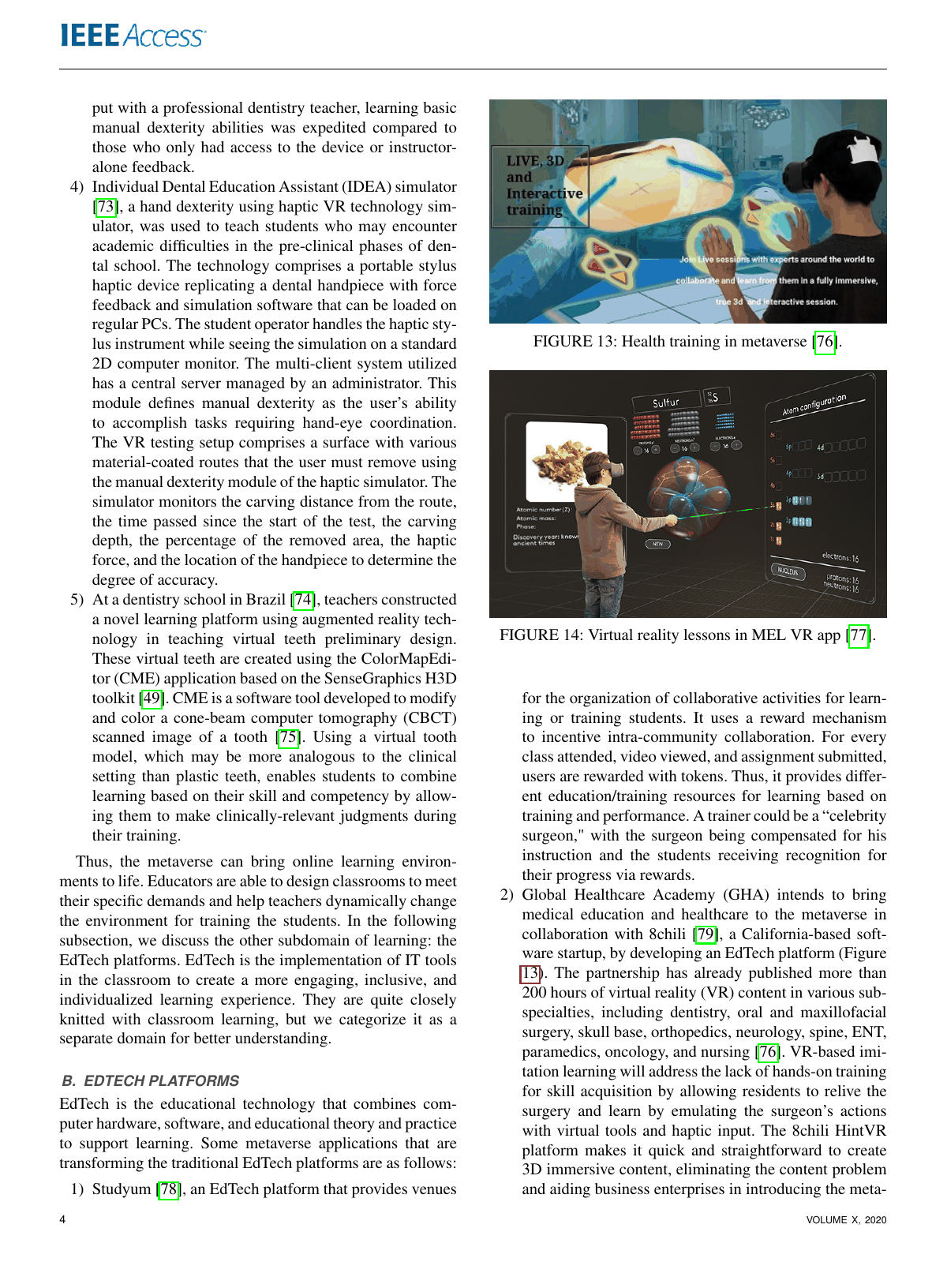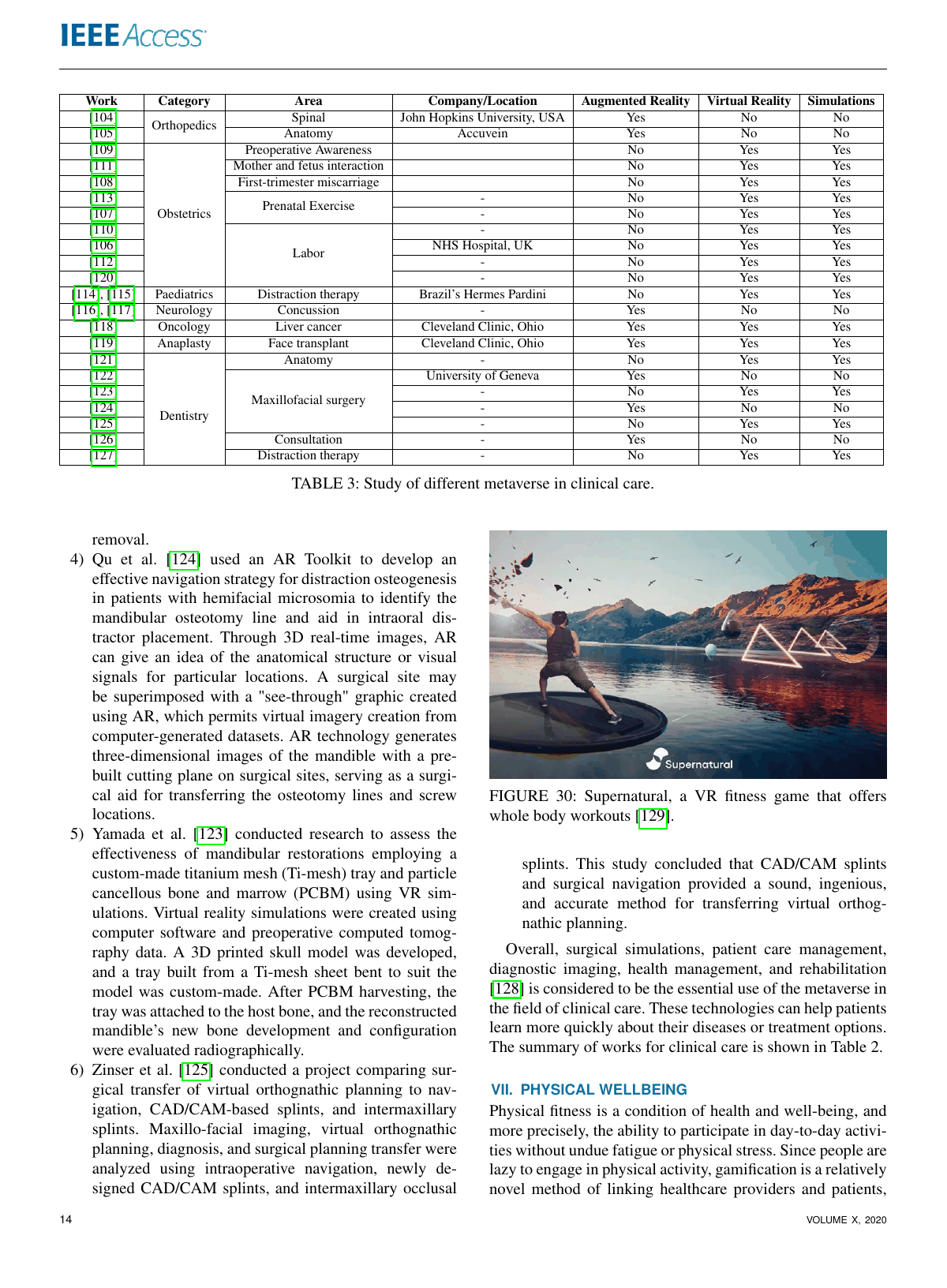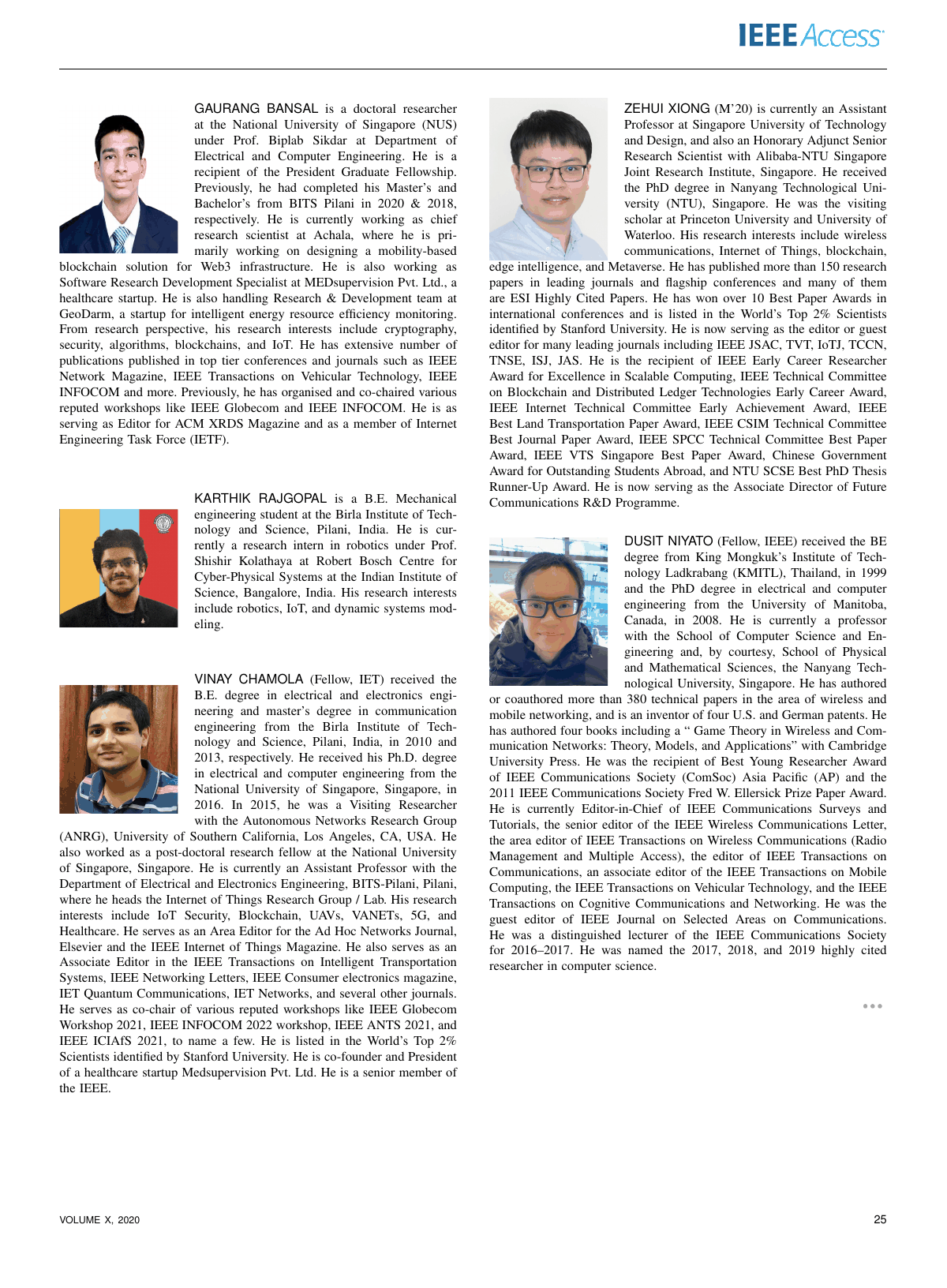 Healthcare in Metaverse: A Survey On Current Metaverse Applications in HealthcareGaurang Bansal, Karthik Rajgopal, Vinay Chamola, Zehui Xiong, and Dusit NiyatoIEEE Access, 2022
Healthcare in Metaverse: A Survey On Current Metaverse Applications in HealthcareGaurang Bansal, Karthik Rajgopal, Vinay Chamola, Zehui Xiong, and Dusit NiyatoIEEE Access, 2022The COVID-19 pandemic has revealed several limitations of existing healthcare systems. Thus, there is a surge in healthcare innovation and new business models using computer-mediated virtual environments to provide an alternative healthcare system. Today, digital transformation is not limited to virtual communication alone but encompasses digitalizing the network of social connections in the healthcare industry using metaverse technology. The metaverse is a universal and immersive virtual world facilitated by virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). This paper presents the first effort to offer a comprehensive survey that examines the latest metaverse developments in the healthcare industry, which covers seven domains: telemedicine, clinical care, education, mental health, physical fitness, veterinary, and pharmaceuticals. We review metaverse applications and deeply discuss technical issues and available solutions in each domain that can help develop a self-sustaining, persistent, and future-proof solution for medical healthcare systems. Finally, we highlight the challenges that must be tackled before fully embracing the metaverse for the healthcare industry.
2021
- Security and Privacy
 Security service pricing model for UAV swarms: A stackelberg game approachGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIn IEEE INFOCOM 2021-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), 2021
Security service pricing model for UAV swarms: A stackelberg game approachGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIn IEEE INFOCOM 2021-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), 2021Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, popularly known as UAVs, have been used in many applications, from healthcare services to military assignments with diverse capabilities such as data transmission, cellular service provisioning, and computational offloading tasks. UAV’s have been recently used to provide Security as a Service (SaaS). SaaS involves techni- cal solutions like anti-virus and anti-spam software, firewalls, using secure operating systems, etc. UAV’s are resource-constrained devices, and thus they are connected to the base station (BS) so that they may avail the computational facilities of the BS. The UAV’s connect themselves to the base station using cluster heads (intermediary devices). At times several UAVs cooperatively come together to serve a given region and such a group of UAVs is called a swarm of UAVs. In real-world scenarios, many stakeholders come together to form UAV swarm configuration proving services to users. Each stakeholder wants to maximize his gains. In this work, we propose a pricing Stackelberg game among UAVs, Cluster heads, and BS by formulating their behavioral utilities. Using particle swarm optimization on each entity’s utility functions, we create an optimal price strategy for each entity to maximize their profit.
- Deep Learning
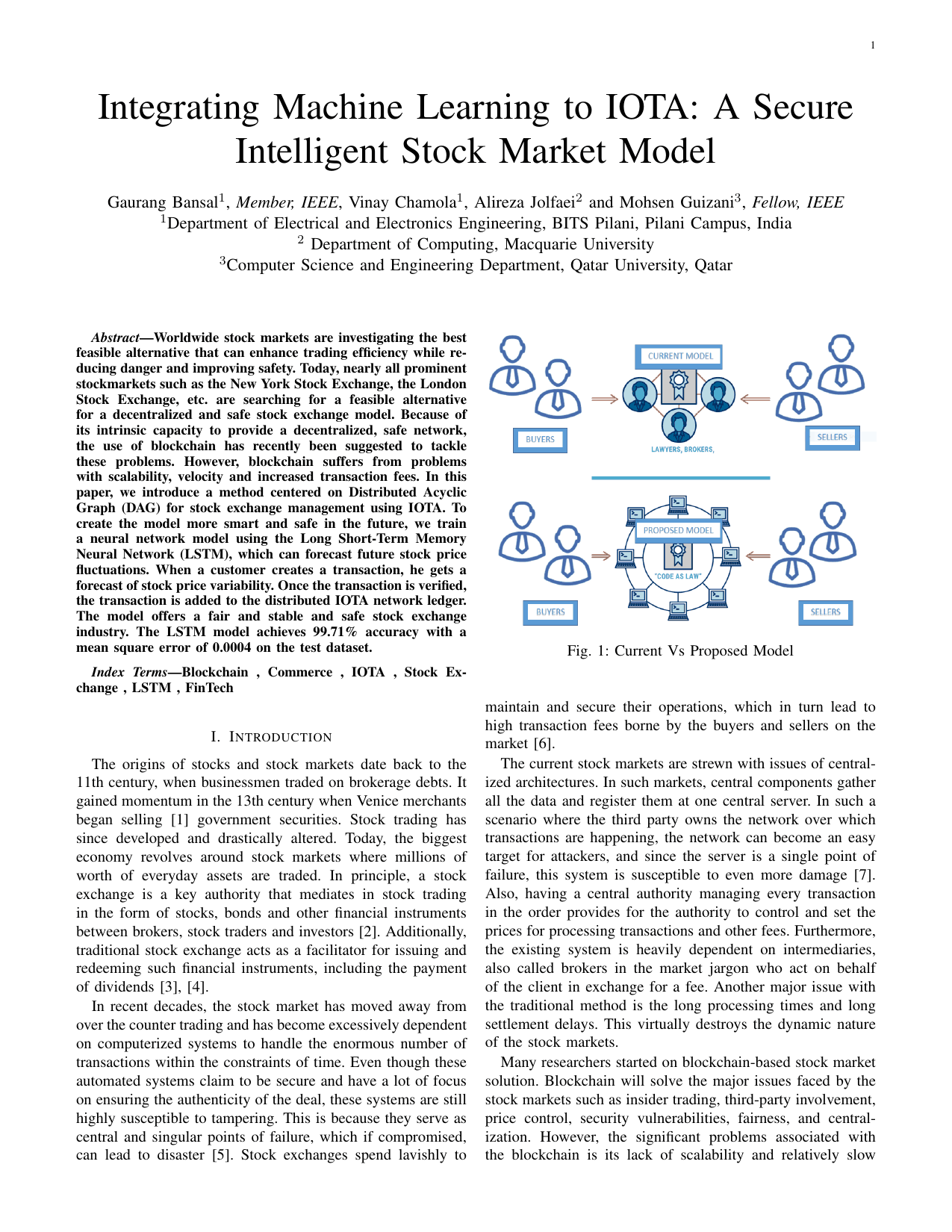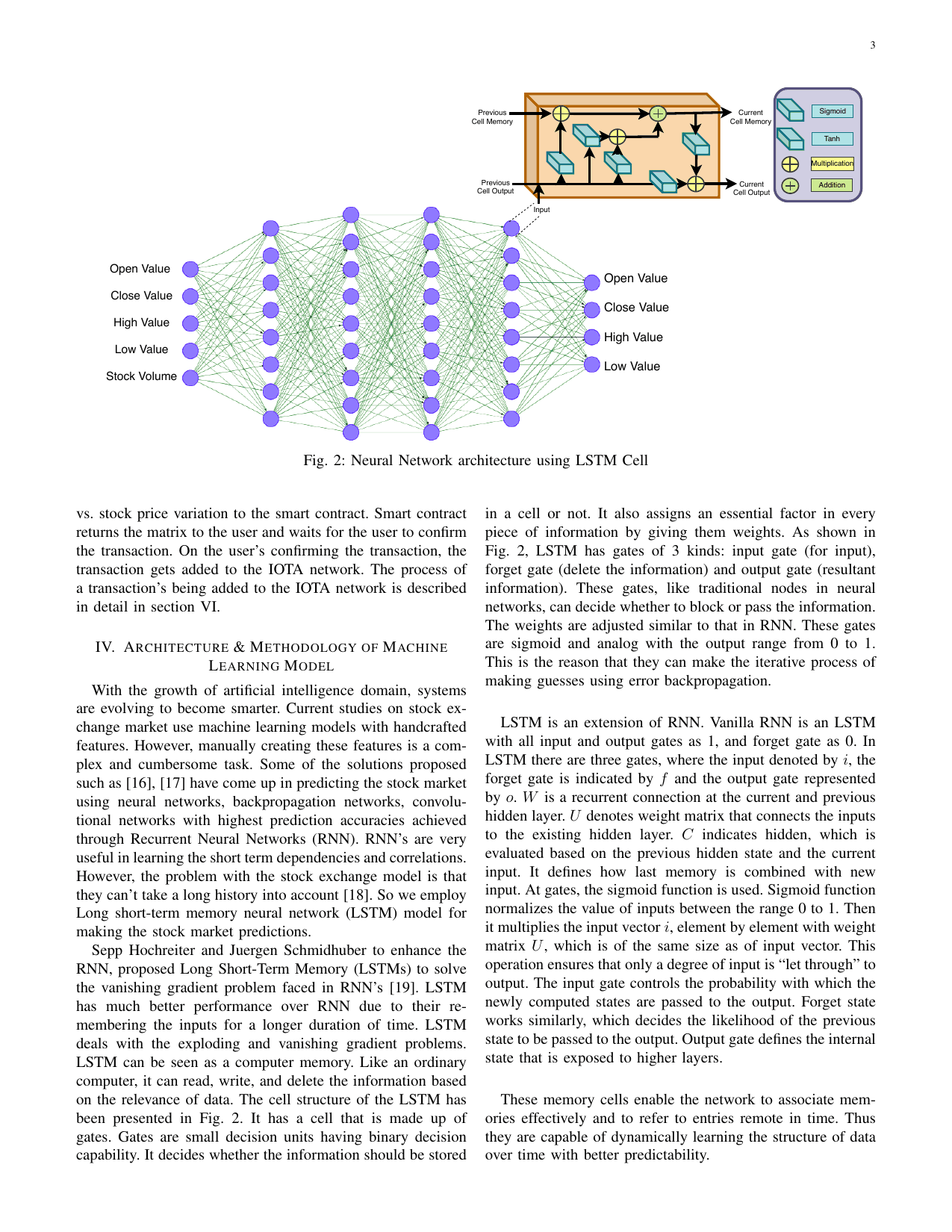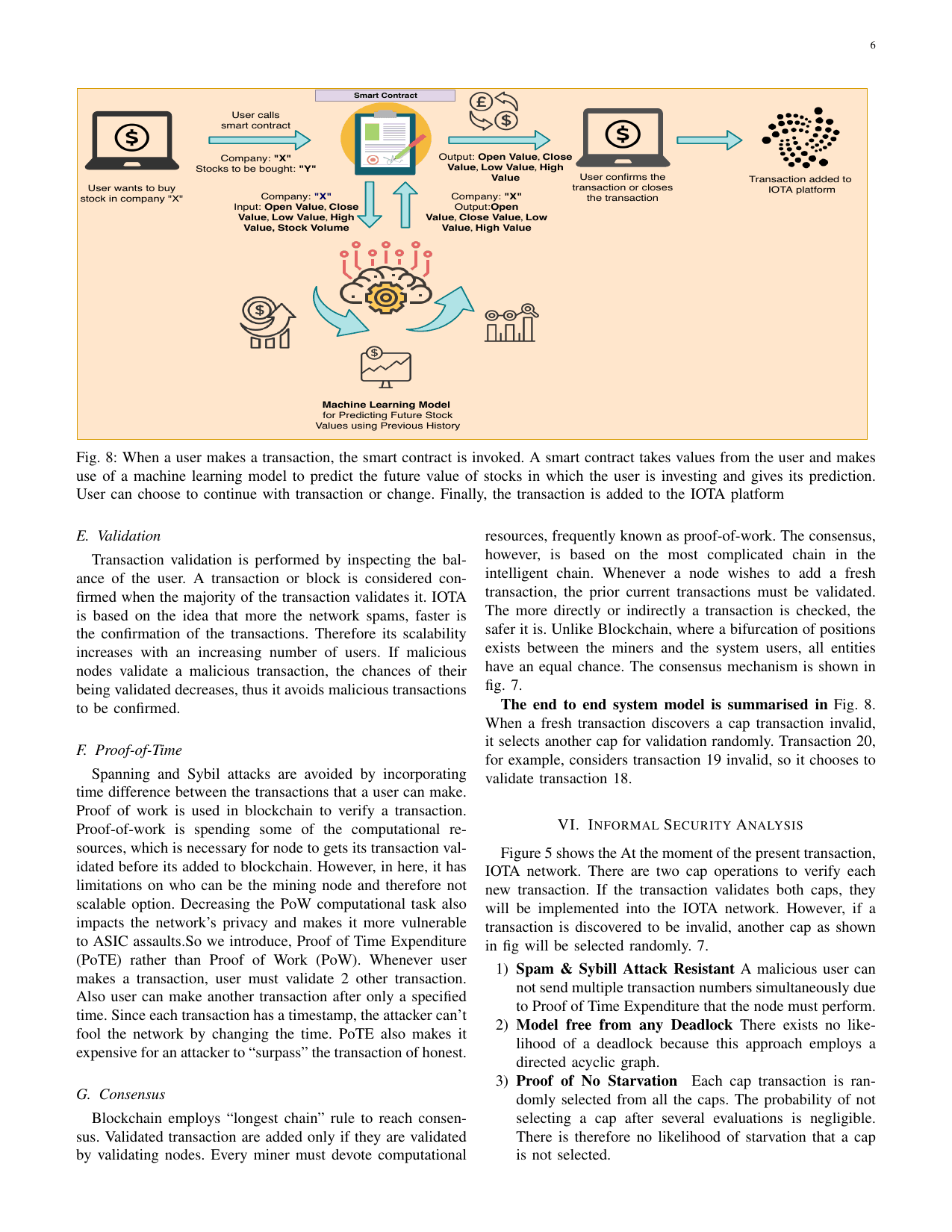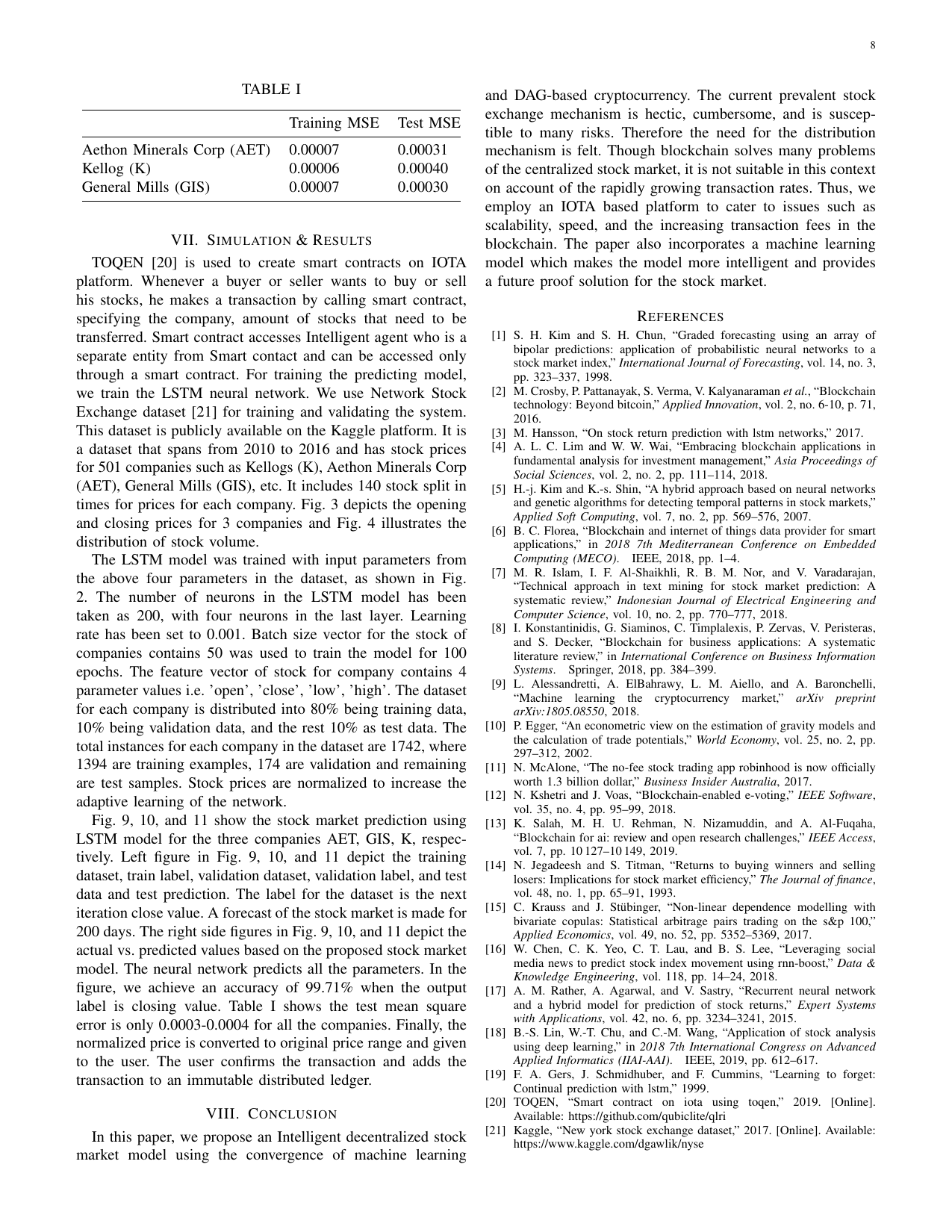 Next generation stock exchange: Recurrent neural learning model for distributed ledger transactionsGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Georges Kaddoum, Md Jalil Piran, and Mubarak AlrashoudComputer Networks, 2021
Next generation stock exchange: Recurrent neural learning model for distributed ledger transactionsGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Georges Kaddoum, Md Jalil Piran, and Mubarak AlrashoudComputer Networks, 2021Worldwide stock markets are investigating the best feasible alternative that can enhance trading efficiency while re- ducing danger and improving safety. Today, nearly all prominent stockmarkets such as the New York Stock Exchange, the London Stock Exchange, etc. are searching for a feasible alternative for a decentralized and safe stock exchange model. Because of its intrinsic capacity to provide a decentralized, safe network, the use of blockchain has recently been suggested to tackle these problems. However, blockchain suffers from problems with scalability, velocity and increased transaction fees. In this paper, we introduce a method centered on Distributed Acyclic Graph (DAG) for stock exchange management using IOTA. To create the model more smart and safe in the future, we train a neural network model using the Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network (LSTM), which can forecast future stock price fluctuations. When a customer creates a transaction, he gets a forecast of stock price variability. Once the transaction is verified, the transaction is added to the distributed IOTA network ledger. The model offers a fair and stable and safe stock exchange industry. The LSTM model achieves 99.71% accuracy with a mean square error of 0.0004 on the test dataset.
- Security and Privacy
 S-MAPS: Scalable mutual authentication protocol for dynamic UAV swarmsGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021
S-MAPS: Scalable mutual authentication protocol for dynamic UAV swarmsGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) domain has seen rapid developments in recent years. UAVs have been deployed for many applications and missions like data transmission, cel- lular service provisioning, and computational offloading tasks etc. Yet, UAV deployment is still limited, partially owing to the security challenges it poses. UAVs are particularly vulnerable to physical capture, cloning attacks, eavesdropping, and man in the middle attacks. To address some of these security problems, this paper develops an authentication protocol for use in UAV swarms. To ensure physical security and rapid authentication, the proposed protocol uses Physical Unclonable Functions (PUFs). The protocol achieves high scalability compared to the state of the art by authenticating multiple devices at once. The proposed protocol supports dynamic topologies and multi-hop communication by using spanning tree-based traversal. It is also resistant to mobility, device failure, etc., and its improve- ments are achieved at significantly lower communication and communication cost as compared to state-of-the-art protocols.
- Security and Privacy
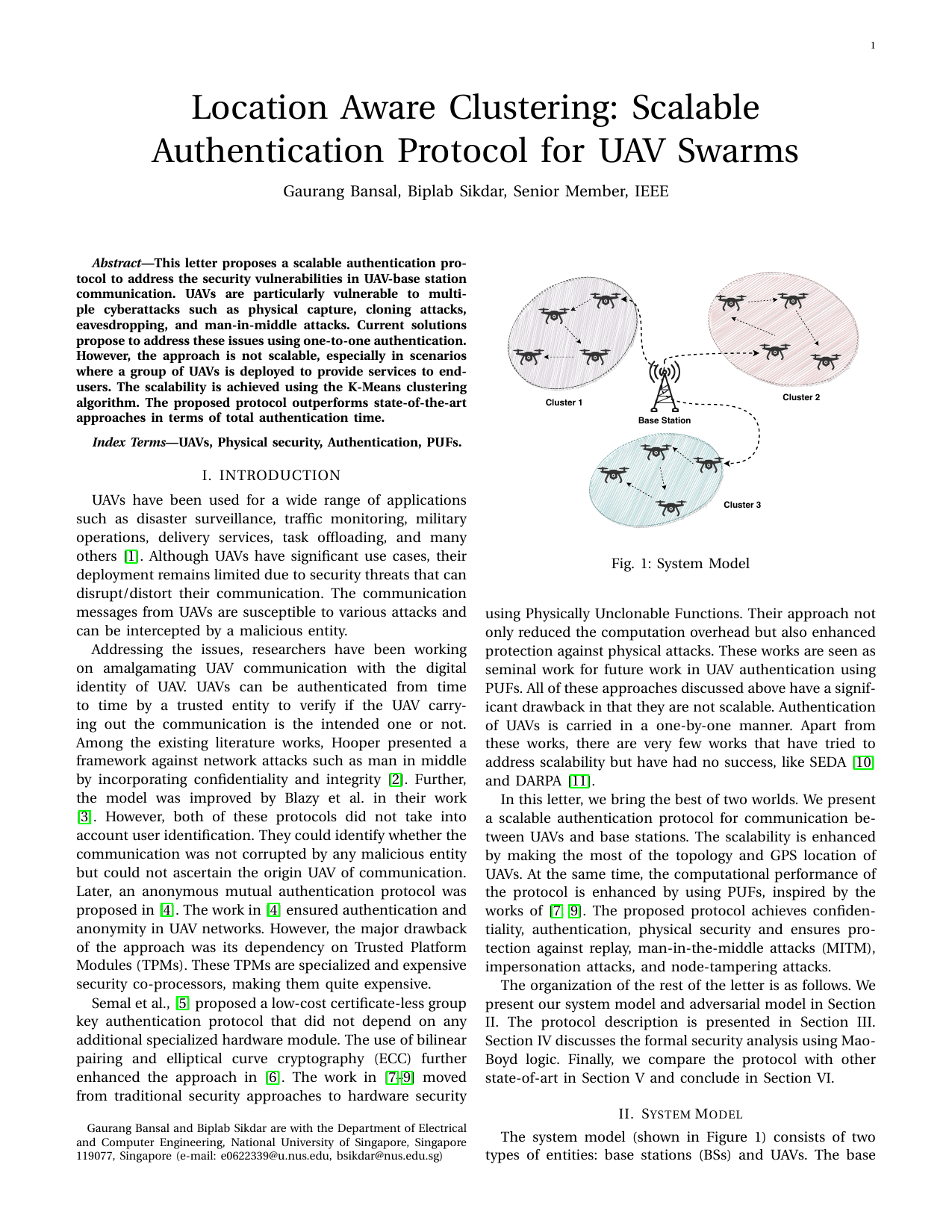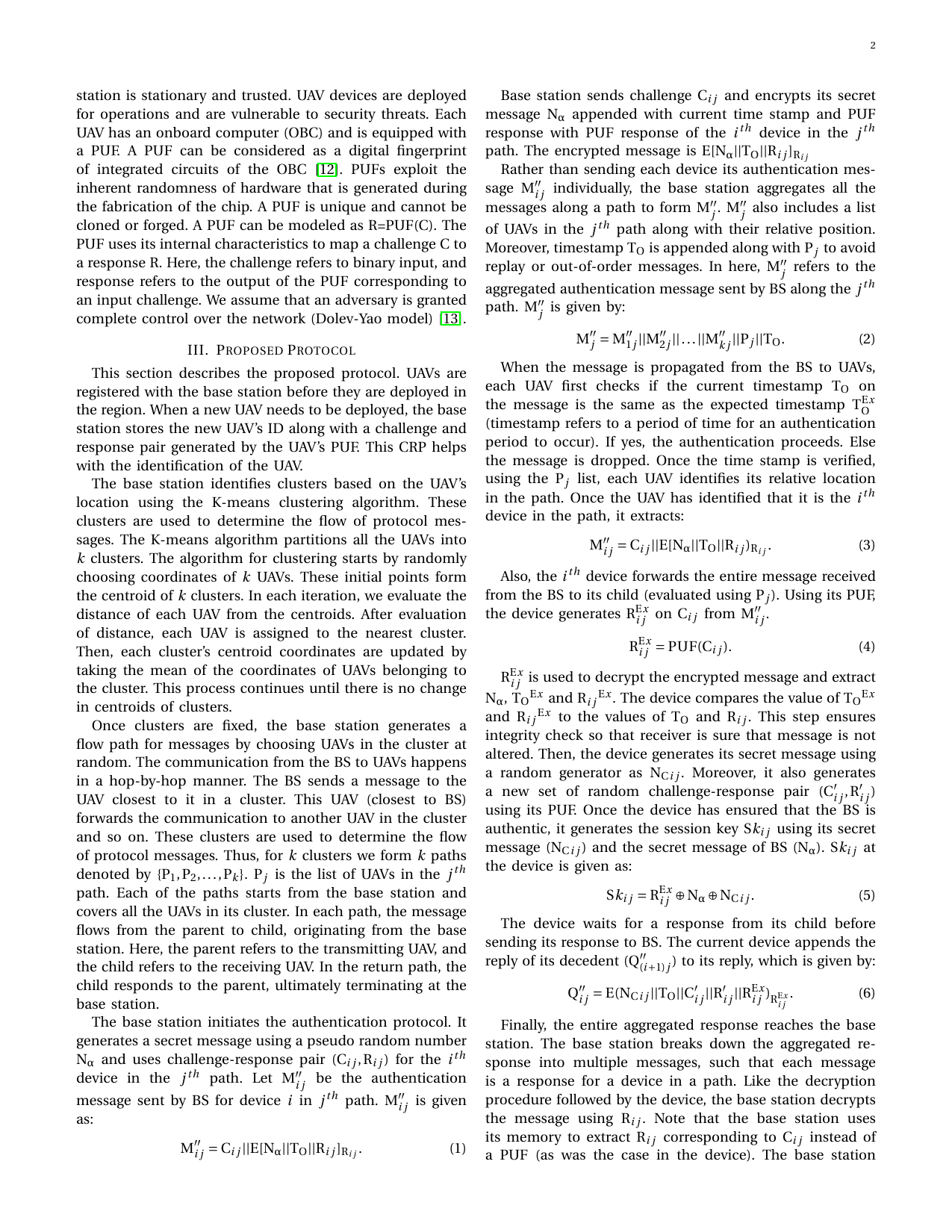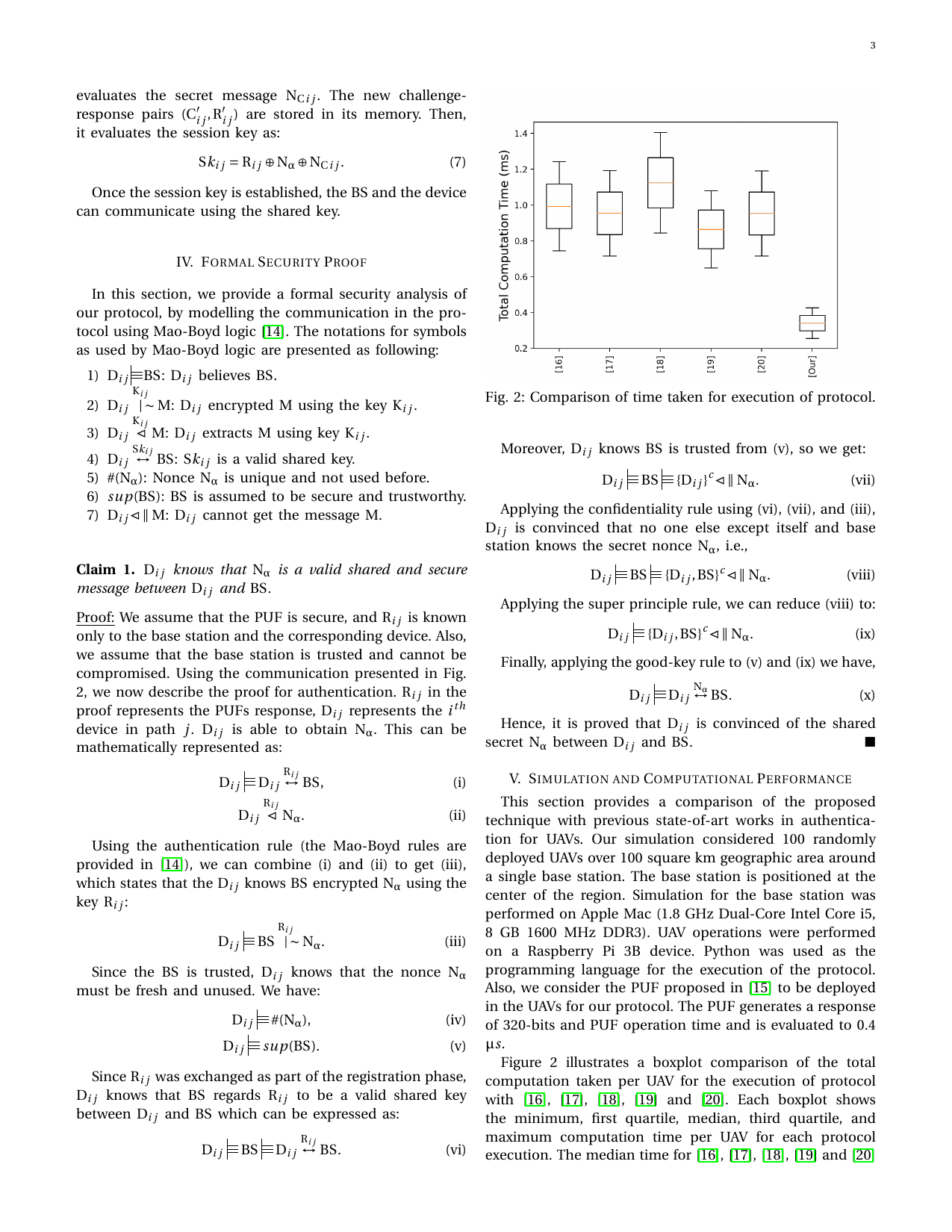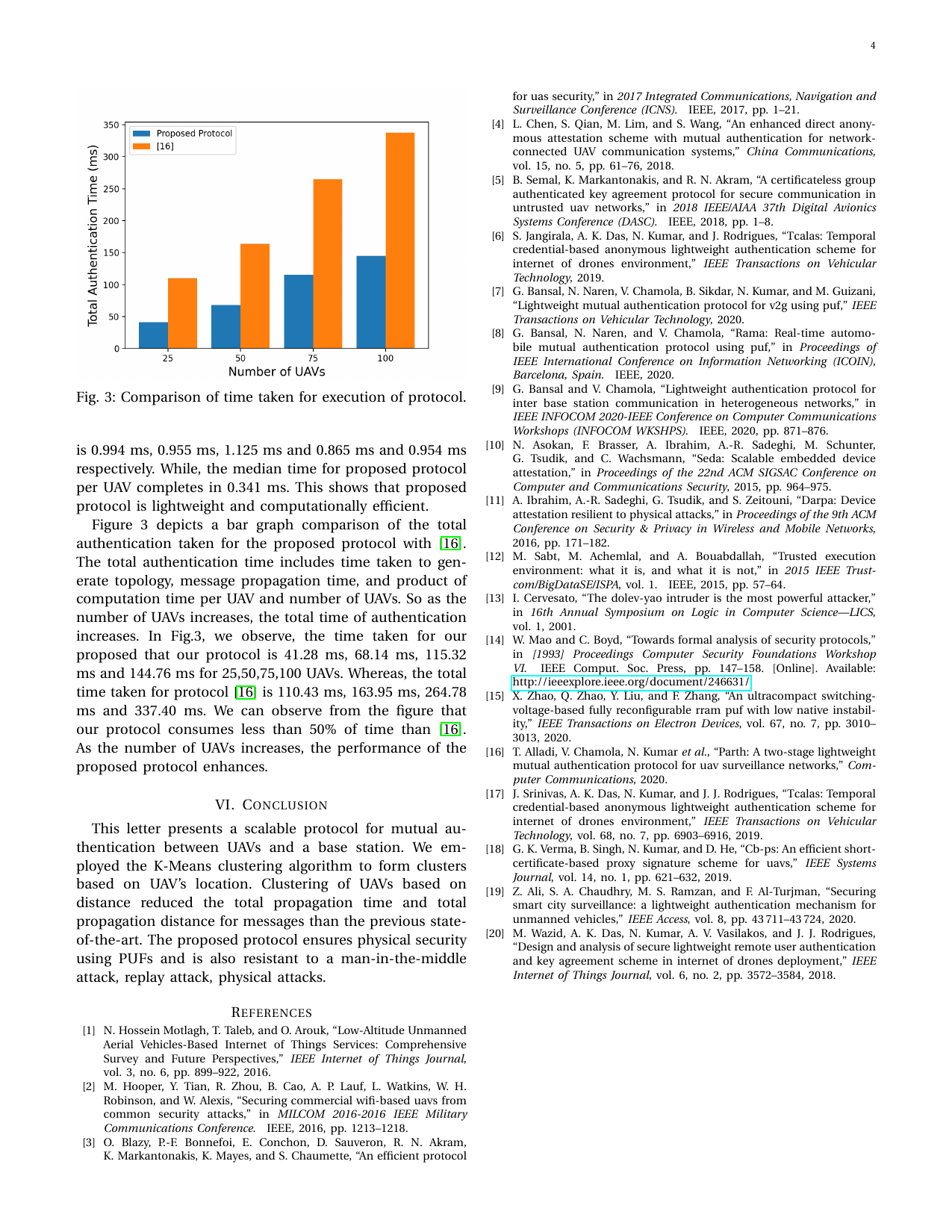 Location aware clustering: Scalable authentication protocol for UAV swarmsGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIEEE Networking Letters, 2021
Location aware clustering: Scalable authentication protocol for UAV swarmsGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIEEE Networking Letters, 2021This letter proposes a scalable authentication pro- tocol to address the security vulnerabilities in UAV-base station communication. UAVs are particularly vulnerable to multi- ple cyberattacks such as physical capture, cloning attacks, eavesdropping, and man-in-middle attacks. Current solutions propose to address these issues using one-to-one authentication. However, the approach is not scalable, especially in scenarios where a group of UAVs is deployed to provide services to end- users. The scalability is achieved using the K-Means clustering algorithm. The proposed protocol outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in terms of total authentication time.
- Security and Privacy
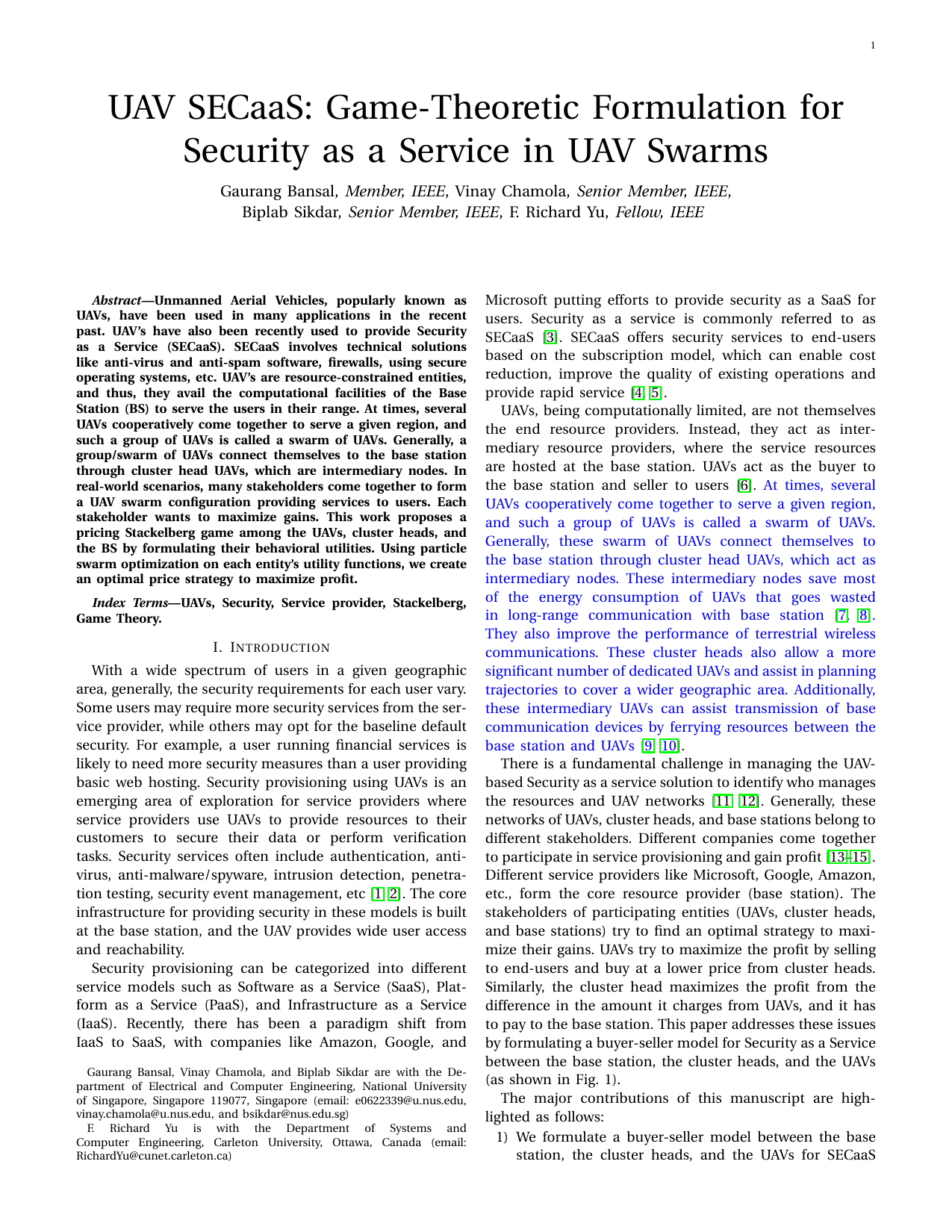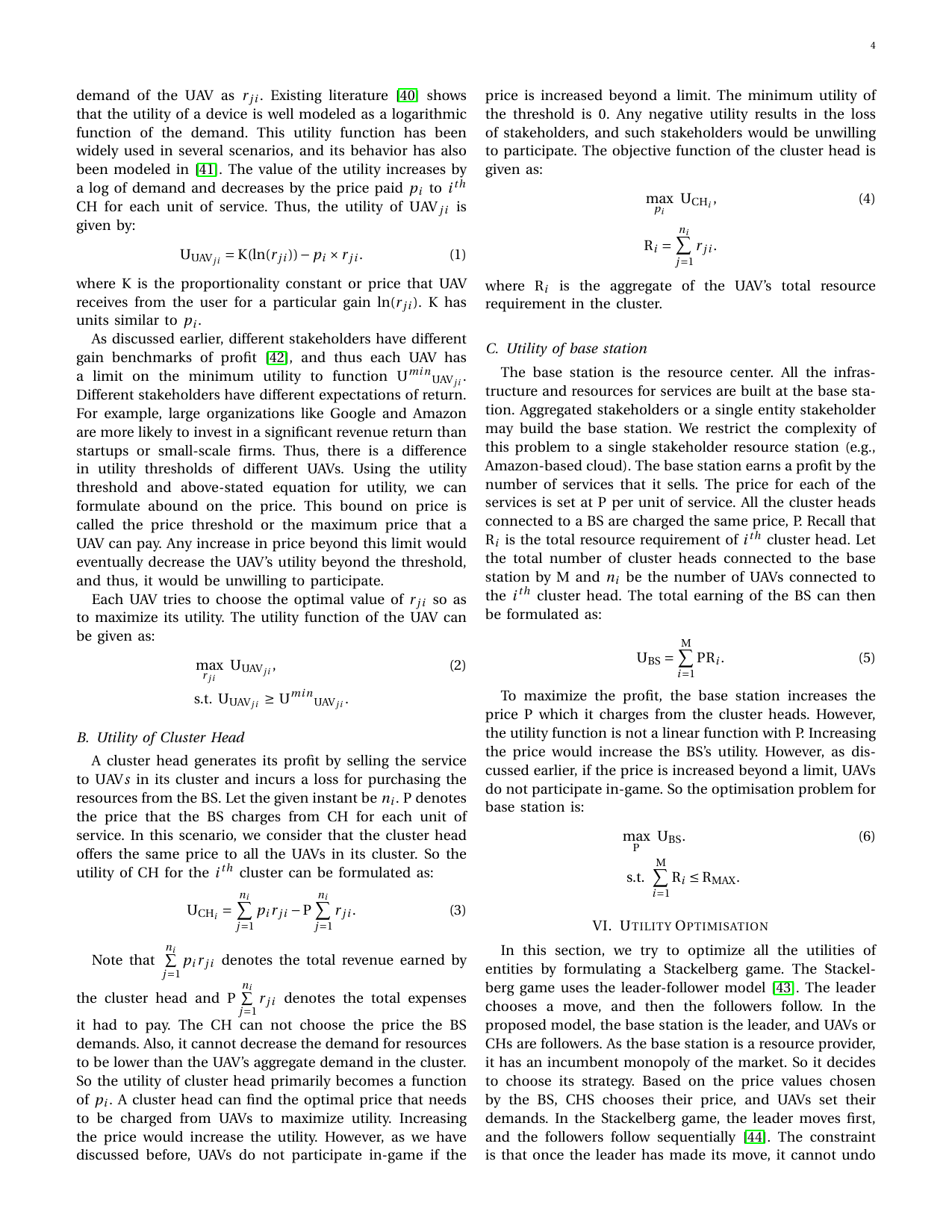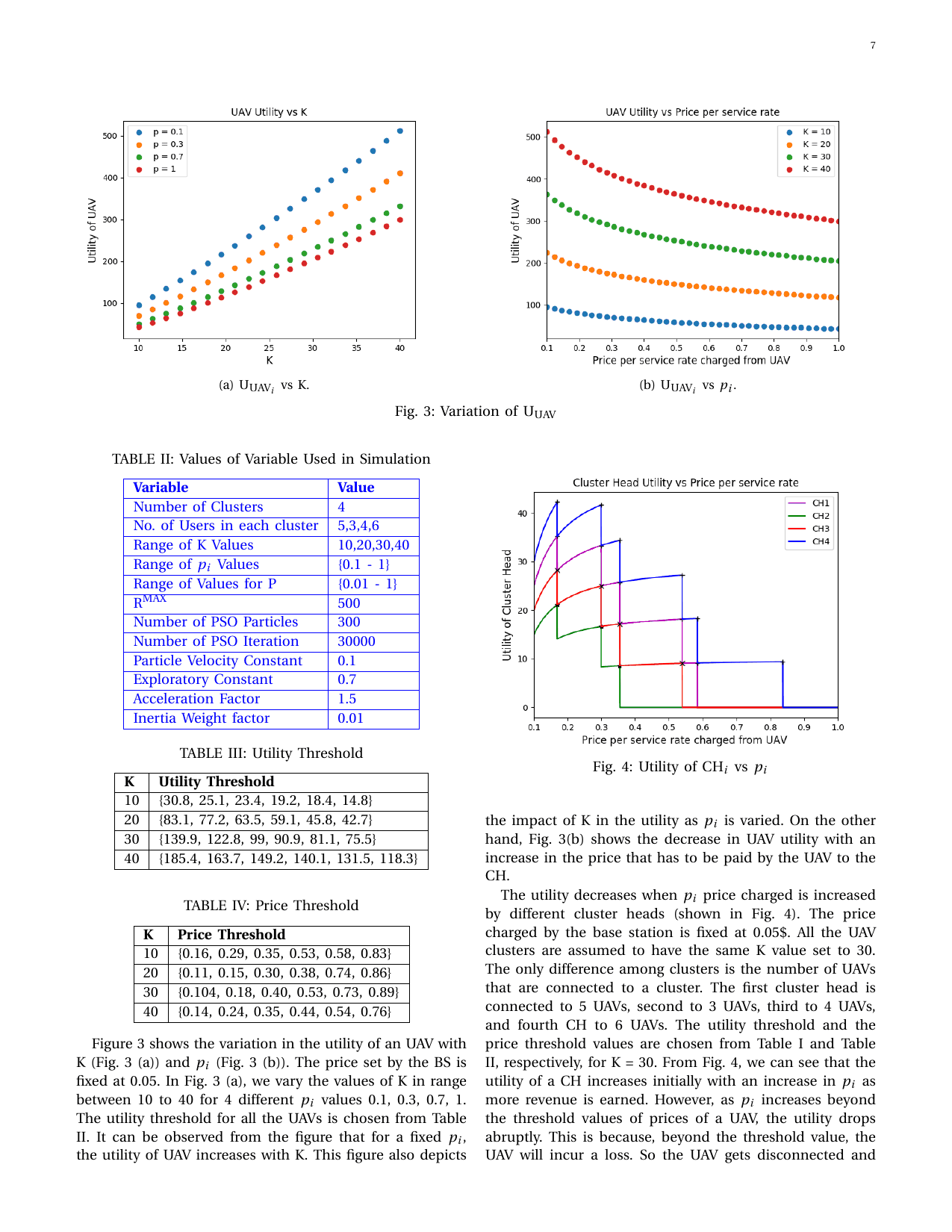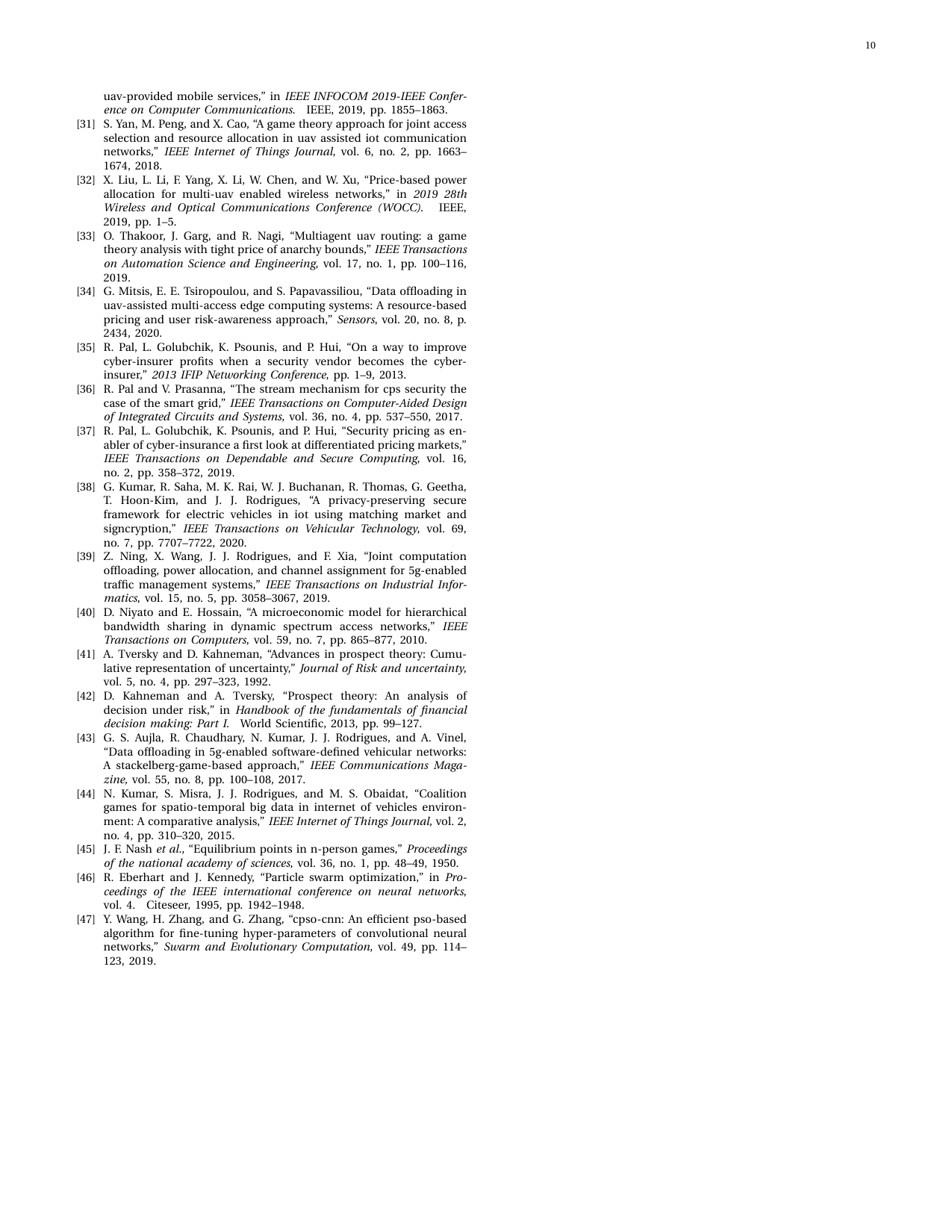 UAV SECaaS: Game-Theoretic Formulation for Security as a Service in UAV SwarmsGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Biplab Sikdar, and Fei Richard YuIEEE Systems Journal, 2021
UAV SECaaS: Game-Theoretic Formulation for Security as a Service in UAV SwarmsGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Biplab Sikdar, and Fei Richard YuIEEE Systems Journal, 2021Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, popularly known as UAVs, have been used in many applications in the recent past. UAV’s have also been recently used to provide Security as a Service (SECaaS). SECaaS involves technical solutions like anti-virus and anti-spam software, firewalls, using secure operating systems, etc. UAV’s are resource-constrained entities, and thus, they avail the computational facilities of the Base Station (BS) to serve the users in their range. At times, several UAVs cooperatively come together to serve a given region, and such a group of UAVs is called a swarm of UAVs. Generally, a group/swarm of UAVs connect themselves to the base station through cluster head UAVs, which are intermediary nodes. In real-world scenarios, many stakeholders come together to form a UAV swarm configuration providing services to users. Each stakeholder wants to maximize gains. This work proposes a pricing Stackelberg game among the UAVs, cluster heads, and the BS by formulating their behavioral utilities. Using particle swarm optimization on each entity’s utility functions, we create an optimal price strategy to maximize profit.
- Performance Modelling
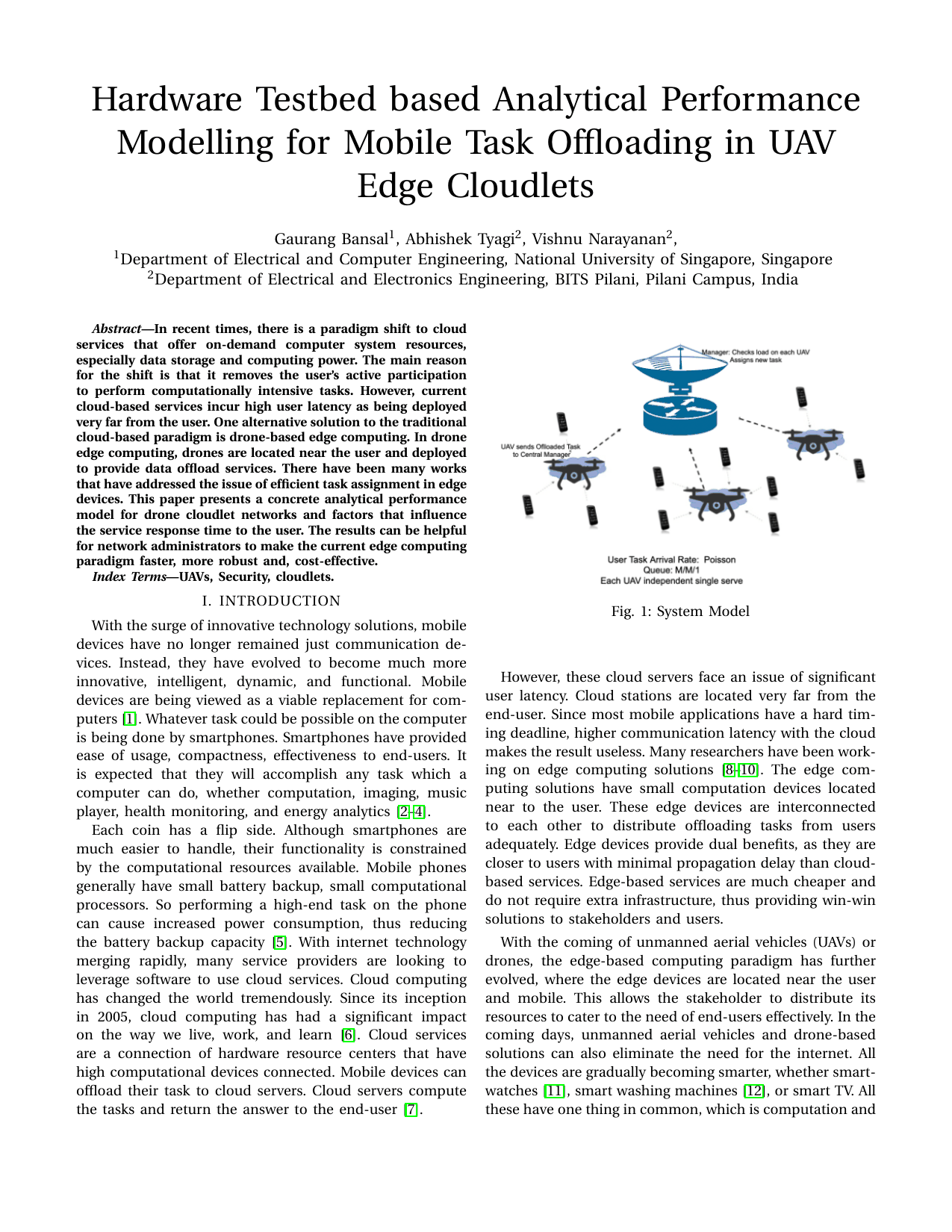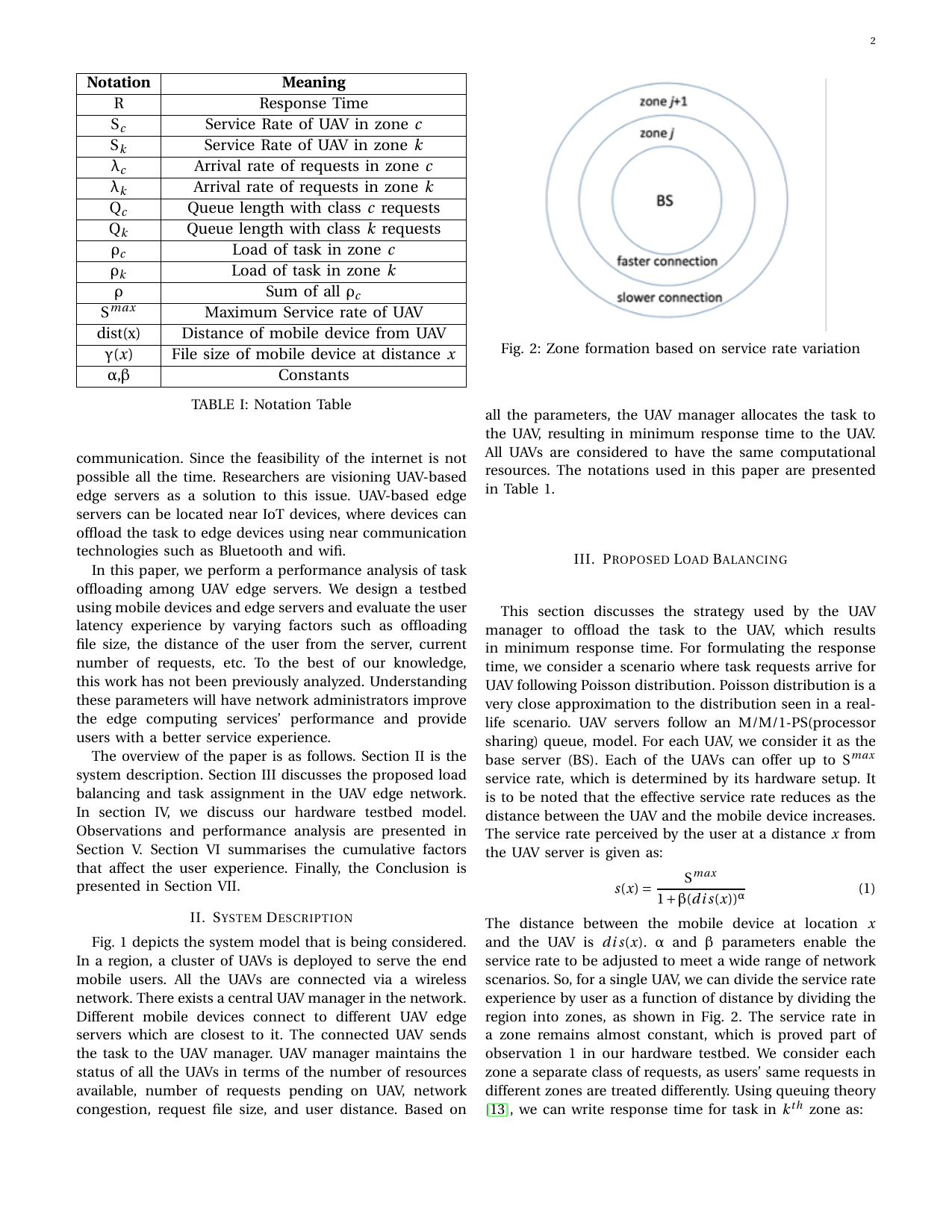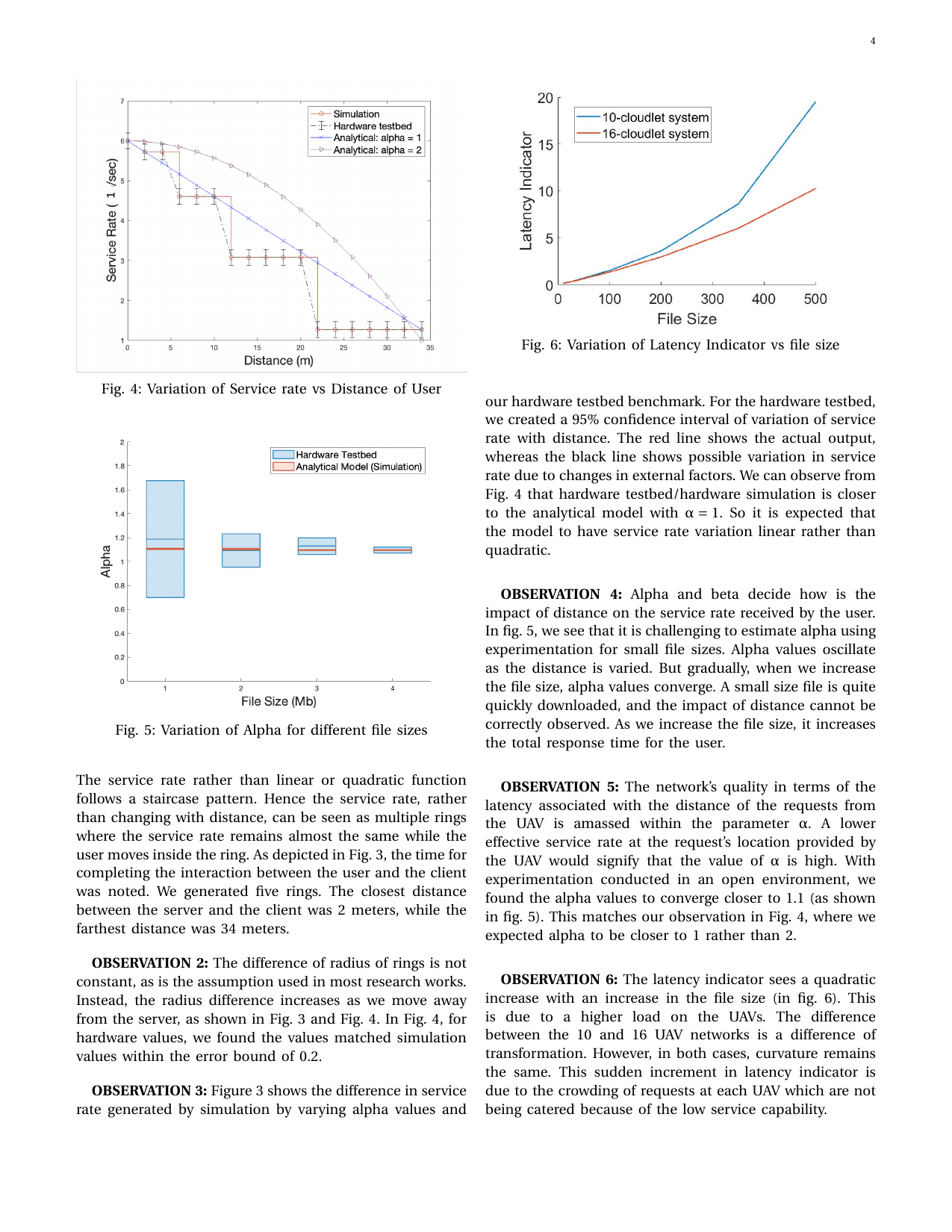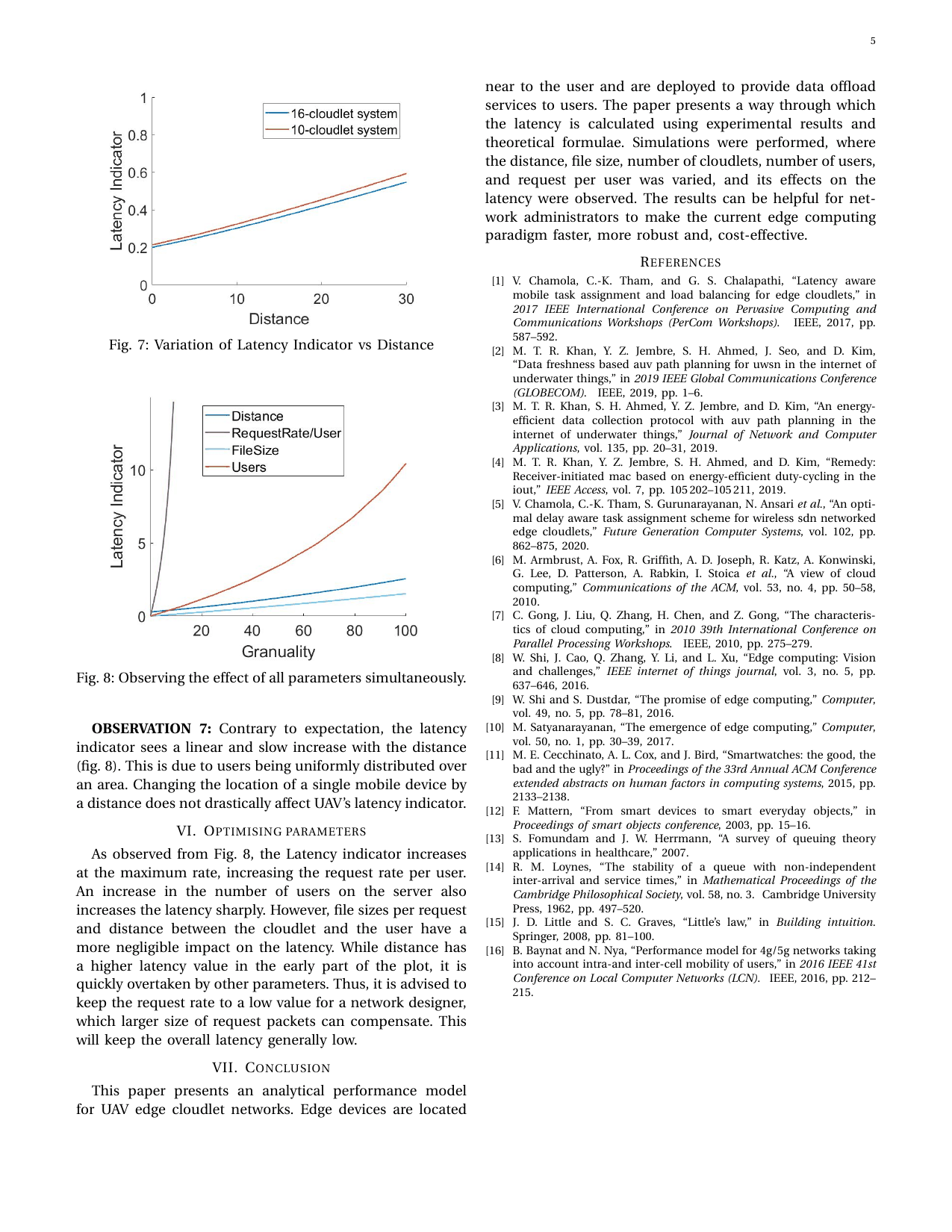 Hardware Testbed based Analytical Performance Modelling for Mobile Task Offloading in UAV Edge CloudletsGaurang Bansal, Abhishek Tyagi, Vishnu Narayanan, and Vinay ChamolaIn IEEE VTC Workshop (Fall) 2021, 2021
Hardware Testbed based Analytical Performance Modelling for Mobile Task Offloading in UAV Edge CloudletsGaurang Bansal, Abhishek Tyagi, Vishnu Narayanan, and Vinay ChamolaIn IEEE VTC Workshop (Fall) 2021, 2021In recent times, there is a paradigm shift to cloud services that offer on-demand computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power. The main reason for the shift is that it removes the user’s active participation to perform computationally intensive tasks. However, current cloud-based services incur high user latency as being deployed very far from the user. One alternative solution to the traditional cloud-based paradigm is drone-based edge computing. In drone edge computing, drones are located near the user and deployed to provide data offload services. There have been many works that have addressed the issue of efficient task assignment in edge devices. This paper presents a concrete analytical performance model for drone cloudlet networks and factors that influence the service response time to the user. The results can be helpful for network administrators to make the current edge computing paradigm faster, more robust and, cost-effective.
- Security and Privacy
 A secure and efficient mutual authentication protocol framework for unmanned aerial vehiclesGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIn 2021 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), 2021
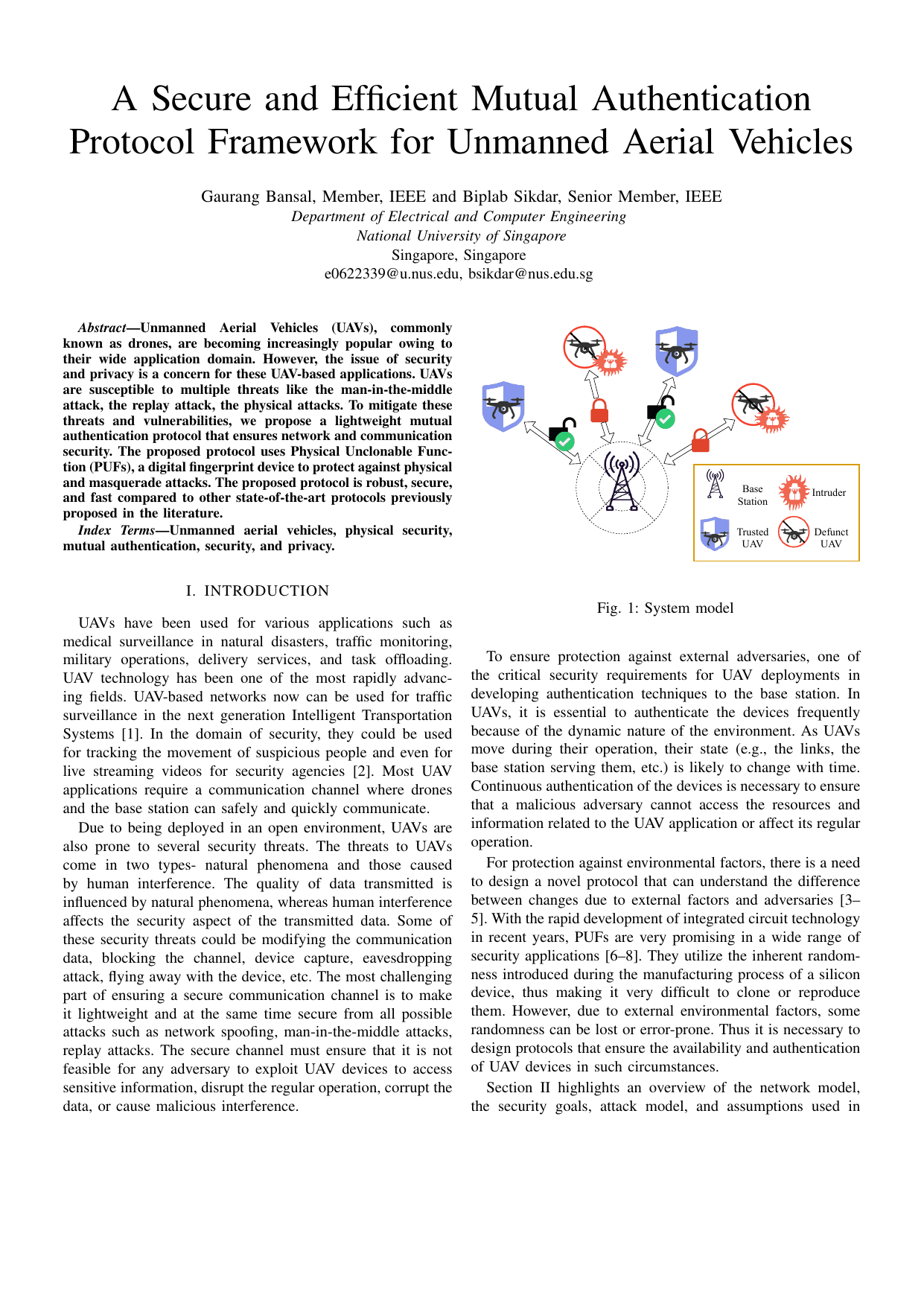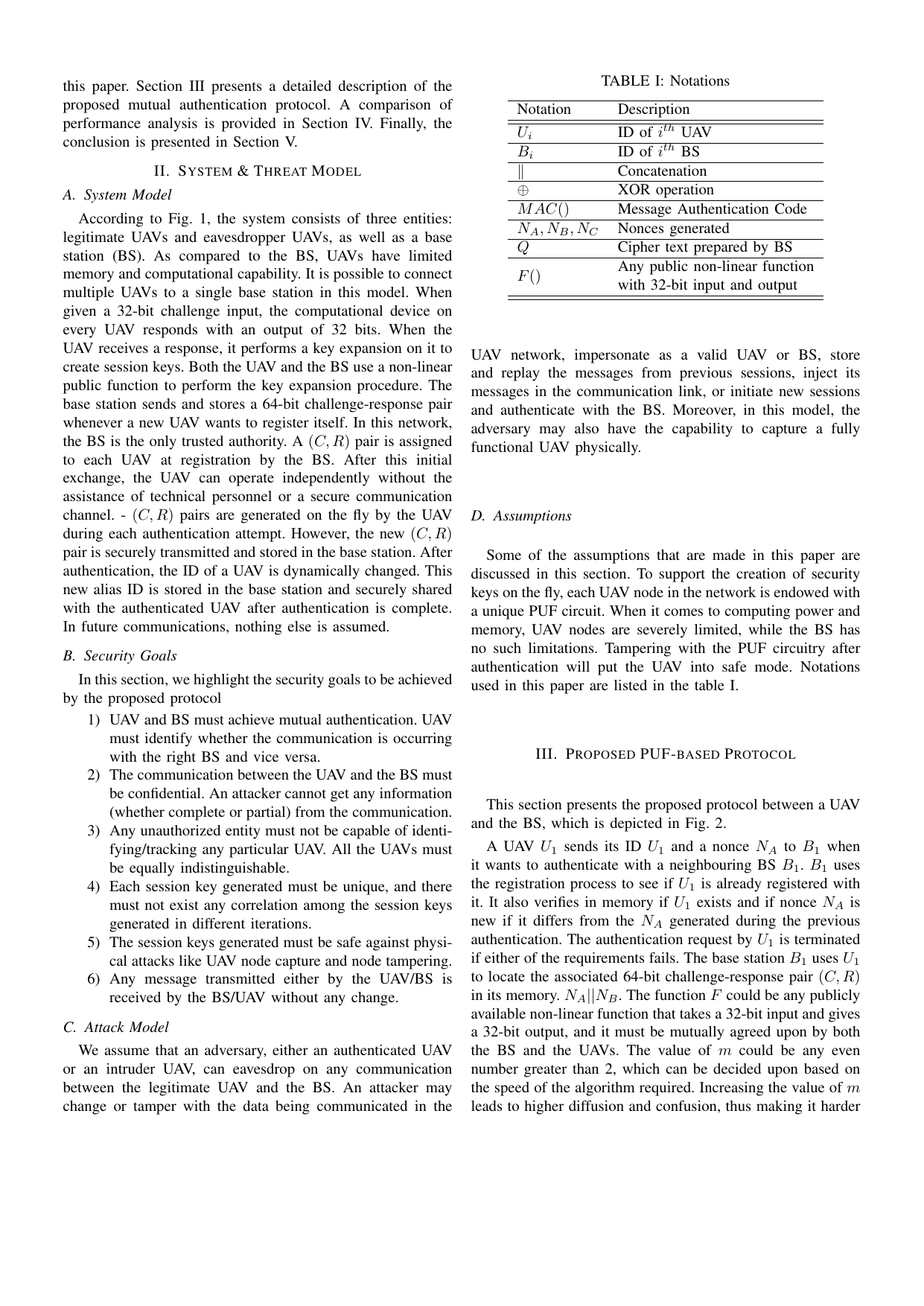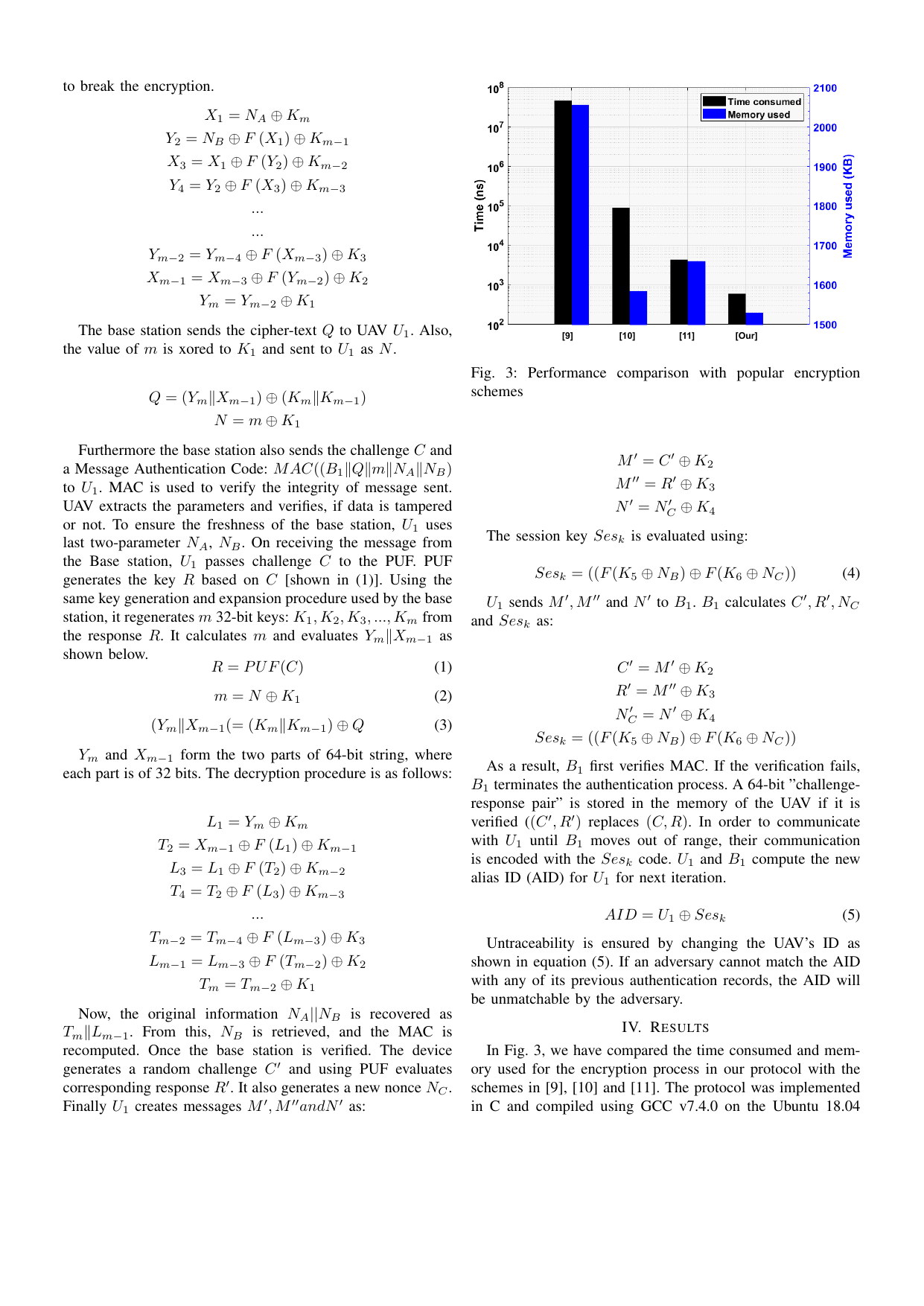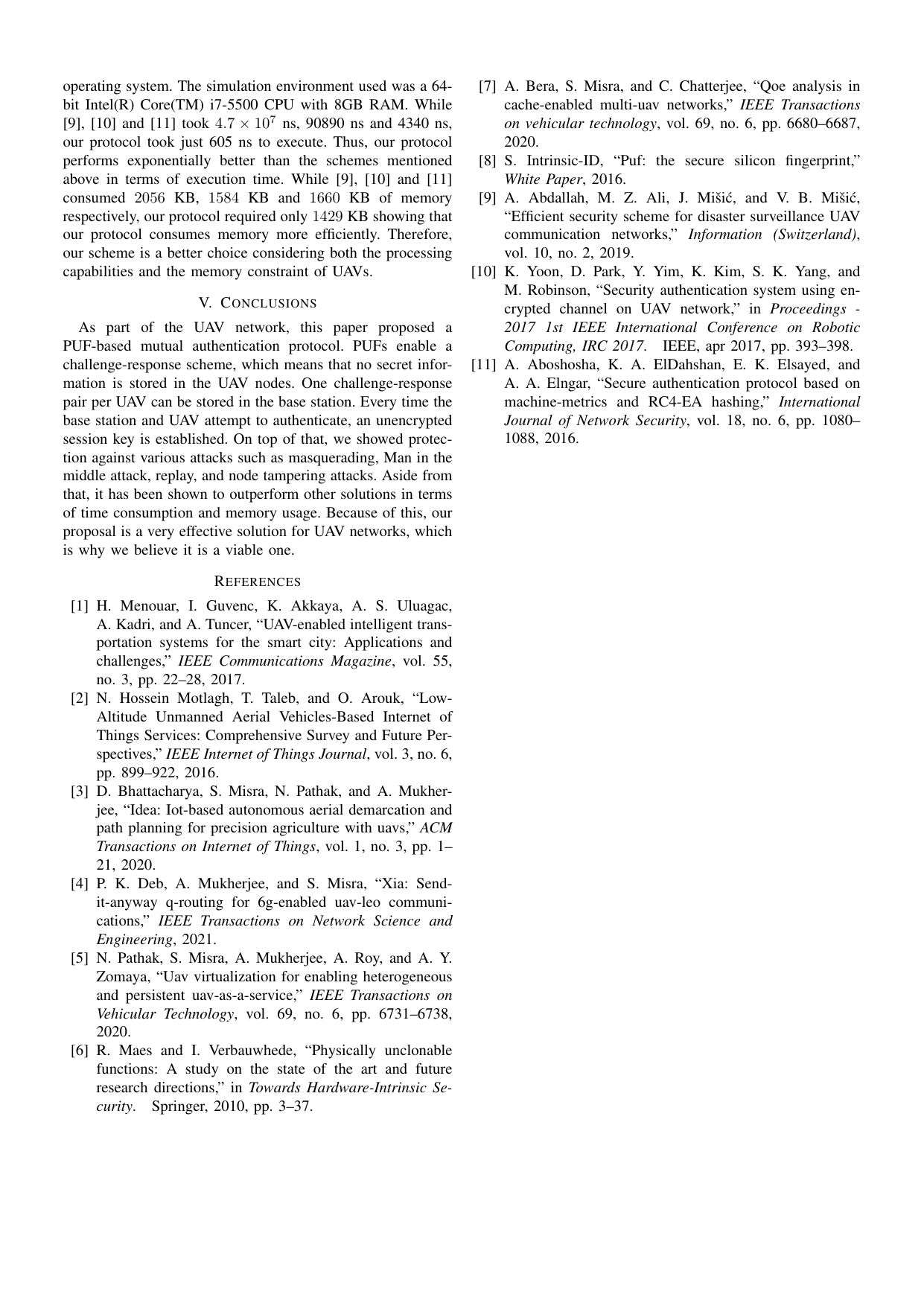
A secure and efficient mutual authentication protocol framework for unmanned aerial vehiclesGaurang Bansal, and Biplab SikdarIn 2021 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), 2021Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, are becoming increasingly popular owing to their wide application domain. However, the issue of security and privacy is a concern for these UAV-based applications. UAVs are susceptible to multiple threats like the man-in-the-middle attack, the replay attack, the physical attacks. To mitigate these threats and vulnerabilities, we propose a lightweight mutual authentication protocol that ensures network and communication security. The proposed protocol uses Physical Unclonable Function (PUFs), a digital fingerprint device to protect against physical and masquerade attacks. The proposed protocol is robust, secure, and fast compared to other state-of-the-art protocols previously proposed in the literature.
2020
- Security and Privacy
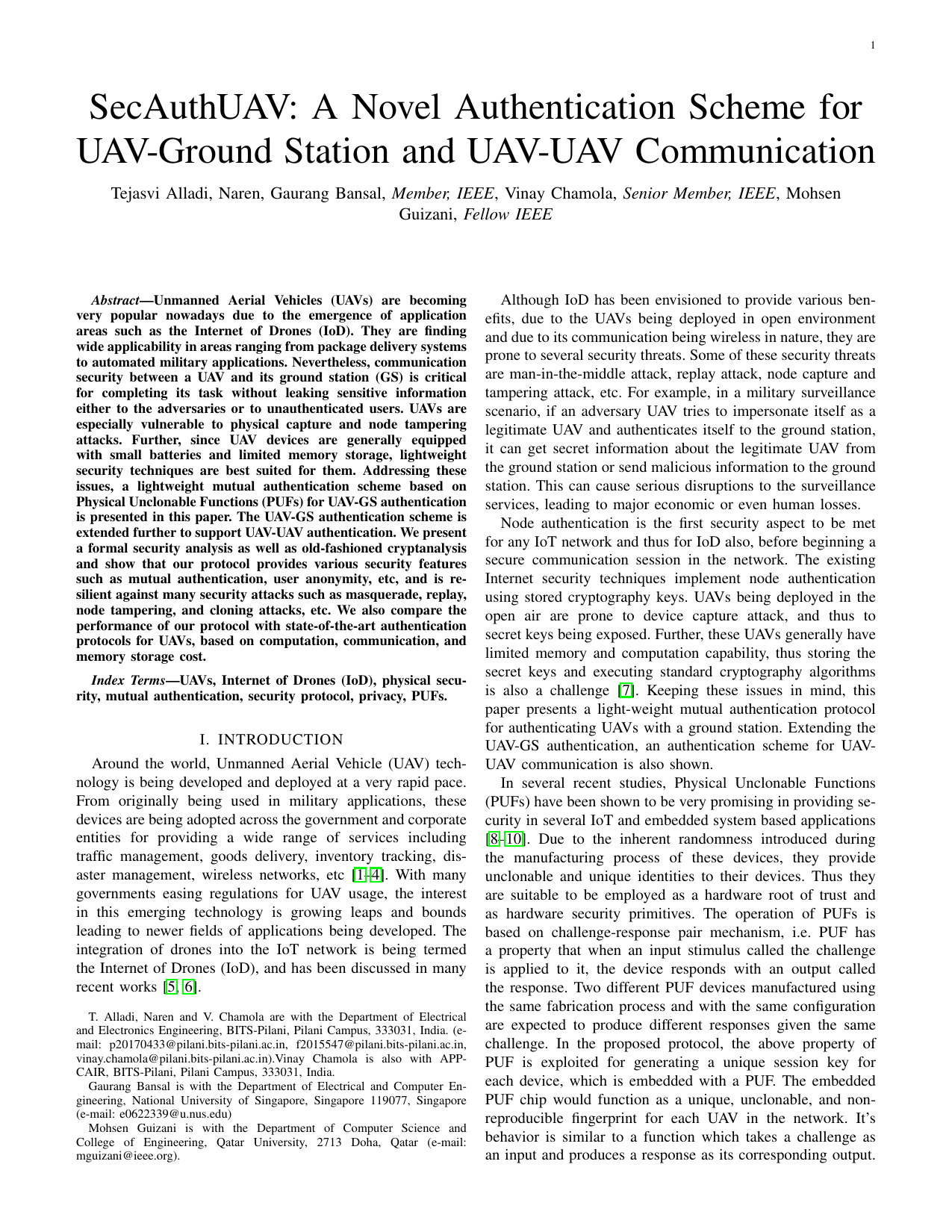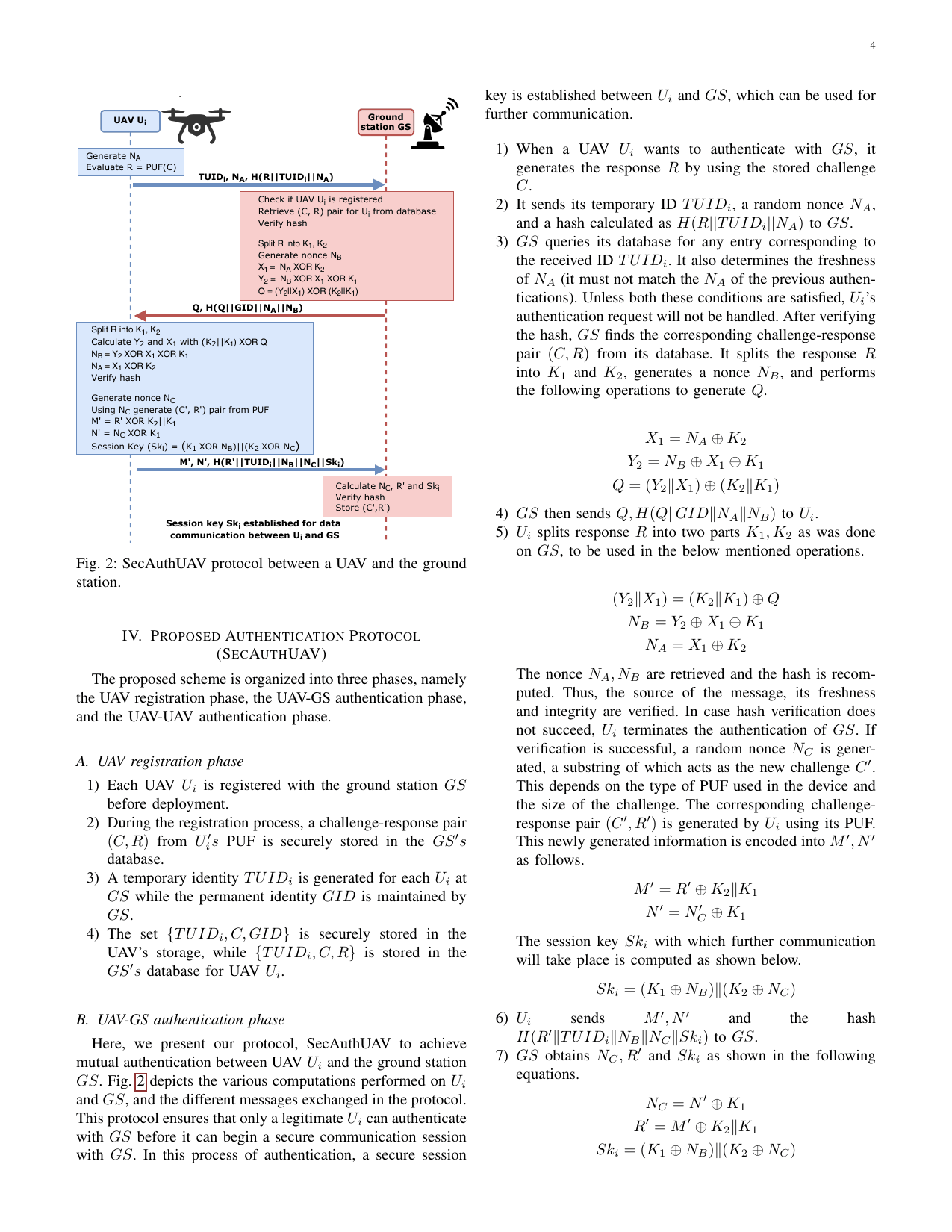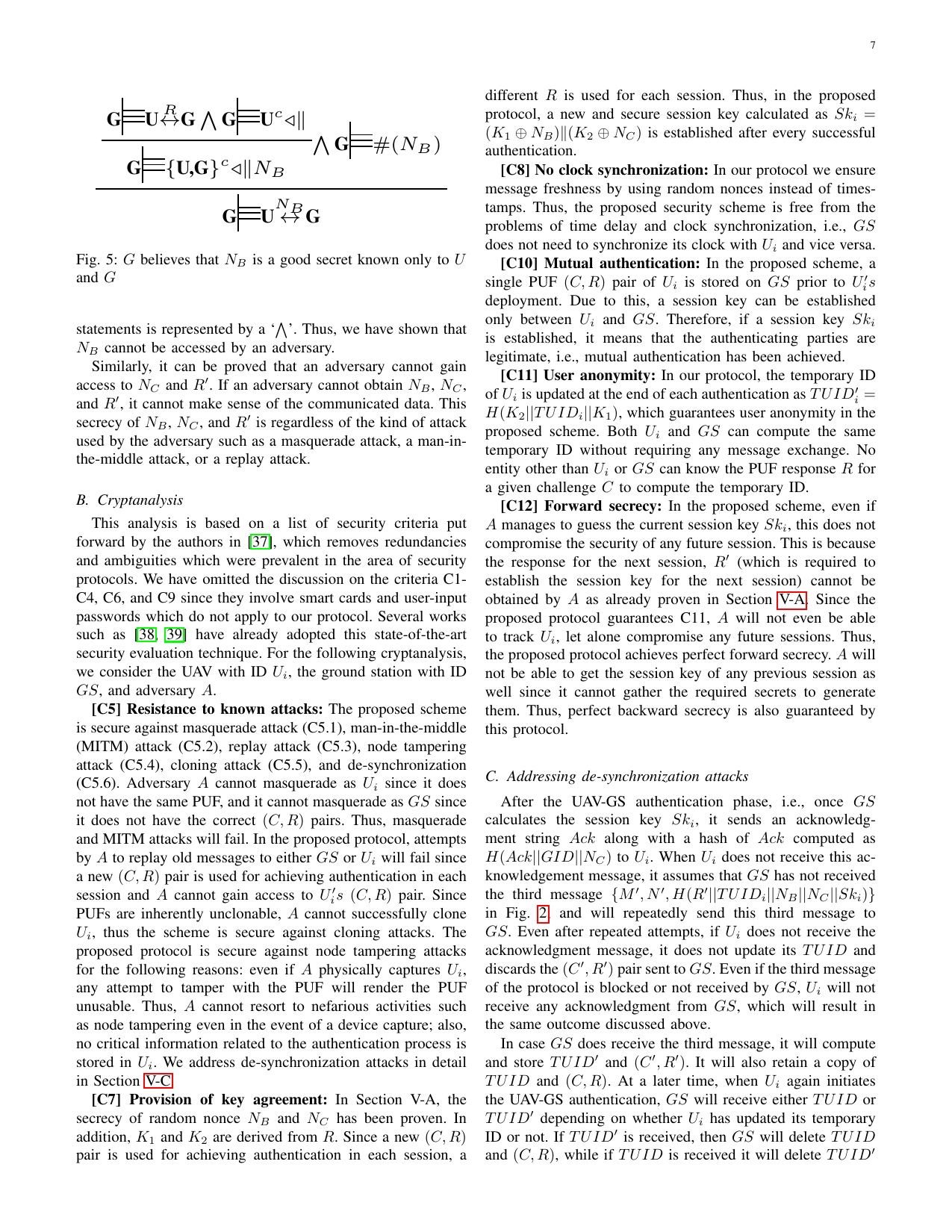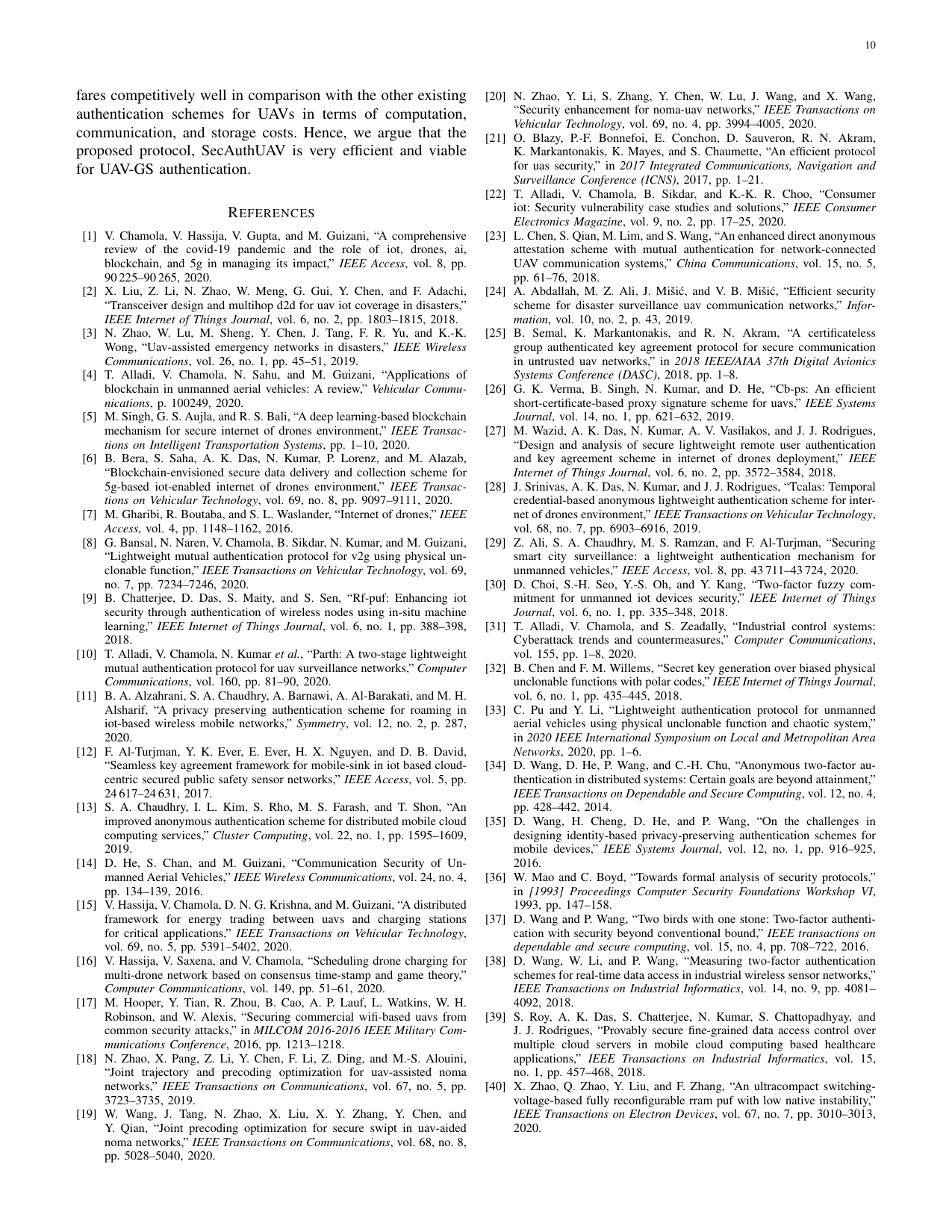 SecAuthUAV: A novel authentication scheme for UAV-ground station and UAV-UAV communicationTejasvi Alladi, Gaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Mohsen Guizani, and othersIEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020
SecAuthUAV: A novel authentication scheme for UAV-ground station and UAV-UAV communicationTejasvi Alladi, Gaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Mohsen Guizani, and othersIEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are becoming very popular nowadays due to the emergence of application areas such as the Internet of Drones (IoD). They are finding wide applicability in areas ranging from package delivery systems to automated military applications. Nevertheless, communication security between a UAV and its ground station (GS) is critical for completing its task without leaking sensitive information either to the adversaries or to unauthenticated users. UAVs are especially vulnerable to physical capture and node tampering attacks. Further, since UAV devices are generally equipped with small batteries and limited memory storage, lightweight security techniques are best suited for them. Addressing these issues, a lightweight mutual authentication scheme based on Physical Unclonable Functions (PUFs) for UAV-GS authentication is presented in this paper. The UAV-GS authentication scheme is extended further to support UAV-UAV authentication. We present a formal security analysis as well as old-fashioned cryptanalysis and show that our protocol provides various security features such as mutual authentication, user anonymity, etc, and is resilient against many security attacks such as masquerade, replay, node tampering, and cloning attacks, etc. We also compare the performance of our protocol with state-of-the-art authentication protocols for UAVs, based on computation, communication, and memory storage cost.
- Security and Privacy
 Rama: Real-time automobile mutual authentication protocol using pufGaurang Bansal, Naren Naren, and Vinay ChamolaIn 2020 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), 2020
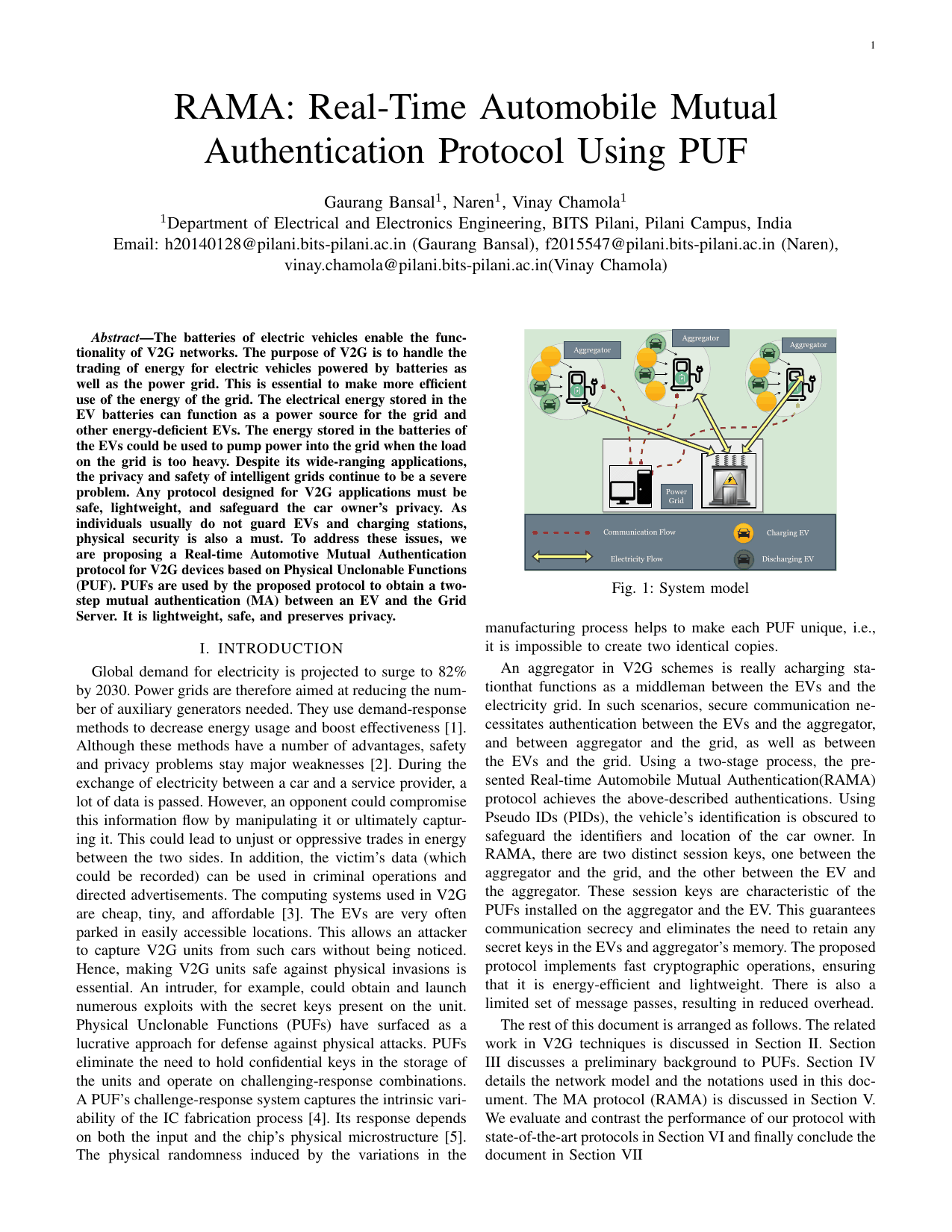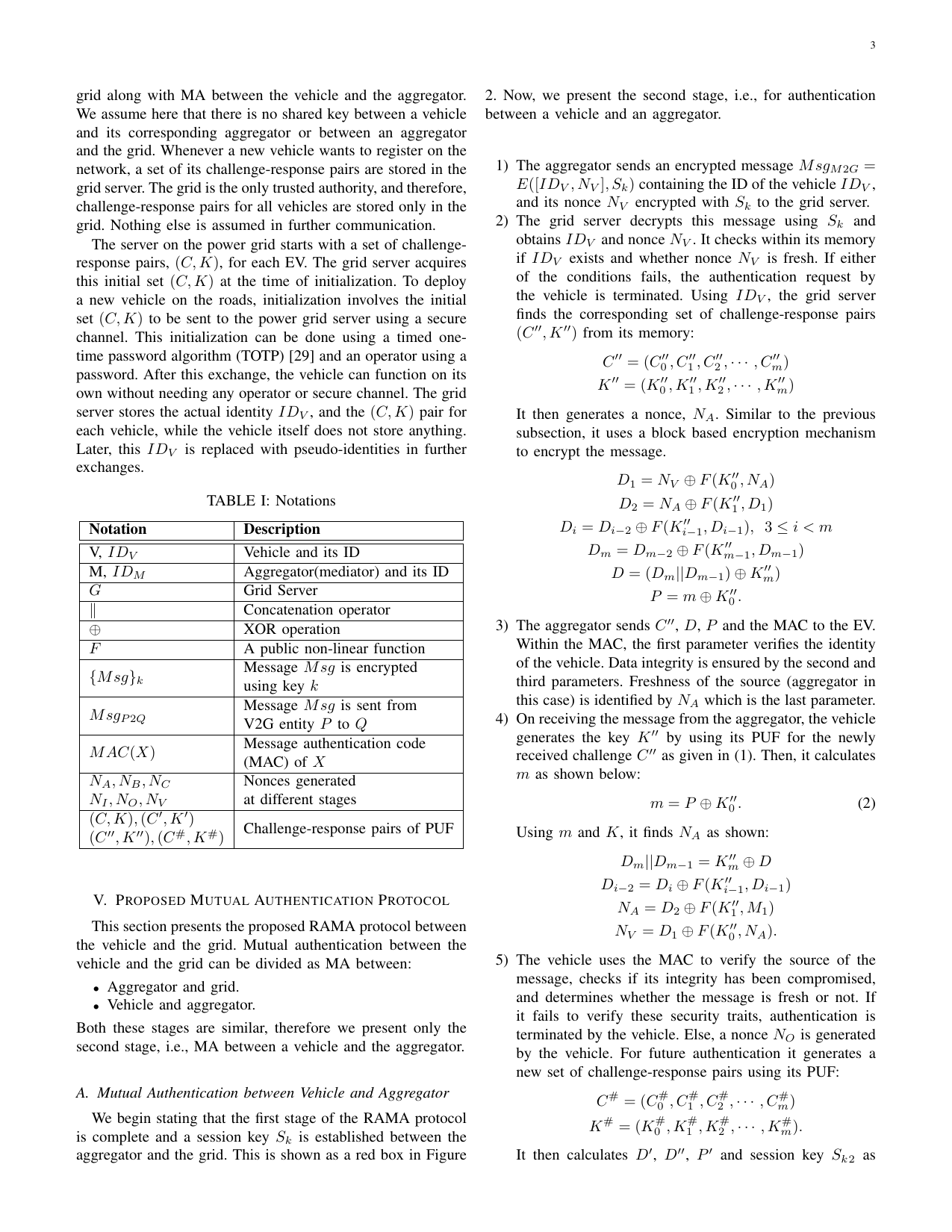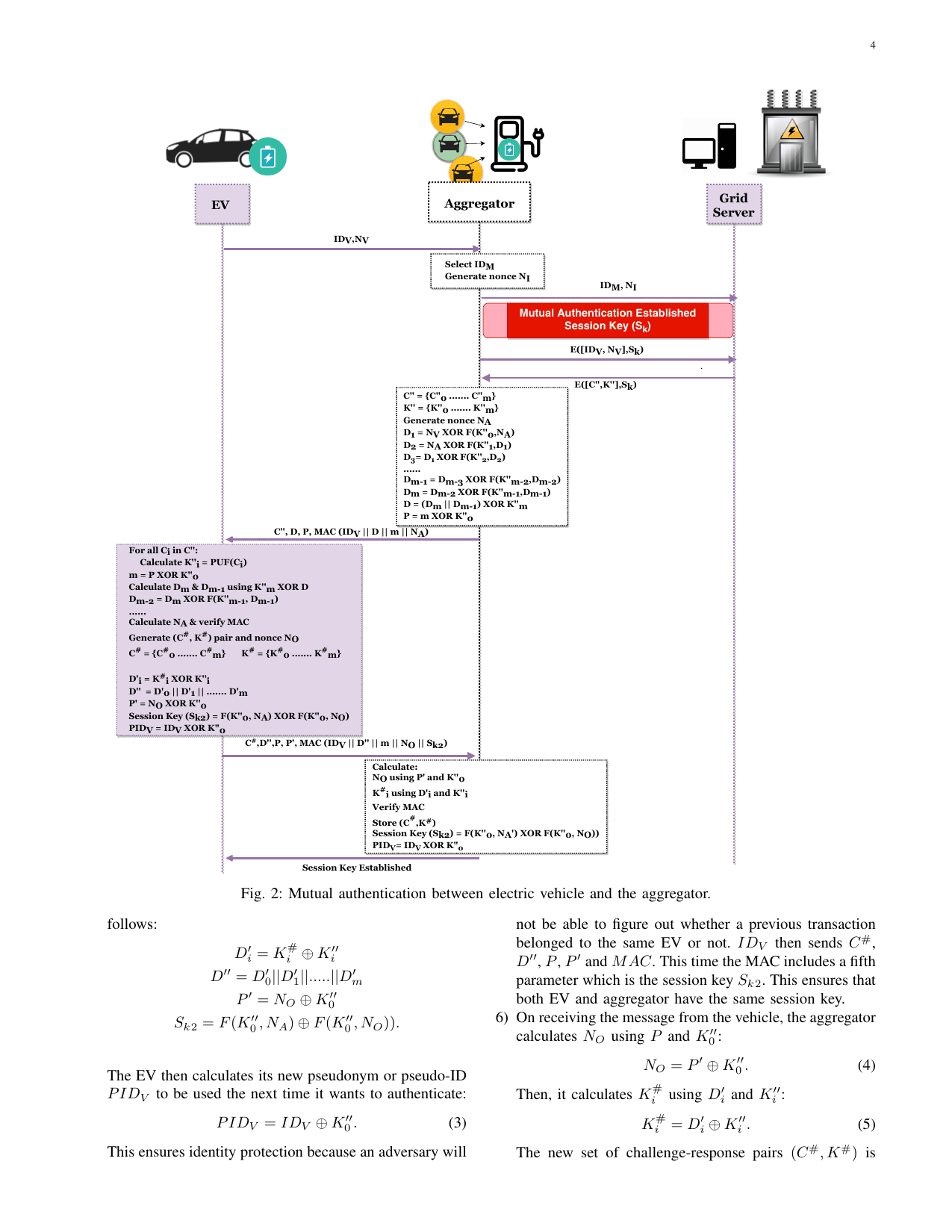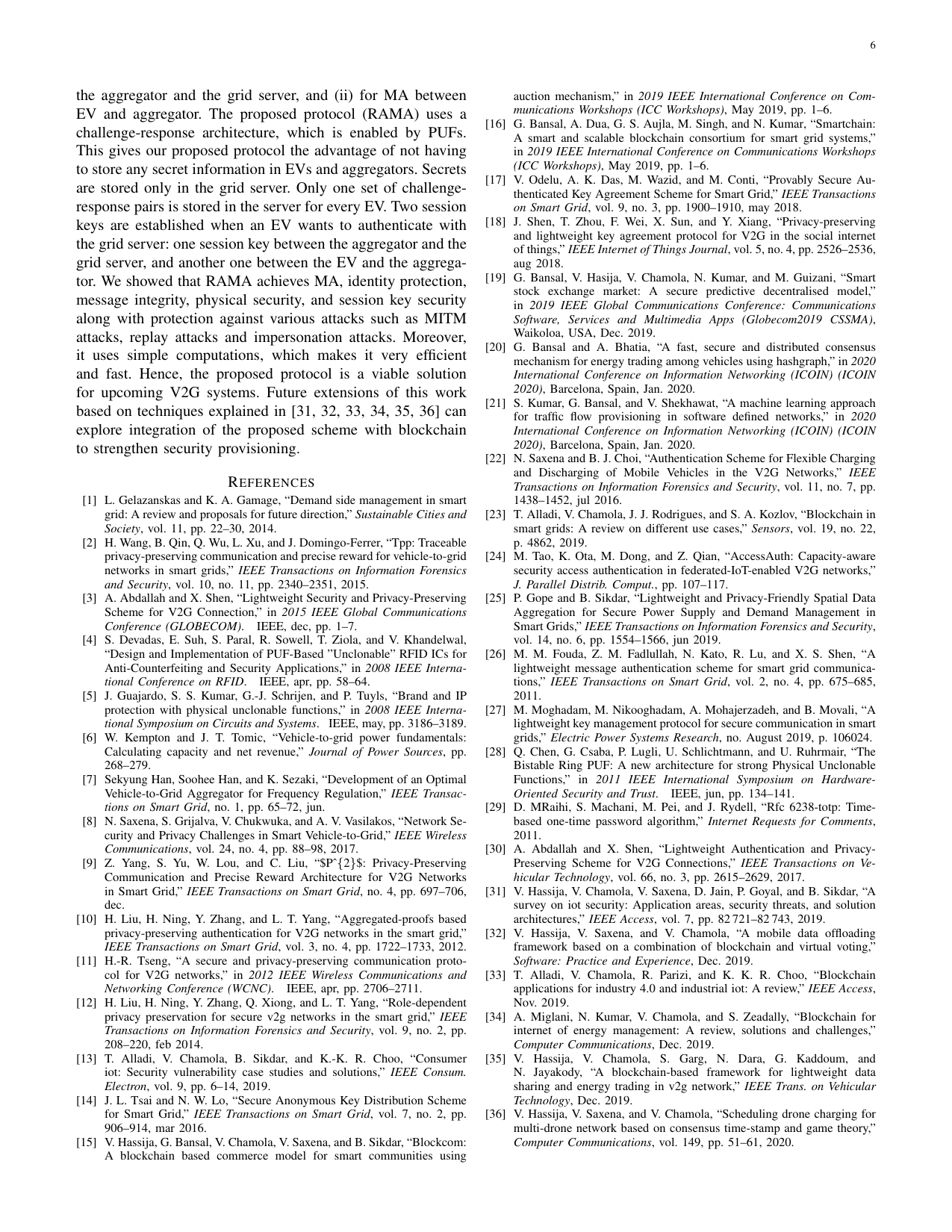
Rama: Real-time automobile mutual authentication protocol using pufGaurang Bansal, Naren Naren, and Vinay ChamolaIn 2020 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), 2020The batteries of electric vehicles enable the func- tionality of V2G networks. The purpose of V2G is to handle the trading of energy for electric vehicles powered by batteries as well as the power grid. This is essential to make more efficient use of the energy of the grid. The electrical energy stored in the EV batteries can function as a power source for the grid and other energy-deficient EVs. The energy stored in the batteries of the EVs could be used to pump power into the grid when the load on the grid is too heavy. Despite its wide-ranging applications, the privacy and safety of intelligent grids continue to be a severe problem. Any protocol designed for V2G applications must be safe, lightweight, and safeguard the car owner’s privacy. As individuals usually do not guard EVs and charging stations, physical security is also a must. To address these issues, we are proposing a Real-time Automotive Mutual Authentication protocol for V2G devices based on Physical Unclonable Functions (PUF). PUFs are used by the proposed protocol to obtain a two- step mutual authentication (MA) between an EV and the Grid Server. It is lightweight, safe, and preserves privacy.
- Blockchain
 A fast, secure and distributed consensus mechanism for energy trading among vehicles using hashgraphGaurang Bansal, and Ashutosh BhatiaIn 2020 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), 2020
A fast, secure and distributed consensus mechanism for energy trading among vehicles using hashgraphGaurang Bansal, and Ashutosh BhatiaIn 2020 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), 2020Energy trading among inter vehicles (V2V) offers an efficient response to all the problems presented by future electricity supply. V2V is often envisioned as a gl-to-peer (P2P) model of electric mercantilism for electric vehicle (EV) merchandising. With security vulnerability increasing, confidence in secured third parties is declining. Blockchain is becoming increasingly common as it provides a system for privacy conser- vation and efficient agreement without the need for trusted third parties. However, all operations in such a scheme are restricted by memory, time, computing capital, energy etc. and it is quite obvious that the mechanism for blockchain agreement is not sufficient to address all of them. In this paper, we present an alternative to the blockchain using Hashgraph which is scalable, fast, fault-tolerant and fair. It is efficient, inexpensive, and DoS resistant fulfilling the requirement of V2V energy trading.
- Security and Privacy
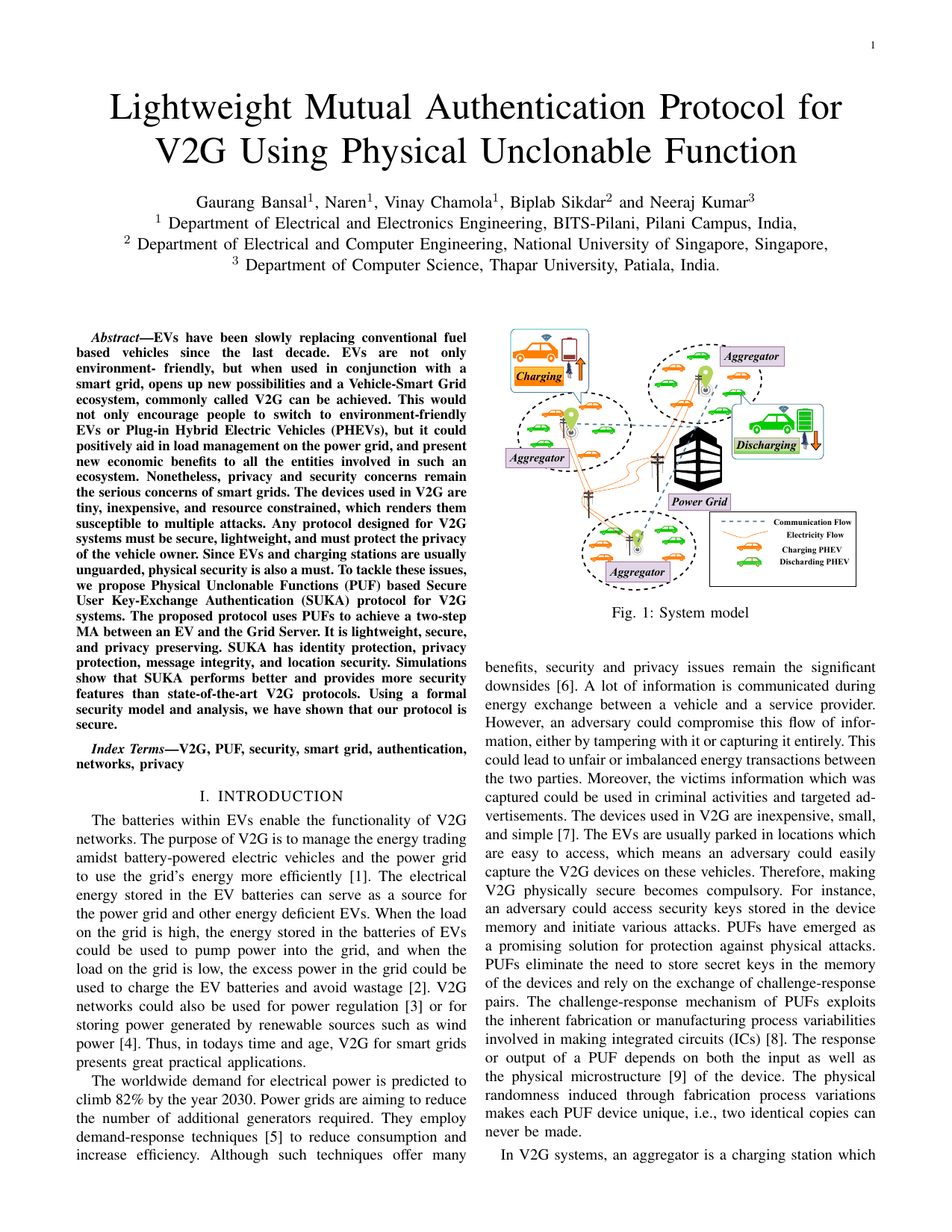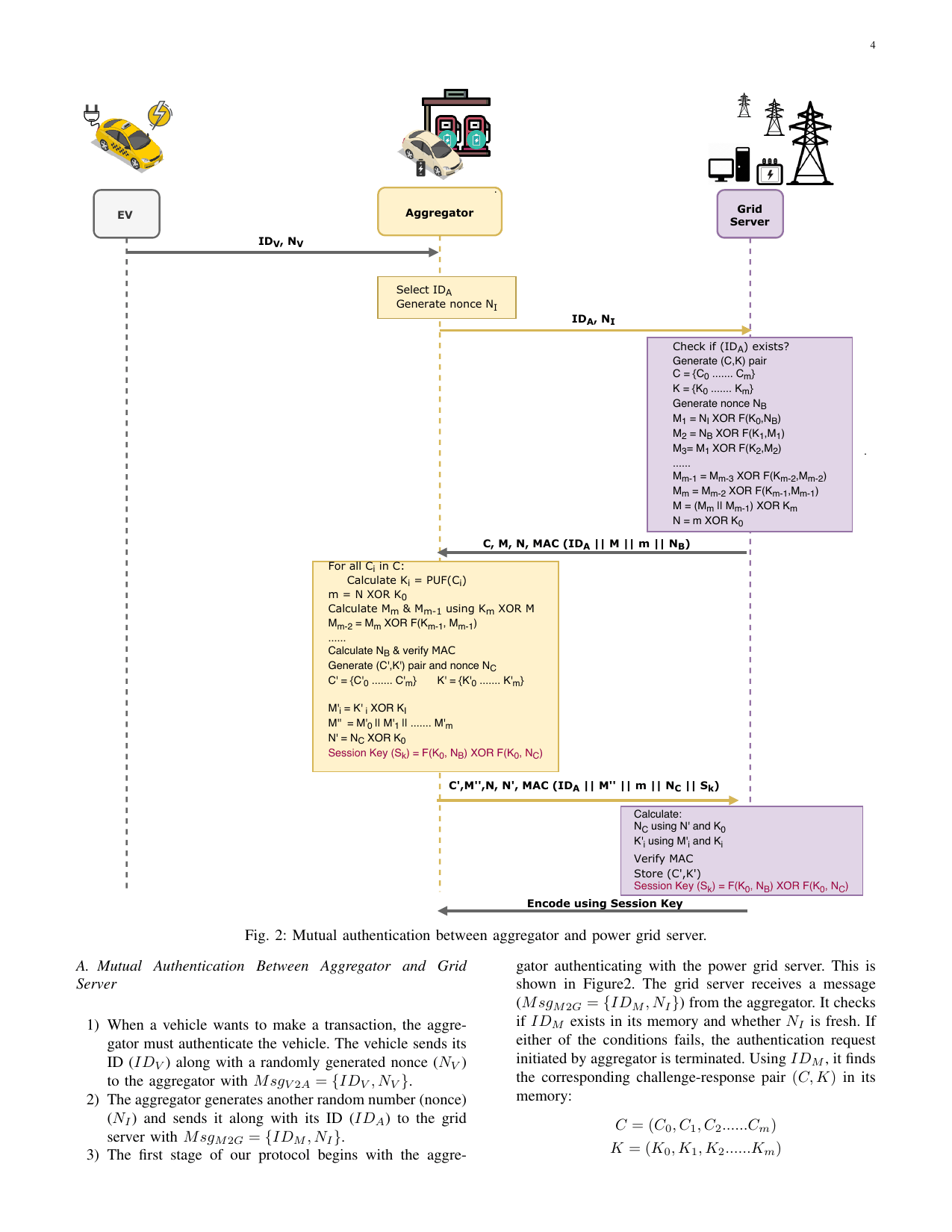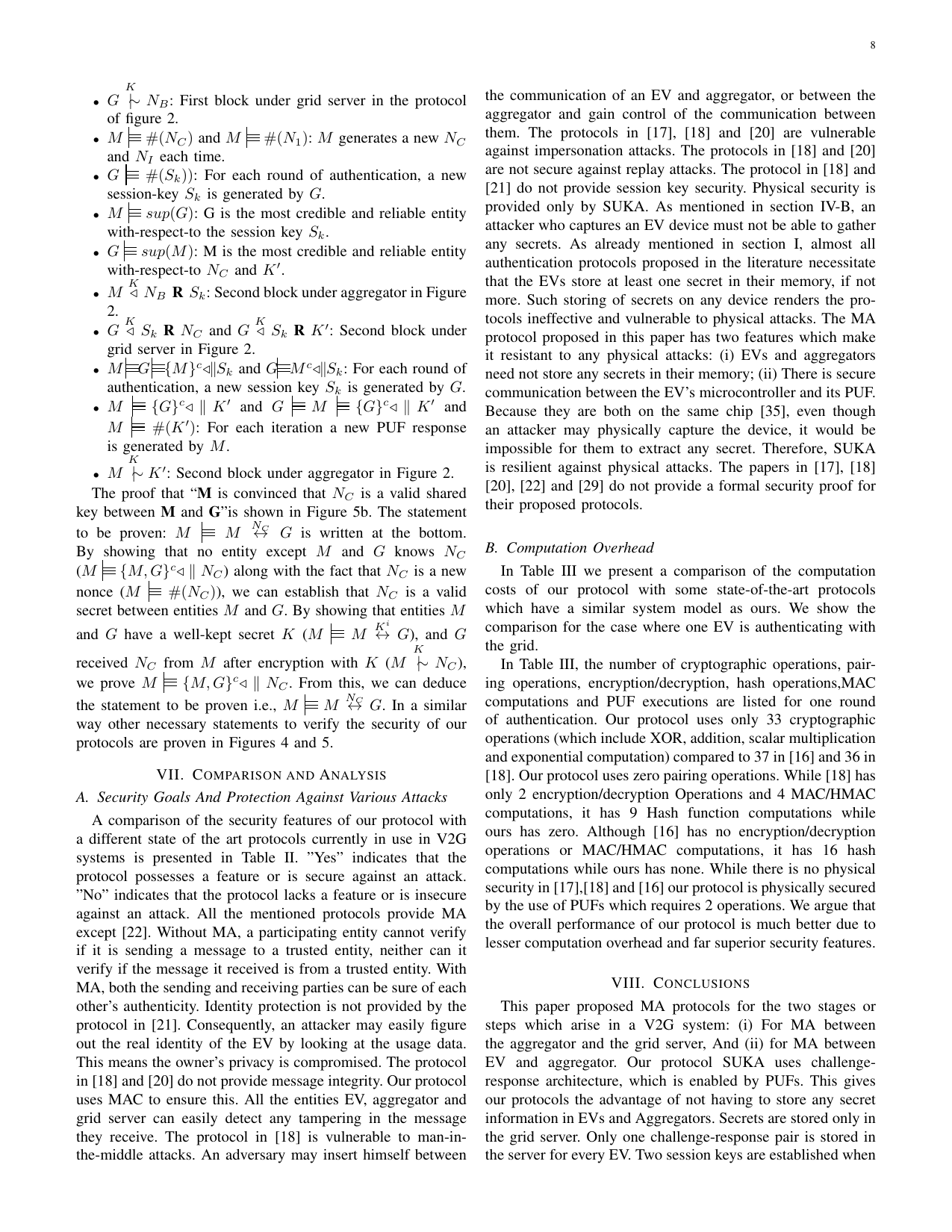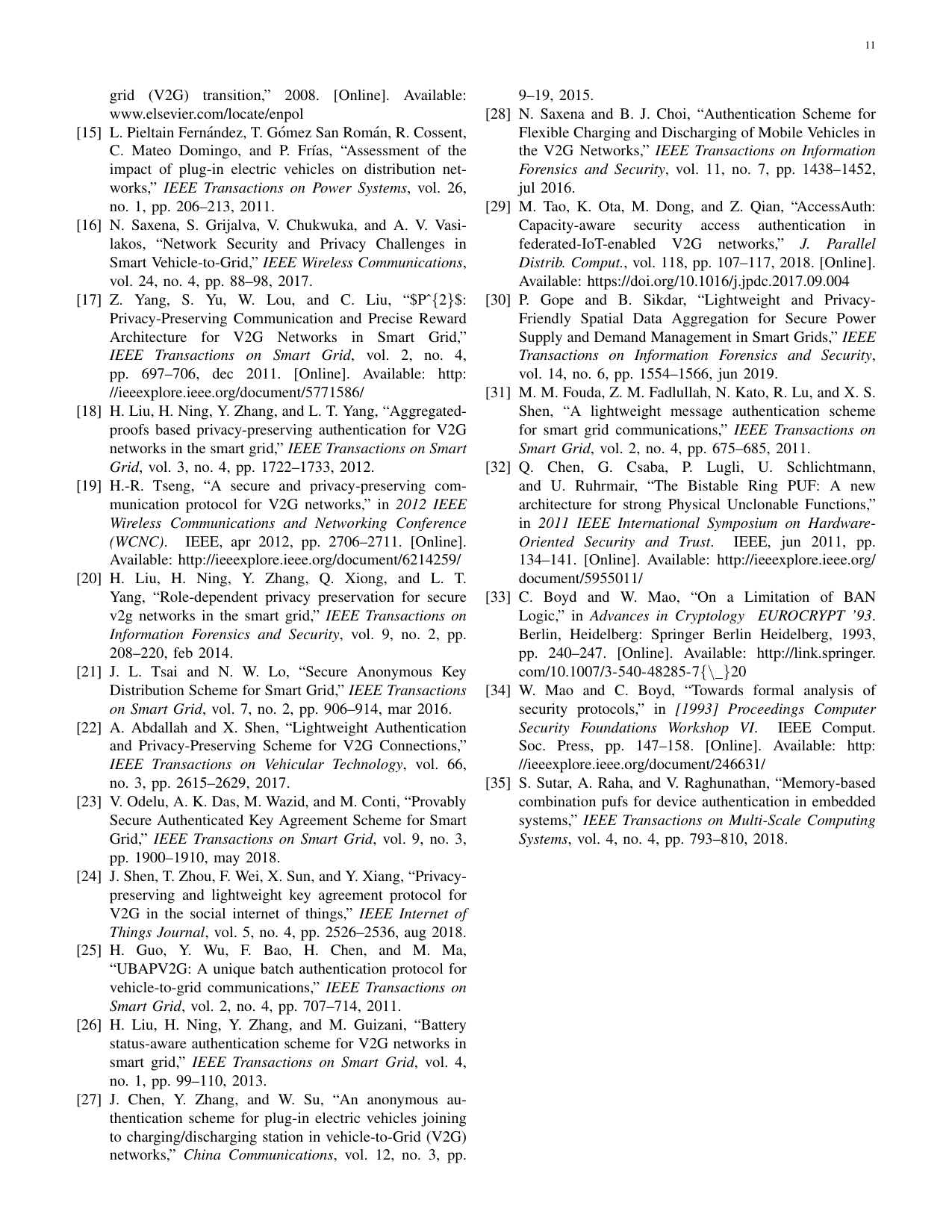 Lightweight mutual authentication protocol for V2G using physical unclonable functionGaurang Bansal, Naren Naren, Vinay Chamola, Biplab Sikdar, Neeraj Kumar, and Mohsen GuizaniIEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020
Lightweight mutual authentication protocol for V2G using physical unclonable functionGaurang Bansal, Naren Naren, Vinay Chamola, Biplab Sikdar, Neeraj Kumar, and Mohsen GuizaniIEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020EVs have been slowly replacing conventional fuel based vehicles since the last decade. EVs are not only environment- friendly, but when used in conjunction with a smart grid, opens up new possibilities and a Vehicle-Smart Grid ecosystem, commonly called V2G can be achieved. This would not only encourage people to switch to environment-friendly EVs or Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), but it could positively aid in load management on the power grid, and present new economic benefits to all the entities involved in such an ecosystem. Nonetheless, privacy and security concerns remain the serious concerns of smart grids. The devices used in V2G are tiny, inexpensive, and resource constrained, which renders them susceptible to multiple attacks. Any protocol designed for V2G systems must be secure, lightweight, and must protect the privacy of the vehicle owner. Since EVs and charging stations are usually unguarded, physical security is also a must. To tackle these issues, we propose Physical Unclonable Functions (PUF) based Secure User Key-Exchange Authentication (SUKA) protocol for V2G systems. The proposed protocol uses PUFs to achieve a two-step MA between an EV and the Grid Server. It is lightweight, secure, and privacy preserving. SUKA has identity protection, privacy protection, message integrity, and location security. Simulations show that SUKA performs better and provides more security features than state-of-the-art V2G protocols. Using a formal security model and analysis, we have shown that our protocol is secure.
- Machine Learning
 A machine learning approach for traffic flow provisioning in software defined networksSubham Kumar, Gaurang Bansal, and Virendra Singh ShekhawatIn 2020 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), 2020
A machine learning approach for traffic flow provisioning in software defined networksSubham Kumar, Gaurang Bansal, and Virendra Singh ShekhawatIn 2020 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), 2020With the recent surge of machine learning and artificial intelligence, many research groups are applying these techniques to control, manage, and operate networks. Soft- ware Defined Networks (SDN) transform the distributed and hardware-centric legacy network into an integrated and dynamic network that provides a comprehensive solution for managing the network efficiently and effectively. The network-wide knowledge provided by SDN can be leveraged for efficient traffic routing in the network. In this work, we explore and illustrate the applicability of machine learning algorithms for selecting the least congested route for routing traffic in a SDN enabled network. The proposed method of route selection provides a list of possible routes based on the network statistics provided by the SDN controller dynamically. The proposed method is implemented and tested in Mininet using Ryu controller.
- Security and Privacy
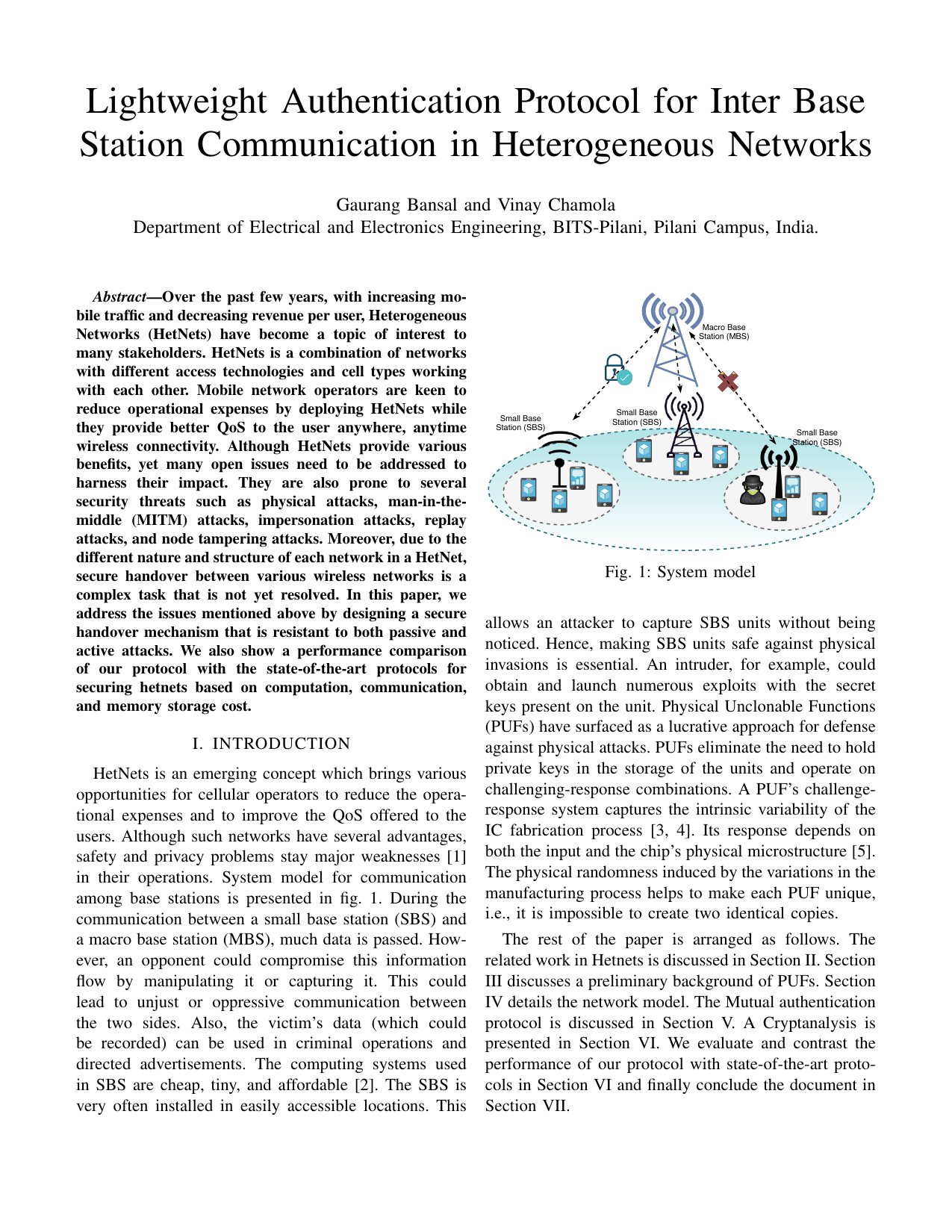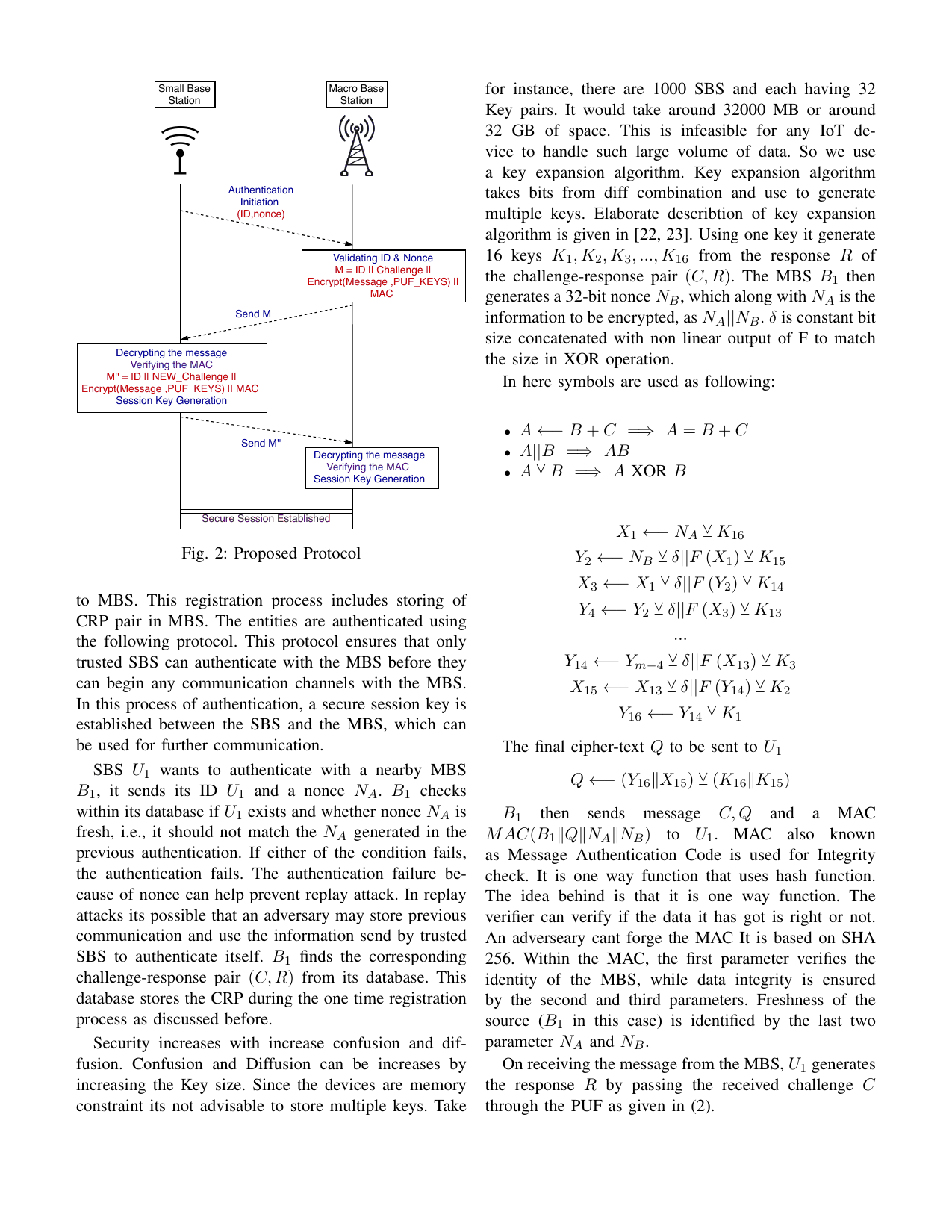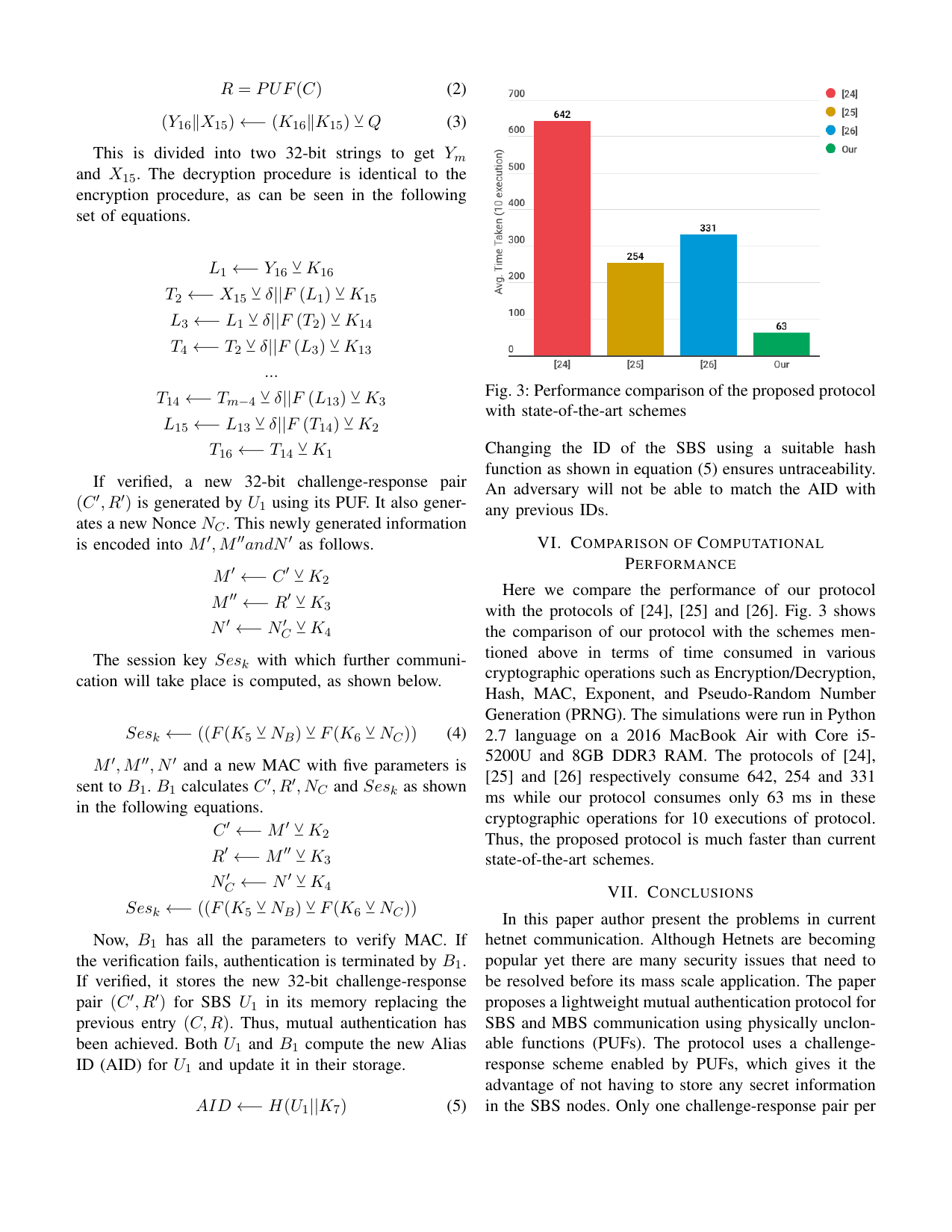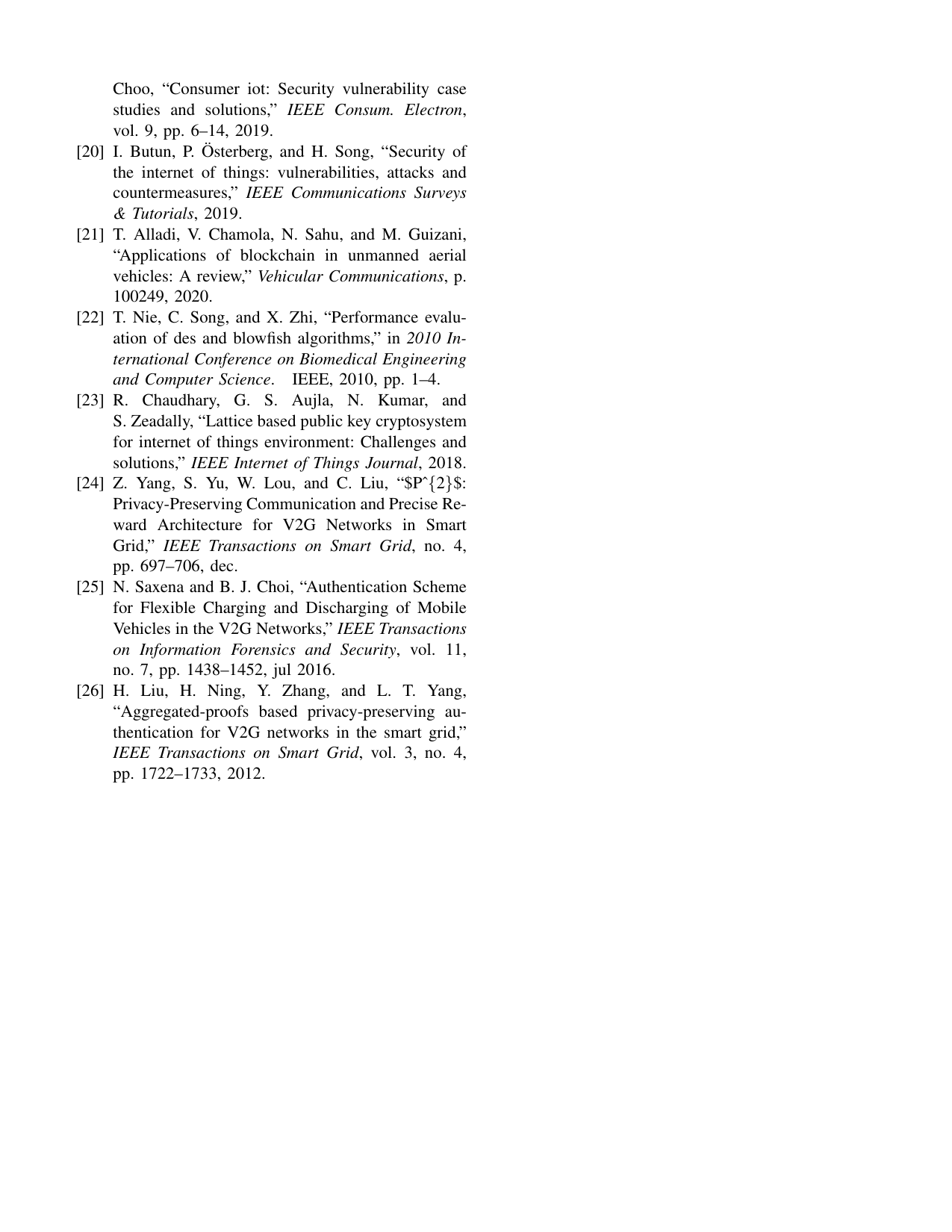 Lightweight authentication protocol for inter base station communication in heterogeneous networksGaurang Bansal, and Vinay ChamolaIn IEEE INFOCOM 2020-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), 2020
Lightweight authentication protocol for inter base station communication in heterogeneous networksGaurang Bansal, and Vinay ChamolaIn IEEE INFOCOM 2020-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), 2020Over the past few years, with increasing mo- bile traffic and decreasing revenue per user, Heterogeneous Networks (HetNets) have become a topic of interest to many stakeholders. HetNets is a combination of networks with different access technologies and cell types working with each other. Mobile network operators are keen to reduce operational expenses by deploying HetNets while they provide better QoS to the user anywhere, anytime wireless connectivity. Although HetNets provide various benefits, yet many open issues need to be addressed to harness their impact. They are also prone to several security threats such as physical attacks, man-in-the- middle (MITM) attacks, impersonation attacks, replay attacks, and node tampering attacks. Moreover, due to the different nature and structure of each network in a HetNet, secure handover between various wireless networks is a complex task that is not yet resolved. In this paper, we address the issues mentioned above by designing a secure handover mechanism that is resistant to both passive and active attacks. We also show a performance comparison of our protocol with the state-of-the-art protocols for securing hetnets based on computation, communication, and memory storage cost.
- Deep Learning
 Deep3DSCan: Deep residual network and morphological descriptor based framework for lung cancer classification and 3D segmentationGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Pratik Narang, Subham Kumar, and Sundaresan RamanIET Image Processing, 2020
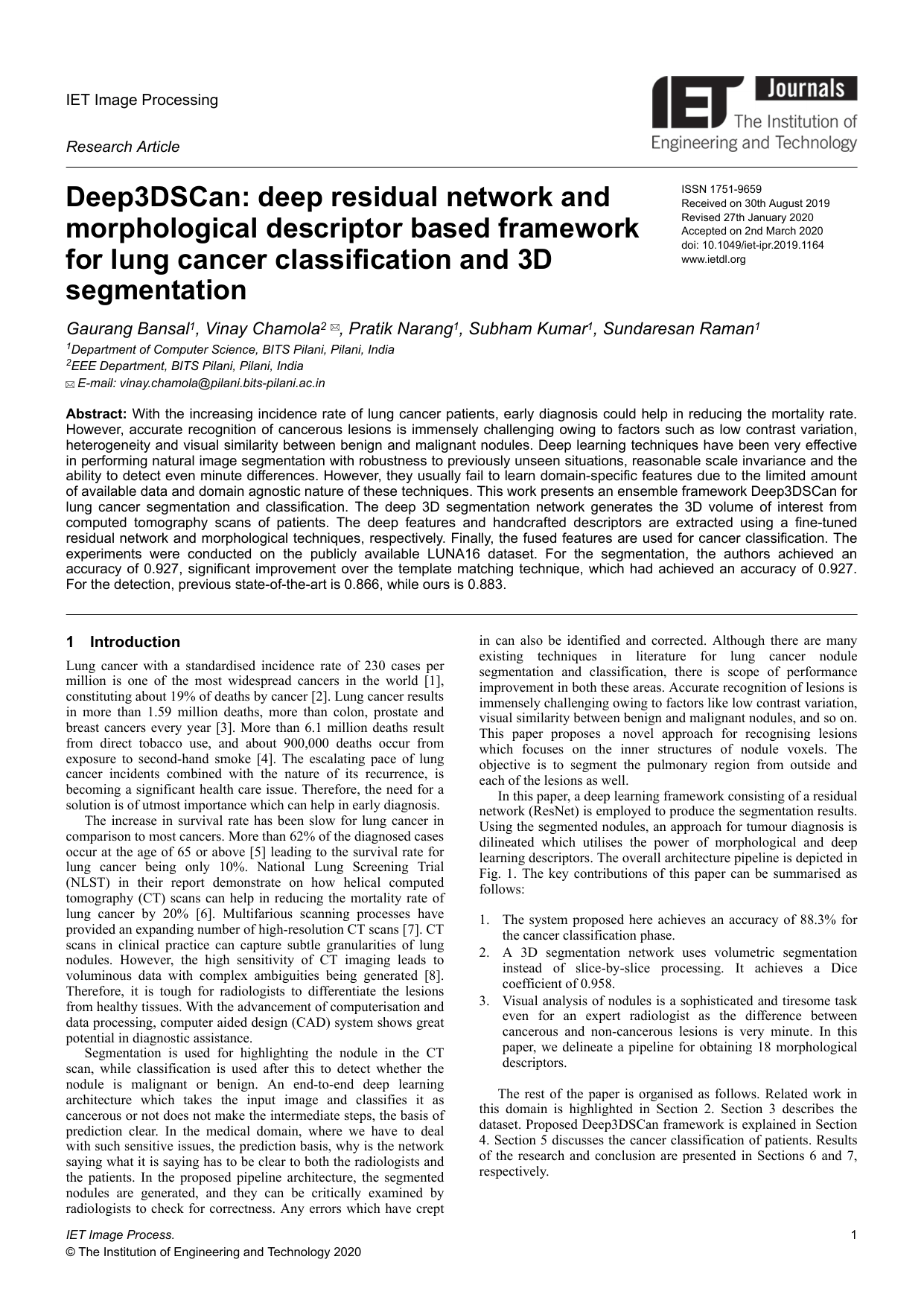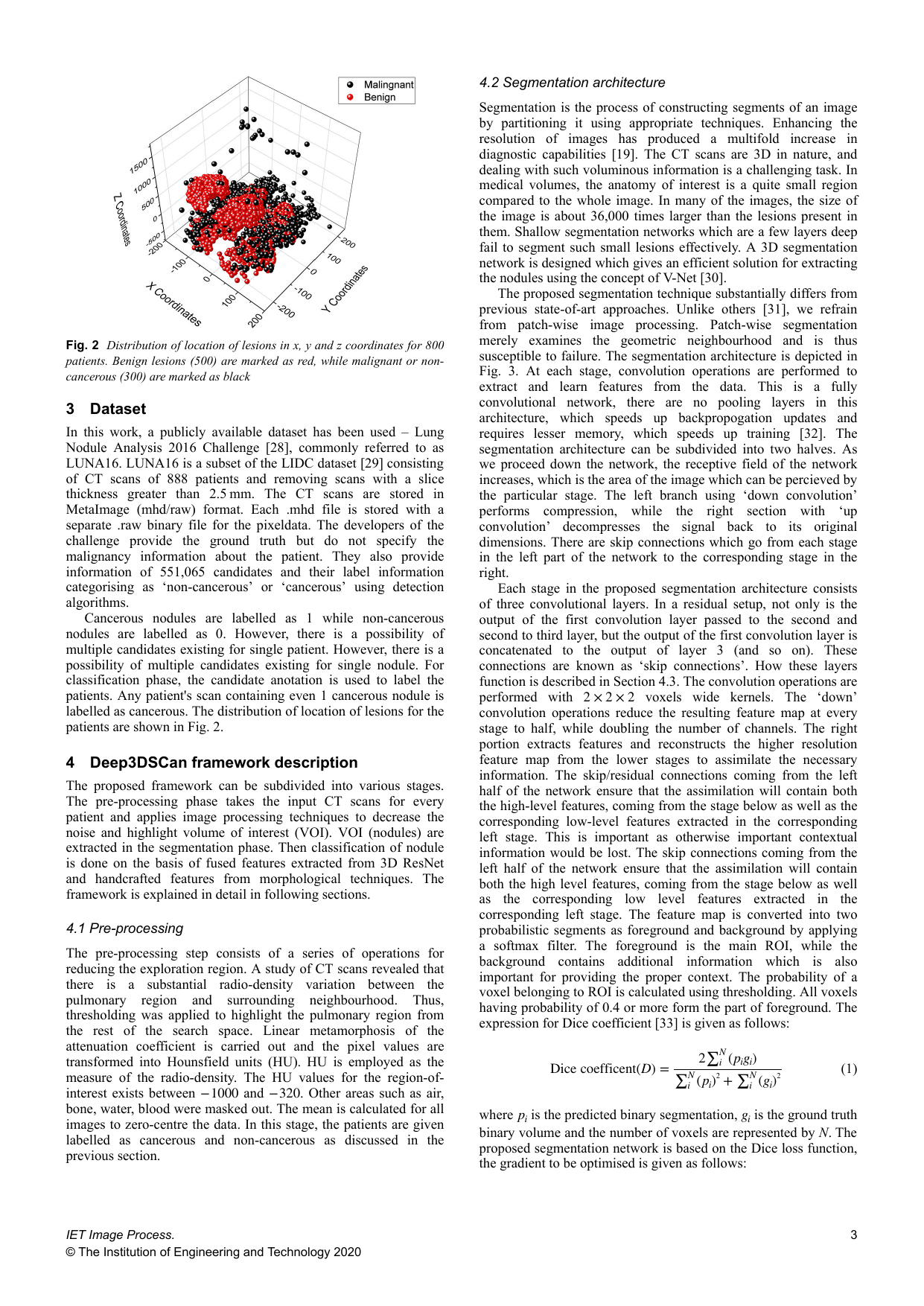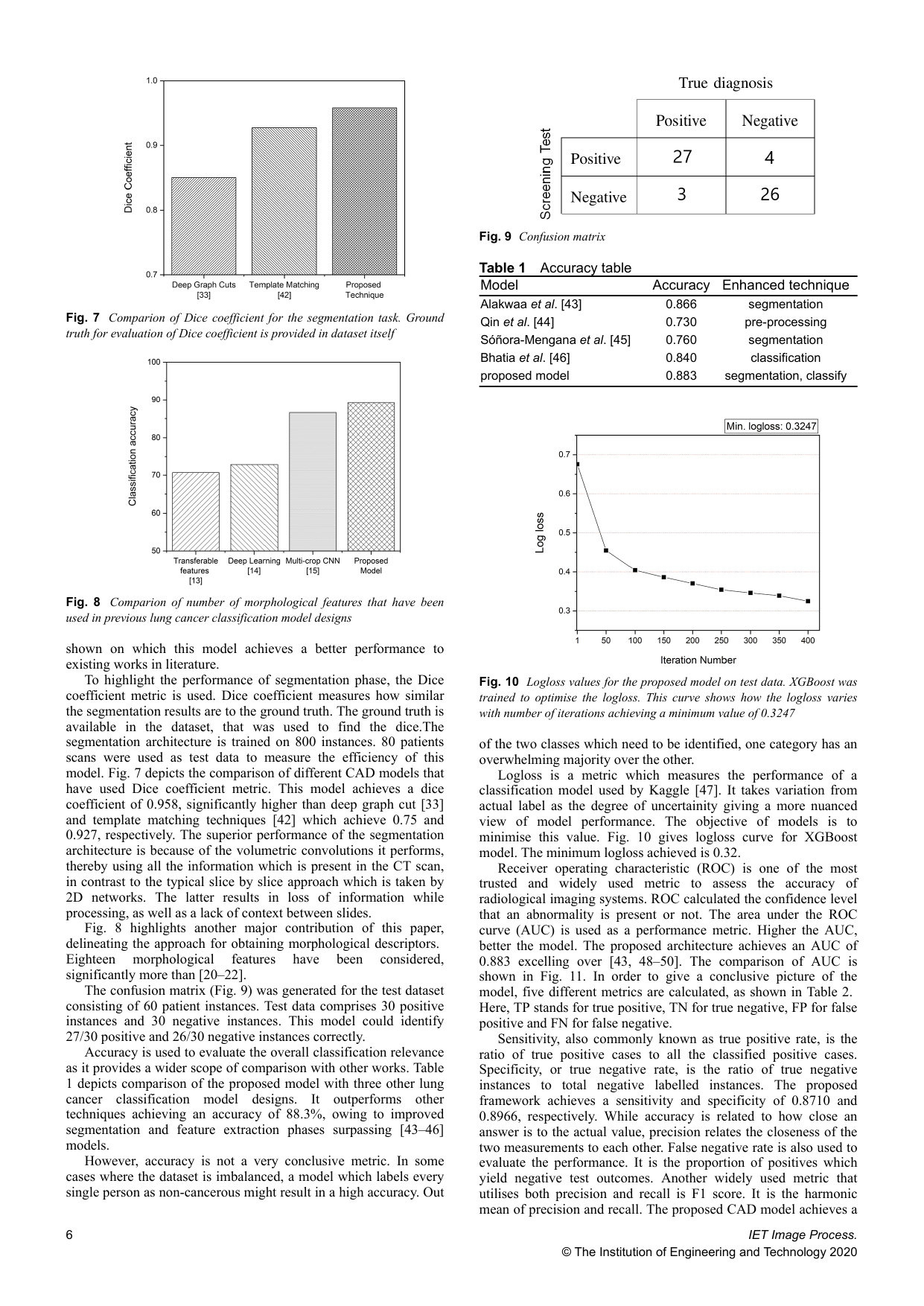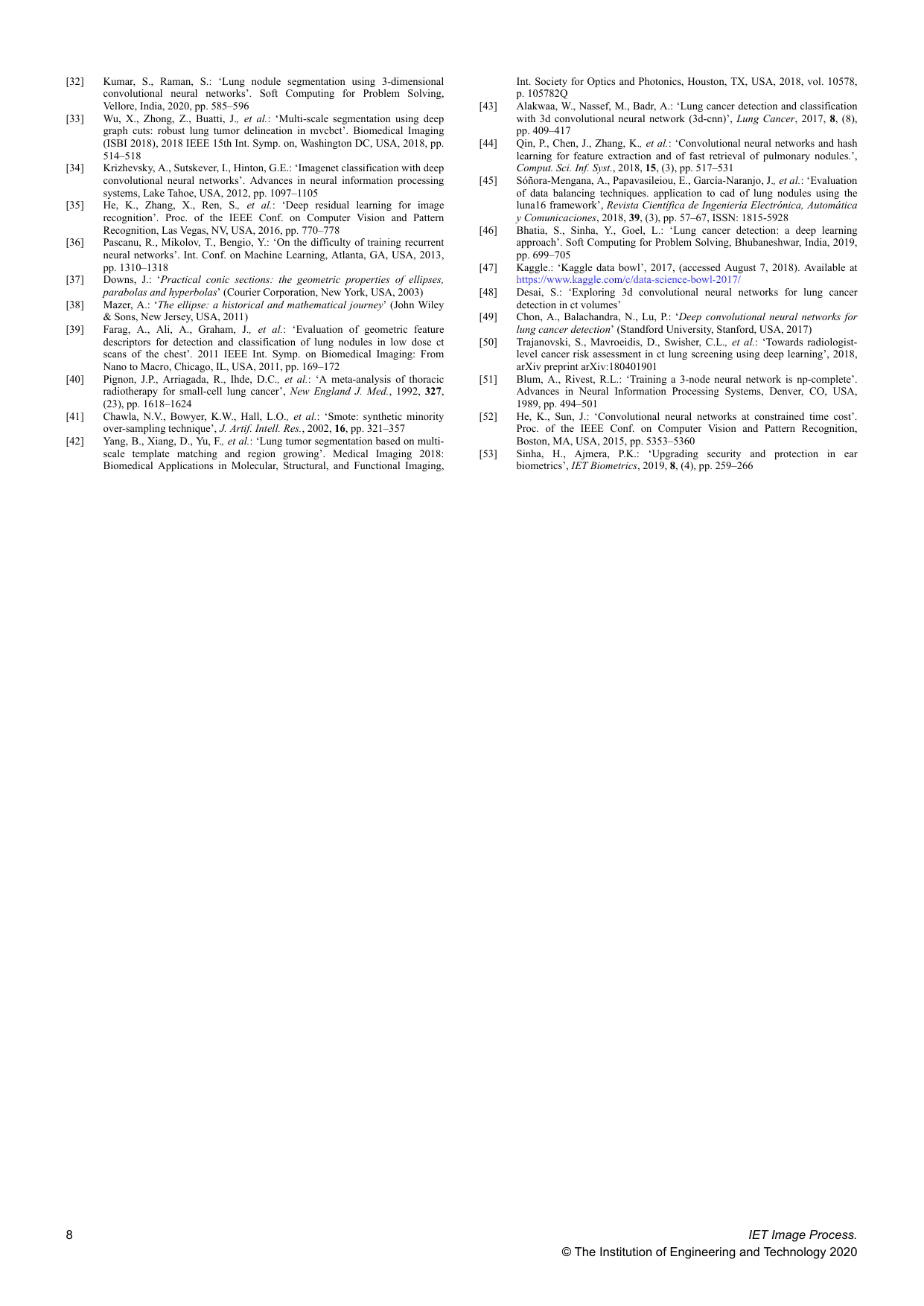
Deep3DSCan: Deep residual network and morphological descriptor based framework for lung cancer classification and 3D segmentationGaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Pratik Narang, Subham Kumar, and Sundaresan RamanIET Image Processing, 2020With the increasing incidence rate of lung cancer patients, early diagnosis could help in reducing the mortality rate. However, accurate recognition of cancerous lesions is immensely challenging owing to factors such as low contrast variation, heterogeneity and visual similarity between benign and malignant nodules. Deep learning techniques have been very effective in performing natural image segmentation with robustness to previously unseen situations, reasonable scale invariance and the ability to detect even minute differences. However, they usually fail to learn domain-specific features due to the limited amount of available data and domain agnostic nature of these techniques. This work presents an ensemble framework Deep3DSCan for lung cancer segmentation and classification. The deep 3D segmentation network generates the 3D volume of interest from computed tomography scans of patients. The deep features and handcrafted descriptors are extracted using a fine-tuned residual network and morphological techniques, respectively. Finally, the fused features are used for cancer classification. The experiments were conducted on the publicly available LUNA16 dataset. For the segmentation, the authors achieved an accuracy of 0.927, significant improvement over the template matching technique, which had achieved an accuracy of 0.927. For the detection, previous state-of-the-art is 0.866, while ours is 0.883.
- Blockchain
 Secure lending: Blockchain and prospect theory-based decentralized credit scoring modelVikas Hassija, Gaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Neeraj Kumar, and Mohsen GuizaniIEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2020
Secure lending: Blockchain and prospect theory-based decentralized credit scoring modelVikas Hassija, Gaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Neeraj Kumar, and Mohsen GuizaniIEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2020Credit scoring is a rigorous statistical analysis car- ried out by lenders and other third parties to access an indi- vidual’s creditworthiness. Lenders use credit scoring to estimate the degree of risk in lending money to an individual. However, credit score evaluation is primarily based on a transaction record, payment history, professional background, etc. sourced from different credit bureaus. So, evaluating a credit score is a laborious and tedious task involving a lot of paperwork. In this paper, we propose how blockchain can provide the solution to decentralized credit scoring evaluation and reducing the amount of dependence of paperwork. Lending money is not always objective but subjective to every lender. The decision of lending involves different levels of risk and uncertainty, depending on their perspective. This paper uses the prospect theory to model the optimal investment strategy for different risk vs. return scenarios.
2019
- Blockchain
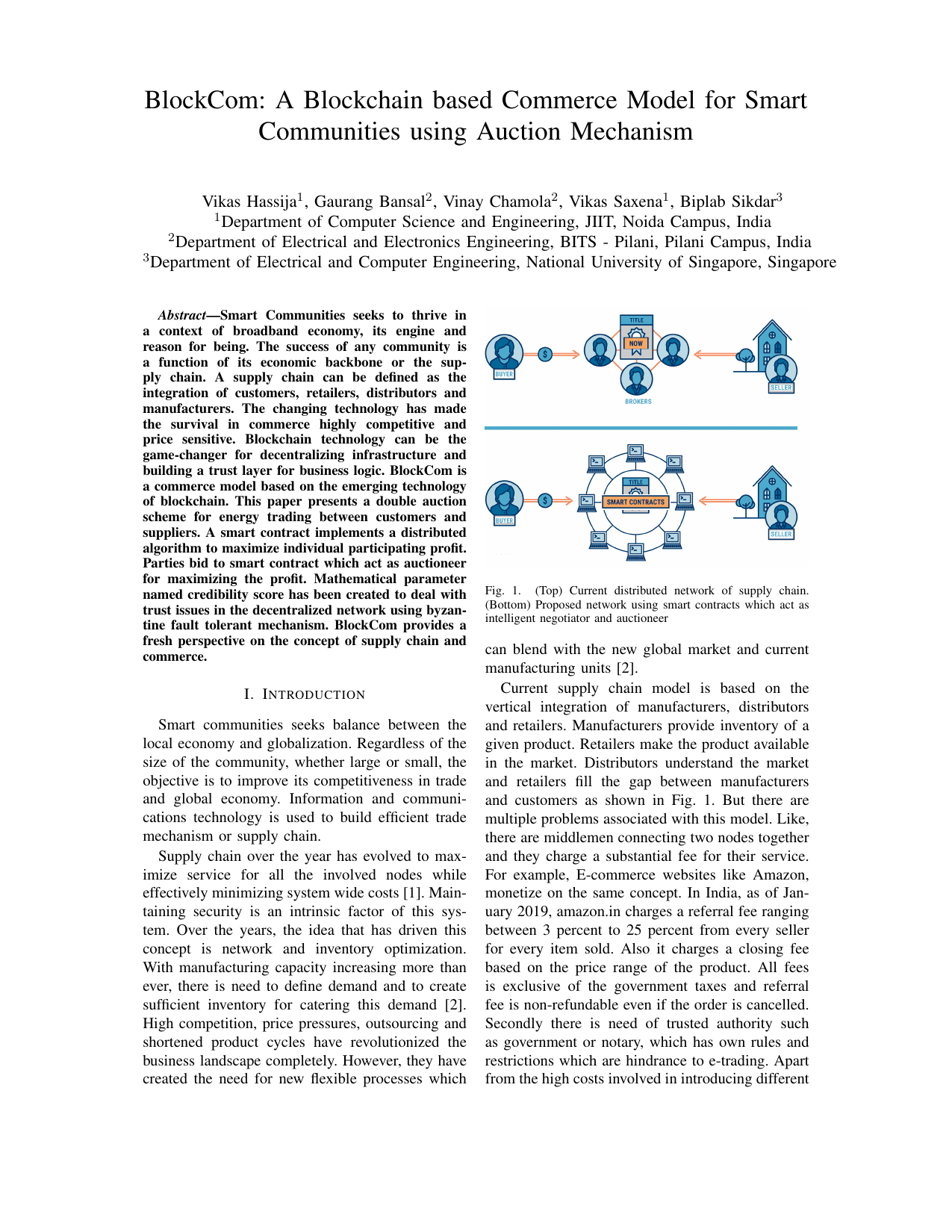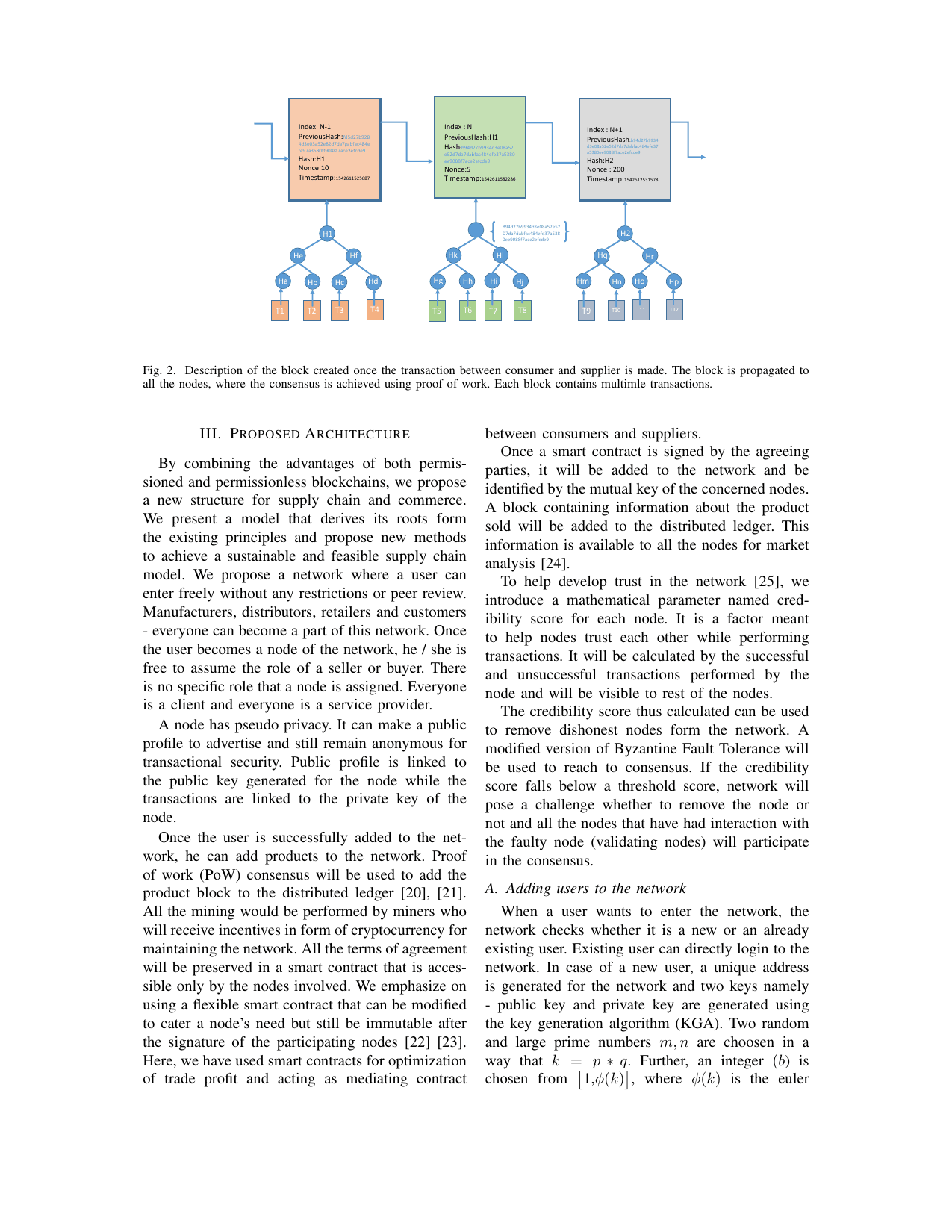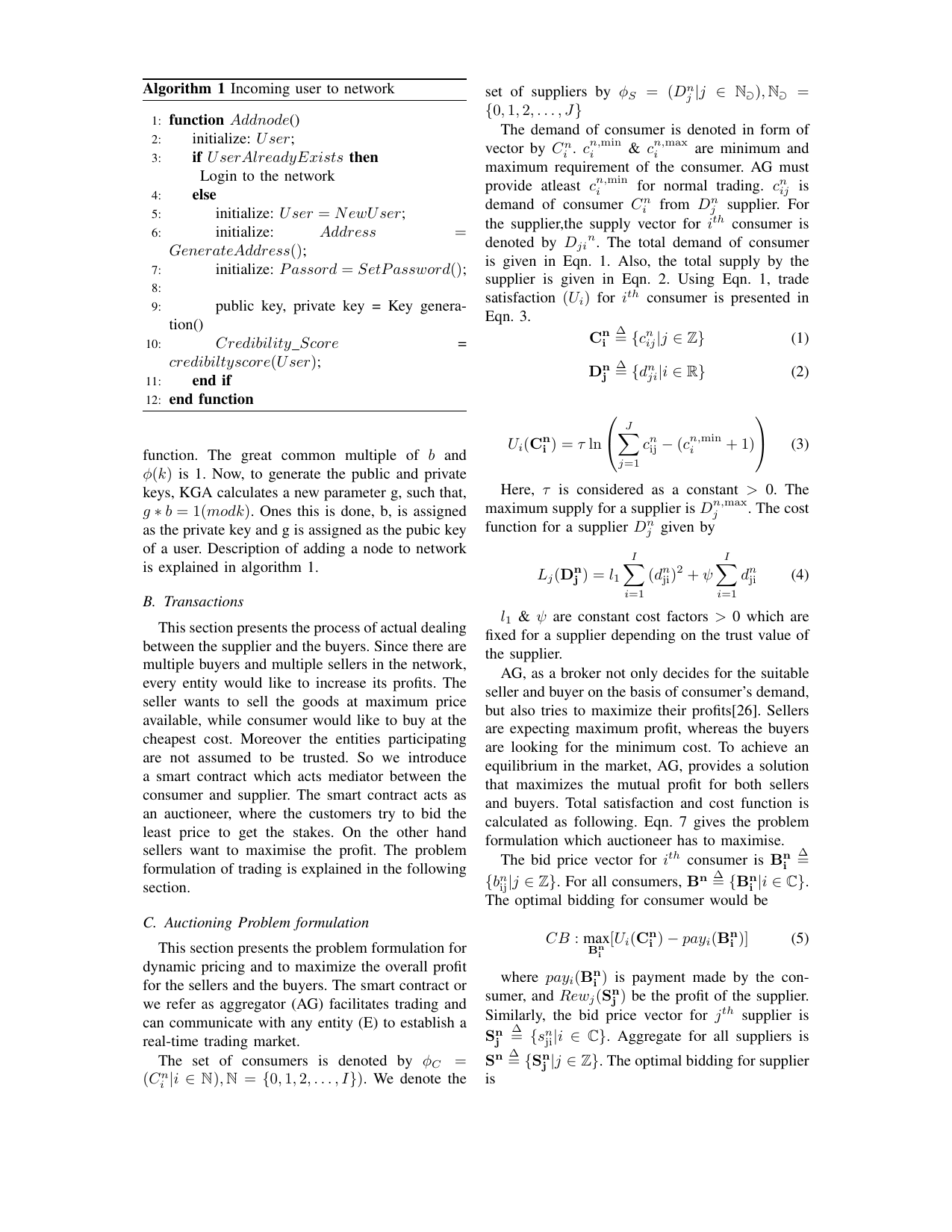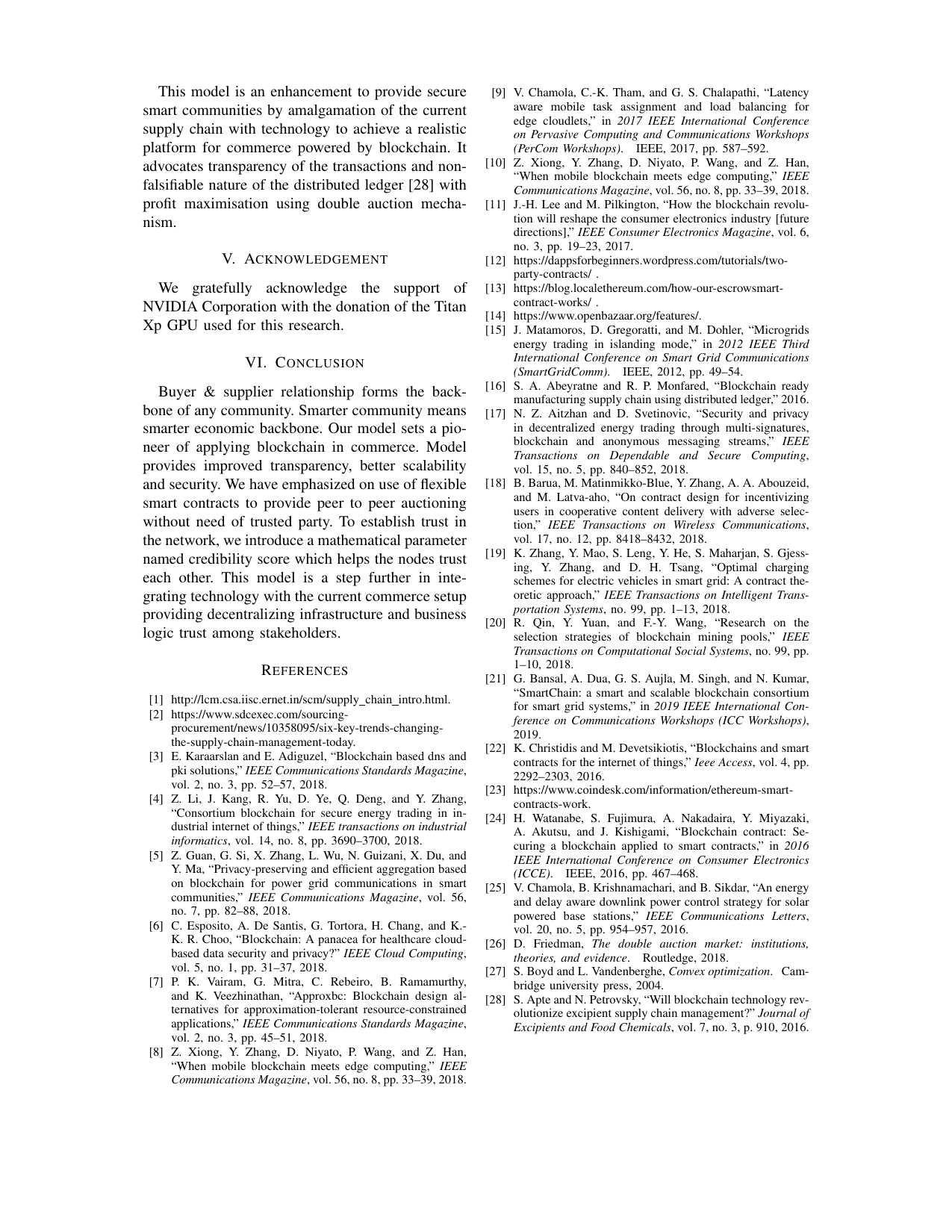 Blockcom: A blockchain based commerce model for smart communities using auction mechanismVikas Hassija, Gaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Vikas Saxena, and Biplab SikdarIn 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), 2019
Blockcom: A blockchain based commerce model for smart communities using auction mechanismVikas Hassija, Gaurang Bansal, Vinay Chamola, Vikas Saxena, and Biplab SikdarIn 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), 2019Supply chain is a complex system of organizations, people, information, and resources involved in providing services from supplier to customer. The changing technology has made the survival in commerce highly competitive and price sensitive. Blockchain technology can be the game-changer for decentraliz- ing infrastructure and building a trust layer for business logic. BitCom is a commerce model based on the emerging technology of blockchain. It is a framework deriving its roots from both permissioned and permissionless blockchains to achieve a feasible solution to the problem of automating commerce. The model caters to need of profit maximization for suppliers and consumers using iterative auction mechanism. Parties bid to smart contract which act as auctioneer for maximizing the profit. It uses flexible smart contracts for negotiations and transactions while permissionless entry is provided to the users. Mathematical parameter named credibility score has been created to deal with trust issues in the decentralized network. BitCom provides a fresh perspective on the concept of supply chain and commerce. The objective of model remains to provide enhanced transparency, greater scalability, better security and scope of innovation. It is likely to propel the next industrial revolution, providing a new paradigm for doing business in finance, transportation, shared economy.
- Blockchain
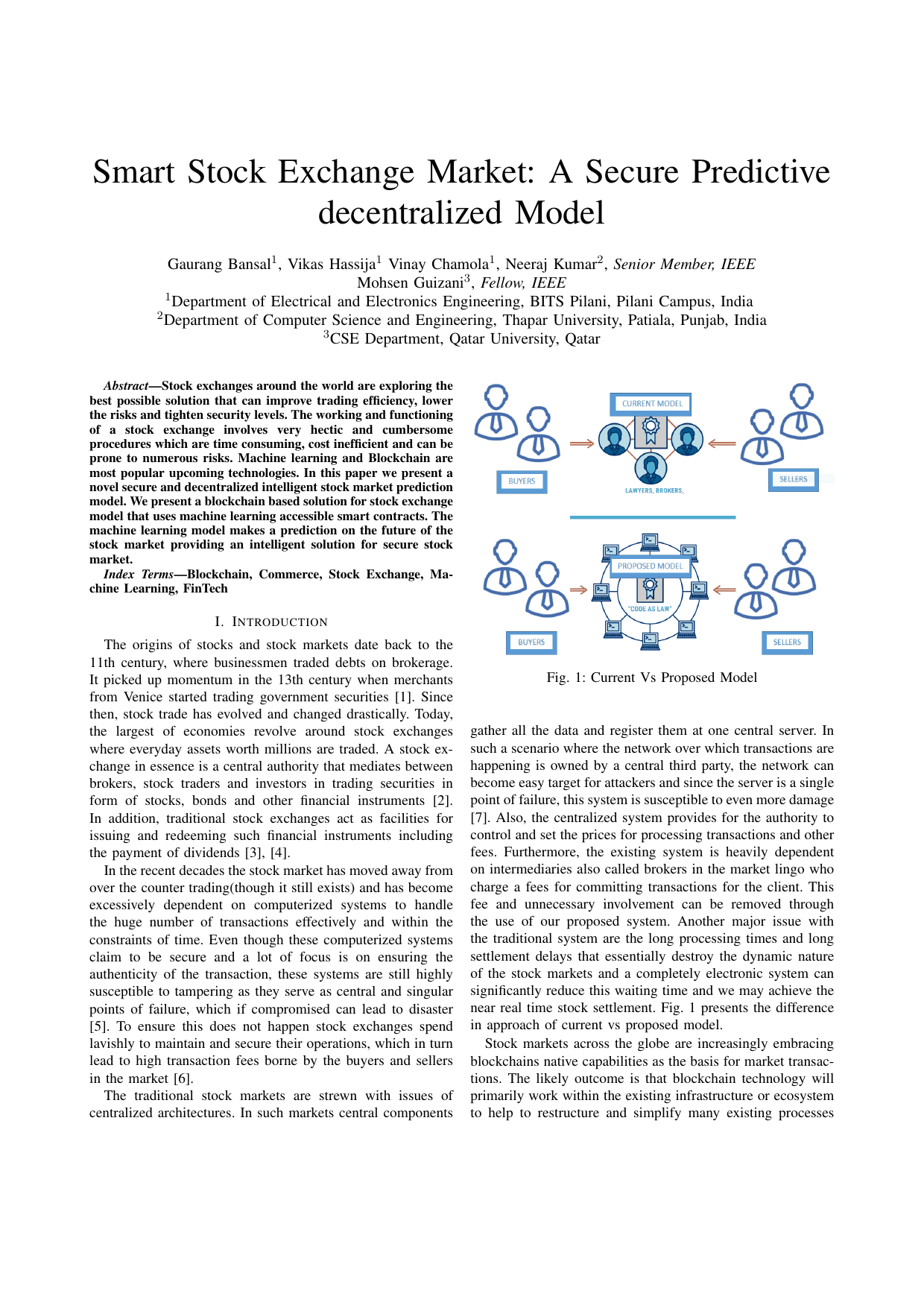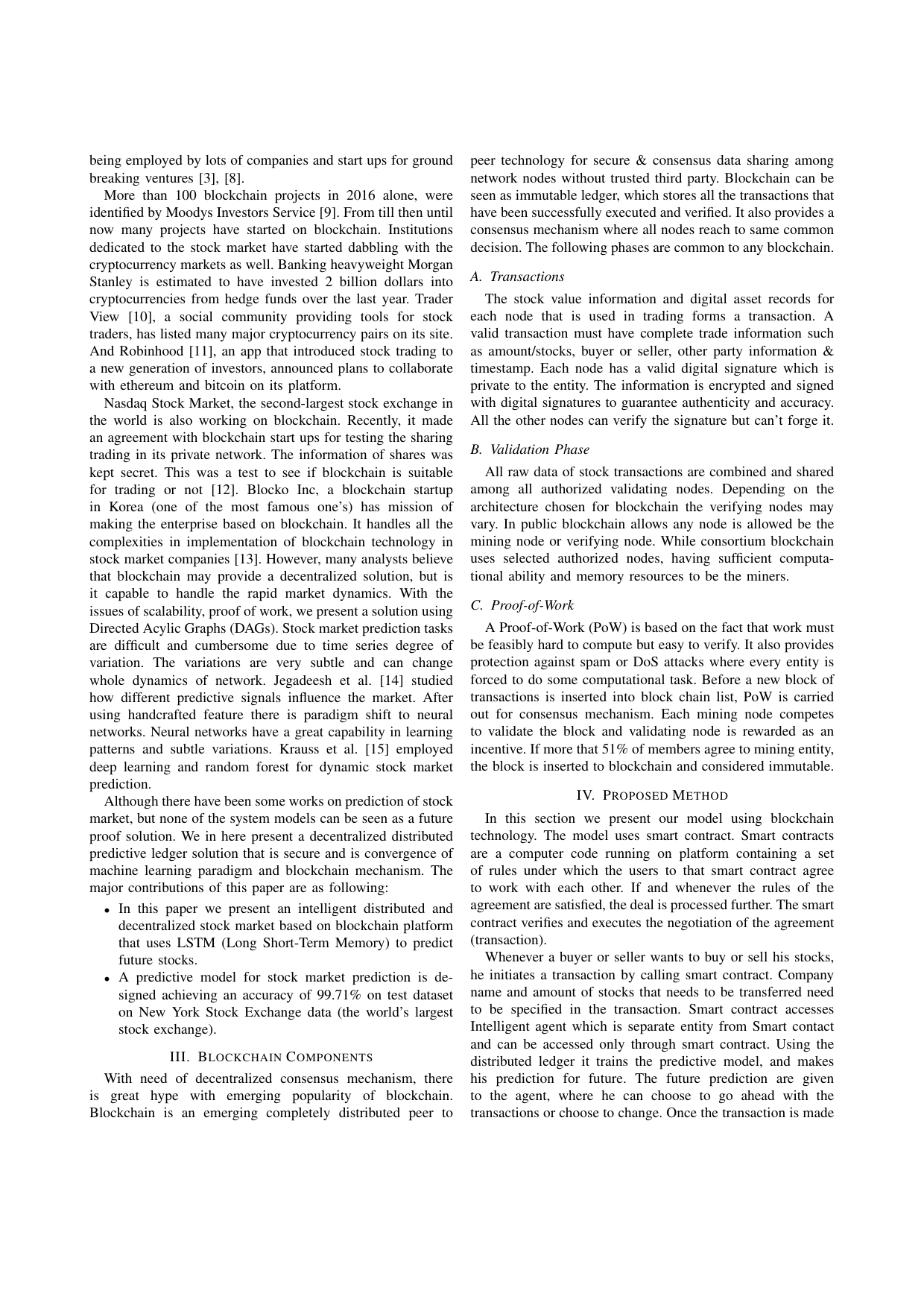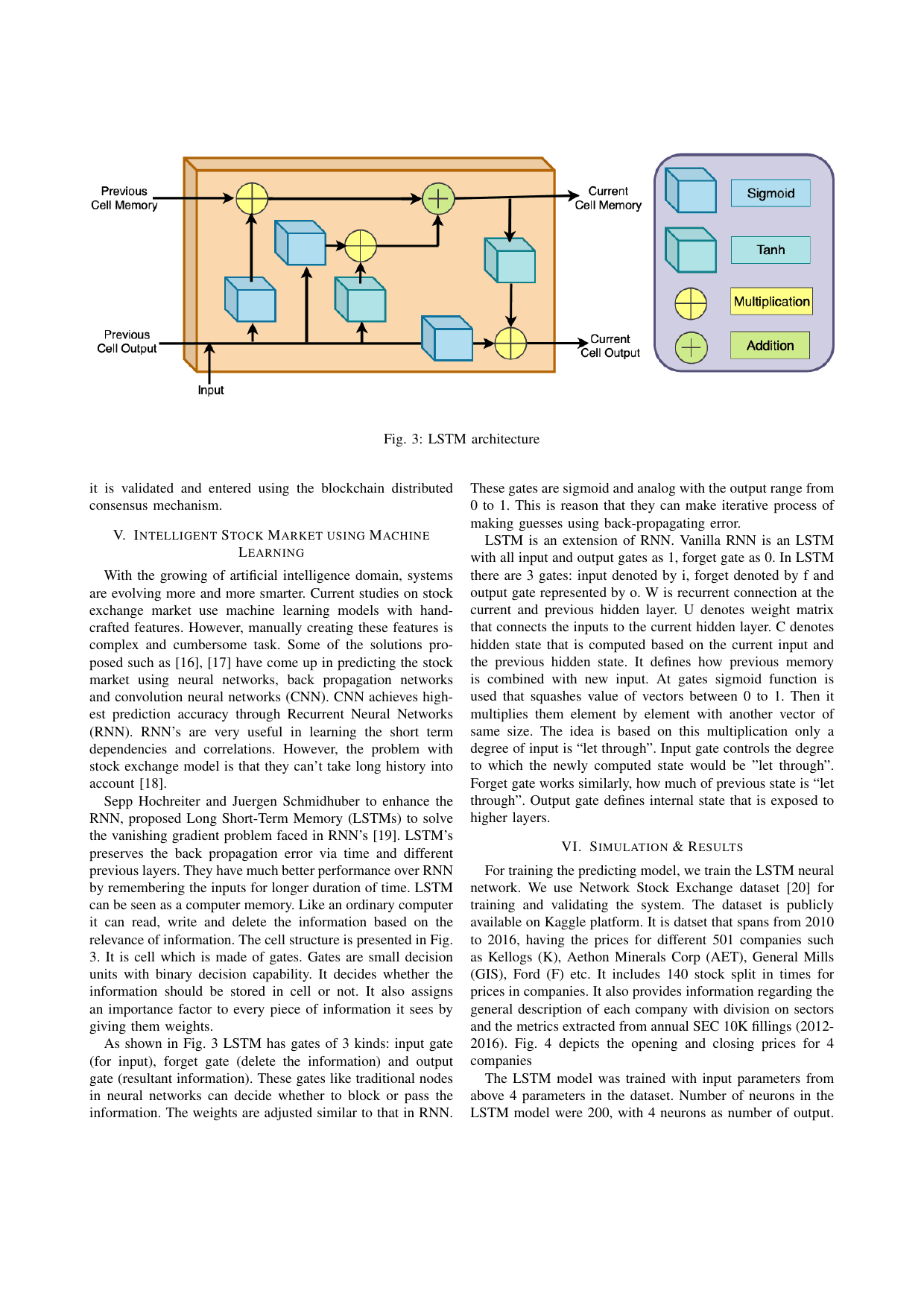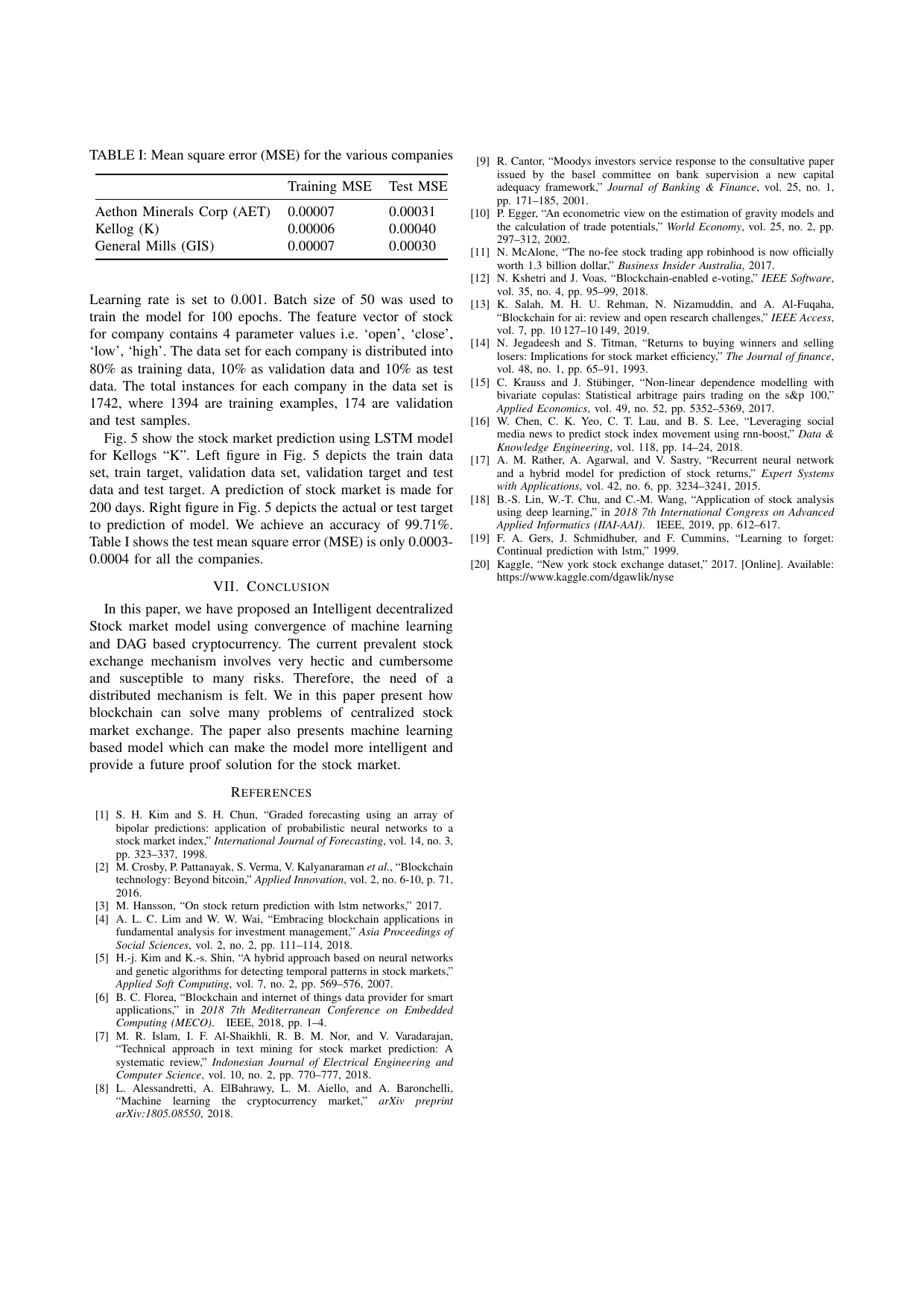 Smart stock exchange market: A secure predictive decentralized modelGaurang Bansal, Vikas Hassija, Vinay Chamola, Neeraj Kumar, and Mohsen GuizaniIn 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), 2019
Smart stock exchange market: A secure predictive decentralized modelGaurang Bansal, Vikas Hassija, Vinay Chamola, Neeraj Kumar, and Mohsen GuizaniIn 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), 2019Stock exchanges around the world are exploring the best possible solution that can improve trading efficiency, lower the risks and tighten security levels. The working and functioning of a stock exchange involves very hectic and cumbersome procedures which are time consuming, cost inefficient and can be prone to numerous risks. Machine learning and Blockchain are most popular upcoming technologies. In this paper we present a novel secure and decentralized intelligent stock market prediction model. We present a blockchain based solution for stock exchange model that uses machine learning accessible smart contracts. The machine learning model makes a prediction on the future of the stock market providing an intelligent solution for secure stock market.
- Blockchain
 SmartChain: a smart and scalable blockchain consortium for smart grid systemsGaurang Bansal, Amit Dua, Gagangeet Singh Aujla, Maninderpal Singh, and Neeraj KumarIn 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), 2019
SmartChain: a smart and scalable blockchain consortium for smart grid systemsGaurang Bansal, Amit Dua, Gagangeet Singh Aujla, Maninderpal Singh, and Neeraj KumarIn 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), 2019Smart grid (SG) provides a peer-to-peer energy trading mechanism wherein the electric vehicles (EVs) can trade for energy with their peers using the information and communi- cation technologies. However, the dependence on third party for coordinating the energy trading decisions leads to a bottleneck for any distributed environment. Therefore, blockchain technol- ogy can provide a privacy-preserving and effective consensus mechanism without the control of trusted third party. Although blockchain provides inherent secure framework for transactional process, but the this security is because of computational com- plexity enforced. In SG environment, the conventional blockchain process could not be employed due to limited computational resources with EVs, which makes it difficult to solve the tough computational puzzles to validate the transactions. On the other hand, any compromise on the computation difficulty makes it more vulnerable to various types of attacks. Therefore, in this paper, SmartChain: a blockchain inspired smart and scalable ledger framework which does not require much computational complexity is designed for secure peer-to-peer energy trading in SG ecosystem. The proposed framework is evaluated using the parameters such as execution and validation time. The results obtained depict the superiority of SmartChain in contrast to the conventional blockchain process.